This paper reviews orthogonal frequencydivision multiple (OFDM) which has been adopted as a standard for various high data rate wireless communication systems. However, implementation of the OFDM system entails several difficulties. One of the major drawbacks is the high peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) which cause large number of sub-carriers, that make restrictions for practical applications. Block Coding, partial transmit sequence and clipping are some PAPR reduction methods that have been proposed to overcome this problem. In this paper, we mainly investigate the PAPR reduction performance using interleaving & PTS, this method is sub-entities of interleaving & phase rotation scheme. A new algorithm using interleaving & PTS technique which shows better PAPR reduction compared to the existing algorithms is proposed. Results are verified using MATLAB software.
Keywords |
| Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM); partial transmits sequences (PTS); Interleaving ;
peak-to average power ratio (PAPR). |
INTRODUCTION |
| Long Term Evolution (LTE) is standardized by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) as an evolution of the
3G systems to meet the requirements of increasing the data rates, high mobility and low latency over a bandwidth of up
to 20 MH.Researchers have been trying for the next evolutionary fourth generation (4G) communication systems to
provide a comprehensive and secure IP solution where voice, data, and multimedia can be offered to users at "anytime,
anywhere" with higher data rates than previous generations [1]. Multiple input multiple outputs (MIMO) and (OFDM)
modulation have therefore been adopted due to their superior performance. These developing modulation used in LTE
which promise to become the key for high-speed wireless communication technologies and combining them can
provide wireless industry evolution from 3G to 4G systems. In OFDM systems which are use MIMO state that, the
output is the superposition of multiple sub-carriers in this case,instantaneous power outputs increases and may demand
higher powers than the mean power of the system since the phases of these carriers are the same. OFDM is multicarrier
multiplexing access Technique for Transmitting Large data over Radio waves. One of the major drawbacks of OFDM
signals is its large PAPR, which causes poor power efficiency to transmit amplifier`s power [16].And to reduce the
PAPR, many techniques have been proposed, such as clipping, coding, PTS, selected mapping (SLM),
interleaving[17][18], nonlinear companding transforms[14][19], hadamard transforms[20]. These schemes can mainly
be categorized into signal scrambling techniques, such as PTS, and signal distortion techniques such as clipping,
companding techniques, in this Paper all techniques which can be used to reduce PAPR in OFDM system are listed. |
| The outline for the paper is as follows: After system Structure, which is presented in Section ΙΙ, definition of PAPR and
its reduction techniques focusing on signal scrambling techniques specially (PTS) is investigated in section ΙΙΙ,
comprehensive analysis are conducted in terms of all possible influencing factors on PTS PAPR reduction performance
and some research findings are reported based on the simulation results in section ΙV Finally conclusions of this paper
are presented in section V. |
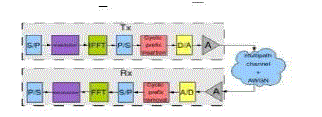
| Figure 1 shows the end-to-end block diagram of an OFDM system in which the discrete-time signal {X[n]} after
applying IFFT at the transmitter can be expressed: |
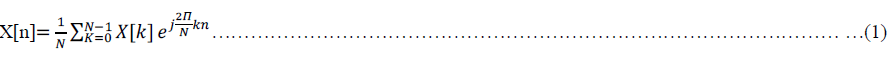 |
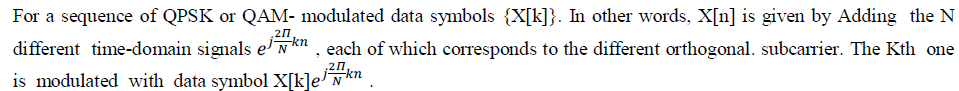 |
PEAK-TO-AVERAGE POWER RATIO IN MIMO OFDM SYSTEM |
| The PAPR definition states that the instantaneous output of an OFDM system often has large fluctuations compared to
traditional single-carrier systems. Ts requires that system devices, such as power amplifiers, A/D converters and D/A
