ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Anitha. K 1, Saranya. J2, Dr. S.Vasantha3
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
In today's hi-tech world technology support is very important for the successful functioning of the banking. This research focuses on the usage of technology in banking sector. Today banks are the backbone of the Indian economy. Banking in India originated in the last decades of the 18th century. The first banks were Bank of Hindustan (1770-1829) and the General Bank of India (1786). Without information technology and communication we cannot think about the success of a banking sector. It has enlarged the role of banking sector in the economy. The financial transactions and payment can be processed in easy and quick way. The use of ATM, credit card, telebanking, mobile banking internet banking etc, provides more security in banking. It also highlights the effective use of technology in banking and product awareness among people. The study shows how people can make use of technology in banking. Among the total population in Chennai, 200 respondents were taken as sample for this study. Data collected were analysed and drawn meaningful inferences with the help of various tools such as simple percentage analysis, factor analysis and chi square. The study provides various suggestions for the banks to improve the effective soma fitness utilisation of technology.
Keywords |
| Awareness, Banking, Customers, Technology, Usage |
I. INTRODUCTION |
| The term “Banking Technology” refers to the use of sophisticated information and communication technologies together with computers to enable banks to offer better services to its customers in a secure, reliable, affordable manner and sustain competitive advantage over other banks. In the competitive financial market, the banks with the latest technology and techniques are more successful in the modern civilization. Through this banking, business can generate more and more profitability thus retaining customers. Now a day’s Banks are not following the traditional or conventional banking with manual operations. Banks have moved from disbursed to a centralised environment, which shows the impact of technology on banks. Banks are using new tools and techniques to find out their customers’ needs and satisfaction and offer them tailor made products and services to make it convenient. Through this people are benefitted and are comfortable to operate the nearer branch for all payments and transactions. People can take advantage in saving time and distance which was inconvenient in early days. Banks provide a lot of products and services combined with technology are of great use today. |
| The technological development in the banking sector began its usage with Advanced Ledger Posting Machines (ALPM) in the 1980s and later used core banking solution (CBS) for providing better services to their customers. |
| Over the years several studies have proved the impact of Information Technology on banking productivity and profitability. |
II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE |
| Dr. C. Rangarajan Committee [1983] had drawn up in 1983-84 the first blue print for computerisation and mechanisation in banking industry. Computerisation has improvement in customer service, decision making, housekeeping and profitability. |
| W.S. Saraf Committee [1994] the committee looked into technological issues related to the payment system and to make recommendations for widening the use of modern technology in the banking industry. |
| Narasimhan Committee [1998] The committee dealt with the issues on technology up gradation and observed that the most of the technology that could be considered suitable for India in some form or the other has been introduced in some diluted form or as a pilot project, but the desired success has not been achieved because of the reasons inter-alia lack of clarity and certainty on legal issues. |
| Daniel (1999), described e-banking as the newest delivery channel offered by the retail banks in many developing countries. Restriction and limitation within organization to operate the services and its market share or strength were viewed as important to decide and operate the e-banking services. |
| Wenninger (2000) evaluated the emerging role of electronic commerce in banks. E-commerce had created new form of competition and compelled banks to make choices about the services they offer, the size of their branch network and extent of their support to inter- bank payments network. |
| Kamesam (2001) studied the changes that took place in the Indian banking industry which emphasized on technological advancements and profitability in banks. Technology has helped in centralized data storage with decentralized processing which has helped in reduction of costs and NPAs |
| Harris and Spence (2002) explored the ethics of business to business electronic commerce with focus on banking sector. The challenges of e-banking services would be successful for banks only if fraudulent activities could be controlled, transparency in transaction could be maintained, ethical rules and regulation to be followed so that ebanking could be widely acceptable among customers. |
| Arora (2003) made an attempt to prove that technology had a definitive role in facilitating transactions in the banking sector; and the impact of technology had resulted into the introduction of new products and services by various banks in India. Technology was a facilitator for advancement in the core business of banking and not an end in itself. |
| Durkin and Howcroft (2003) evaluated that the banker-customer relationship was improved through mobile, phone and internet banking. Further, the combination of traditional and new delivery channels, if followed, can help to improve their productivity and profitability. |
| Hogarth and Hilgert (2004) highlighted that electronic banking technology represents a variety of services, ranging from common ATM services and direct deposit to Automatic Bill Payment (ABP), Electronic Transfer of Funds (EFT) and computer banking (PC banking). These services help in saving time, decrease the errors, improving inaccurate accounting and preventing in manipulation of data. |
| Ashiya (2006) evaluated developments made by electronic payments. The author evaluated different modes of epayment used across the globe. These electronic ways provided an excellent instrument for payment system. Epayment is a sophisticated technology could be used as a tool for the enhancement of customer loyalty and business of banks as it had reduced the risk & cost and could increase the customer loyalty. |
| Suresh (2008) highlighted that recently developed e-banking technology had created unpredicted opportunities for the banks to organize their financial products, profits, service deliver, and marketing for the better future of Indian economy. |
| Deol (2009) Since the beginning of deregulation of the financial sector in the late 1980s, banks have started operating in the six segments namely retail banking, corporate banking, investment banking, asset management, life insurance and general insurance |
| Malhotra and Singh (2010) in their research study on Indian banking shows that the private and foreign banks are performing relatively better in offering a diversified range of products and services including e-banking facilities as compared to public sector banks. The experience, size, financing pattern and ownership of the bank were found out to be major factors influencing the extent of e-banking services for urban customers. |
III. OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY |
| 1. To examine the awareness of technology in accessing banking products. |
| 2. To analyse the usage of technology in banking. |
| 3. To determine the factors that influences a customer towards technology in banking services. |