converters, must have large linear dynamic ranges. If this is not satisfied, the peak signal goes into the non-linear region
of the device at the transmitter leading to high out of band radiation and inter-modulation distortion [2].Theoretically,
large peaks in OFDM system can be expressed as PAPR. It is defined as: |
 (3) (3) |
| In this paper partial transmit sequence is focused on & PTS is most important methods used to reduce PAPR in
OFDM system & it can be presented in two main presented in two main steps. First, by dividing the original OFDM
signal into a number of sub-blocks. Secondly, adding the phase rotated sub-blocks to develop a number of candidate
signals to pick the one with smallest PAPR for transmission. |
| There is another way that can also be used to express PTS method by multiplying the original OFDM signal with a
number of phase sequences [13]. |
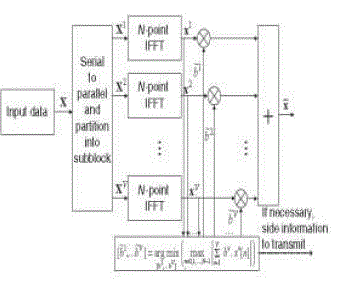
| PTS technique partitions and input data block of N symbols into V disjoint sub-blocks as follows: |
| X=[x0x1x2,……….,xv-1]T……................................................................................……………(4) |
| where xi the subblocks that are consecutively located and are also of equal size, scrambling is applied to each
subblock [11] which rotating its phase independently in the PTS technique as in Fig.4. Then each partitioned subblock
is multiplied by a corresponding complex phase factor bv=eΦv where v = 1,2,…….,V, subsequently taking its IFFT to
yield: |
 |
SIMULATION RESULTS |
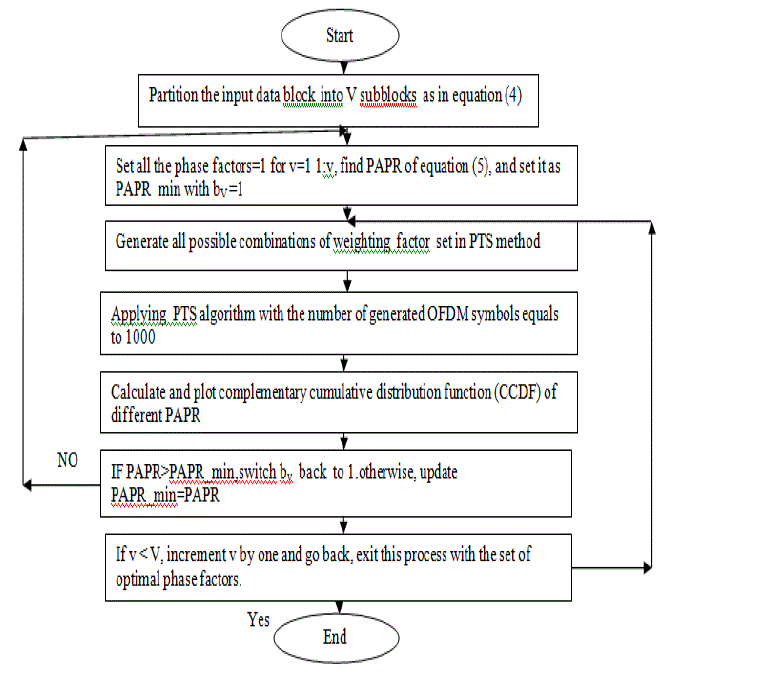
| The following sections propose new techniques to create alternative sequences for PTS and shows through simulation
that the peak regrowth of the proposed techniques after filtering is not as severe as in traditional PTS. This advantage is
combined with reduction in complexity of the new algorithms as shown in flow chart in Fig.5.In this flow chart, new
PTS suboptimal combination algorithm is introduced to get modified results for the complementary cumulative
distribution function (CCDF) of OFDM signals. |
| simplified CCDF will be used as: |
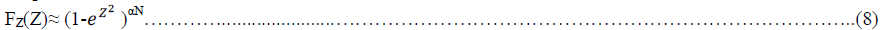 |
| where α has to be determined by fitting the theoretical CDF into the actual one [8]. Using simulation results, it has
been shown that α= 2.8 is appropriate for sufficiently large N . |
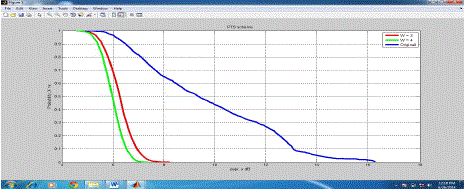
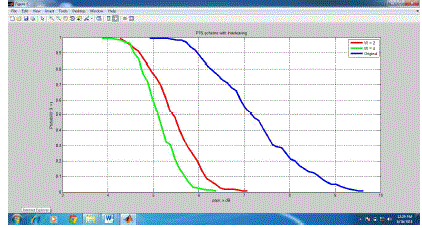
| Figure 6 shows the CCDF of PAPR for a 16-QAM /OFDMA system using PTS technique as the number of
subblock varies. It is seen that the PAPR performance improves as the number of sub blocks increases with V =
1, 2, 4, 8, and 16. |
| As shown in Fig. 6. The original curve has PAPR equals to 16.5 dB.After applying to the proposed algorithms, the value
was significantly reduced to 8.2 dB .This proves that the algorithm gives better results which is superior performance in
PAPR reduction. |
| CCDF of combination of Interleaving and PTS Proposed Scheme |
ANALYSIS: |
CONCLUSION |
| This paper provides an overview of Orthogonal-Frequency-Division-Multiplexing (OFDM).The purpose of this paper
was to reduce the High (PAPR) of OFDM signals. Using the proposed PTS algorithm, this was successfully
achieved..A detailed simulations were conducted and results were obtained for PAPR reduction using Matlab. Using
the above method, it was observed that the CCDF of OFDM signals were improved compared to other literature
searches .In this paper both interleaving & PTS methods are combined and formed a new PTS Algorithm which
shows better PAPRreduction compare to the existing PTS Algorithms. |
Tables at a glance |
|
|
| |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
Figure 7 |
Figure 8 |
|
| |
References |
- Young Kyun Prasad, What is 4G, in 4G Roadmap and Emerging Communication Technologies, Artech House, 2006, pp. 12âÃâ¬Ãâ13
- Jaylath .Side Information in PAPR PTS-OFDM Signals Proceedings 14th IEEE Conference on Personal, Mobile RadioCommunications.2003,vol. 1. PP. 226-230.