| 4. To suggest measures to improve effective utilisation of technology in banking services. |
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY |
| This research is about usage of technology in banking sector and how the people make use of its products and services. To find the factors that attracts people to use technology effectively in banking. |
Research design: |
| Descriptive research design has been used for the study. |
Sampling techniques: |
| Purposive quota sampling has been derived from non- probability sampling method to select people who have bank accounts in Chennai. |
Sample size & Data collection: |
| From the total population of Chennai, 200 people are chosen as sample size for the study and the data is collected through a Structured Questionnaire. |
Tools and Techniques: |
| • Percentage Analysis |
| • Chi Square test |
| • Factor analysis |
Composition |
| The sample constituted about 47% of male and 52% are female. 48 % of the respondents are within the age group of 21-30. About 31% of the respondents are post graduates. |
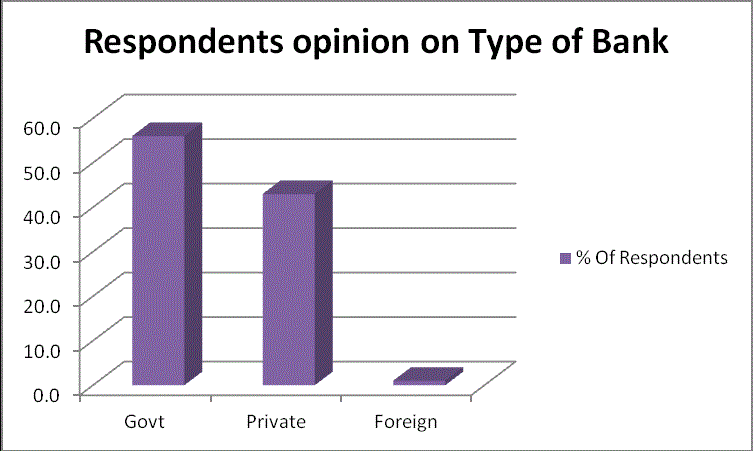 |
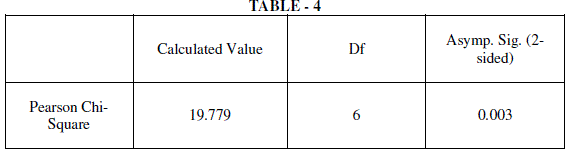
V. DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION |
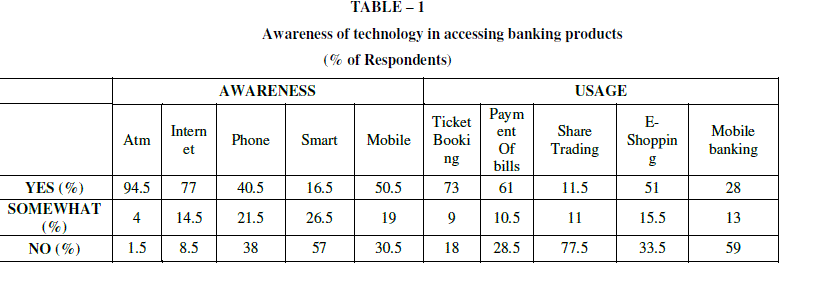 |
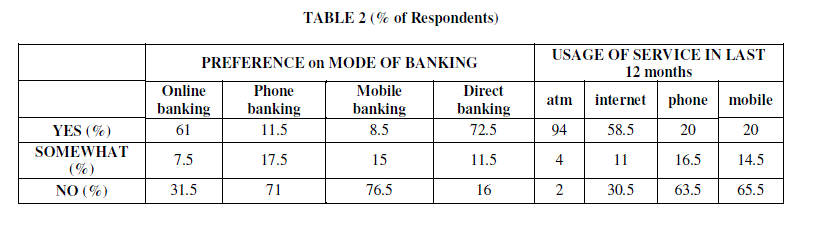 |
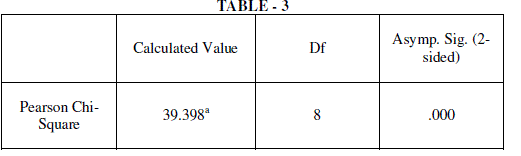 |
 |
VI. FINDINGS |
| • 47% of the respondents are male and 52% of the respondents are female. |
| • 48 % of the respondents are within the age group of 21-30. |
| • 84% of the respondents have their bank account as Savings account. |
| • 94.5 % of the respondents are aware of ATM technology. |
| • 72.5% of the respondents still prefer the mode as direct banking and about 61 % prefer online banking. |
| • About 94% of the respondents have used ATM in the last 12 months. |
| • The mode of using direct banking depends on age of the customers. |
| • The use of banking through mobile depends on education of the customers. |
| • The mode of using online banking depends on gender. |
| • The mode of cash transactions through internet depends on income. |
VII. SUGGESTIONS |
Measures to improve effective utilisation of technology in banking services |
| • People still have a grit to deposit cash through ATM’s. Therefore banks can create awareness among people to effectively utilize the technology provided. Banks can list the instruction procedures on all ATM outlets so that people can use it effectively. |
| • People don’t prefer to use phone banking as language is a major constraint. Banks can consider state language as their first priority instead of national language. This not only refers to the customer service representatives but also statements can be provided in their preferred language. |
| • Another major hurdle why people don’t prefer phone banking is that people are kept on ‘waiting mode’ for a long time. Banks shall take this into consideration and help people to make effective utilization phone banking. |
| • People don’t prefer to use ATM card as the minimum balance is high for a savings account. It is difficult to maintain the same amount. But it is not in the case of salary account as they provide zero balance. This facility should be available to all accounts so that there would be more usage of ATM. |
VIII. CONCLUSION |
| This study reveals that in spite of the advent of technology people still prefer for direct banking for cash transactions which in turn is loaded with crowd in banks. People feel direct banking as a platform of convenience. Customers are forced to go to banks for payments and still they do not to feel comfortable due to long queues. Yet people are not aware of the utmost utilization of technology since they have a threat towards safety. The study emphasizes on the percentage of awareness on maximum utilization of technology. Banks should take effective measures in creating awareness towards the effective usage of technology. |
References |
|