- Ochiai, H. and Imai, K. (2001) On the distribution of the peak-to-average power ratio in OFDM signals. IEEE Trans. Communication., 49(2),282âÃâ¬Ãâ289.
- Bauml, R.W., Fischer, R.F.H., and Huber, J.B. (1996) Reducing the peak-to-average power ratio of multicarrier modulation byselective mapping.Electron. Lett.,32(22), 2056âÃâ¬Ãâ2057.
- Muller, S.H. and Huber, J.B. OFDM with reduced peak-to-average power ratio by optimum combination of partial transmit sequences.1996 ,32(22), 2056âÃâ¬Ãâ 2057.
- Tellado-Mourelo, J. (Sep. 1999) Peak to average power reduction for multicarrier modulation, Ph.D. Dissertation, Stanford Univ.
- Muller, S.H. and Huber, J.B. A novel peak power reduction scheme for OFDM. PIMRCâÃâ¬Ãâ¢97, vol. 3, pp.1090âÃâ¬Ãâ1094.
- Cimini, L.J. Jr (2000) Peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal using partial transmit sequences. IEEE Communication.Letters, 4(3), 86âÃâ¬Ãâ88.
- Tellambura. Coding technique for reducing PAPR in OFDM. IEEE GLOBECOM 1998, vol. 5, pp.2783 2787.
- Reena Chackochan, Dr.Himanshu Soni, âÃâ¬ÃÅComparative Analysis of Distortive and Non- DistortiveOFDMTechniques for PAPR Reduction in SystemsâÃâ¬ÃÂ, Proc. Of Int. Conf. on Advances in Electrical&Electronics 2011.
- Muller, S.H. et al. (1997) OFDM with reduced peak-to-average power ratio by multiple signal representation. In Annals of Telecommunication.52(1âÃâ¬Ãâ2), 58âÃâ¬Ãâ67.
- Mohinder , Peak to average power ratio in Space time codes .Artech House, 2004.
- Guangyue Lu1. PTS Method for Reduction of PAPR in RealUppsala University Uppsala. Sweden
- Van Nee, R. and deWild, A. (May 1998) Reducing the peak-to- average power ratio of OFDM. IEEE VTCâÃâ¬Ãâ¢98, vol 3, pp. 18âÃâ¬Ãâ21.
- Slimane, S.B. (Dec. 2000) Peak-to-average power ratio reduction of OFDM signals using pulse shaping. IEEE GTC, vol. 3.
- H. Rohling, . Broadband OFDM radio transmission for multimedia applications,IEEE,vol.87,pp.1778-1789, 1999.
- T. Jiang and Y. Imai, âÃâ¬ÃÅAn overview: peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. On WirelessCommunications, 200 pp.56-57
- S.H. Han, J. H. Lee, âÃâ¬ÃÅAn overview of peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for Multicarrier transmission,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Transactionon Wireless Communication, 2005, pp. 56-65.
- Xiao bin Wang, âÃâ¬ÃÅReduction of peak-to-average power ratio ofOFDM system using A companding technique,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE TransactiononBroadcasting, Vol.45, No.3, 1999, pp.303-307.
- Park, M., Heeyong, J., Cho, N., Hong, D, and Kang, C., âÃâ¬ÃÅPAPR reduction in OFDM transmission using Hadamard transformâÃâ¬Ã IEEEInternational Conference Communications, Vol.1,2000 pp.430-433.
|