In this paper a PWM based wind turbine model is been presented with three wind turbines. The presented system is able to provide the system stability in case of varying voltage generation because of varying speed of wind turbine as well as capable to handle the fault over the system. To provide the stability over the system, the statcom based model is been presented in this work. The presented model is been developed in Simulink environment. The analysis of the work is been in terms of voltage analysis in statcom based and statcom less wind turbine model. The obtained results show that the presented system is effective enough to provide the stability over the system.
Keywords |
| PMSG, STATCOM, PWM based Wind Turbine, synchronization |
INTRODUCTION |
| Non renewable energy sources are exhausting in near future. So for the sustainable growth and social progress of an
country, it is necessary that energy demand is meet by utility of renewable energy sources like wind, biomass, sun etc. the
renewable sources are inexhaustible and therefore we can readily access to have the supply of energy from the renewable
sources. The various advantages of renewable energy sources are as follows: |
| • The sun, wind, geothermal, ocean energy are available in the abundant quantity and free to use. |
| • The non-renewable sources of energy that we are using are limited and are bound to expire one day. |
| • Renewable sources have low carbon emissions, therefore they are considered as green & environment friendly. |
| • Renewable helps in stimulating the economy and creating job opportunities. The money that is used to build these
plants can provide jobs to thousands to lakhs of people. |
| • You don't have to rely on any third country for the supply of renewable sources as in case of non-renewable
sources. |
| The voltage of wind power generating station generally fluctuates due to nature of wind. When wind power generating
station is integrated to the power grid power quality issues arises like injection of harmonics, poor power factor and
distortion from pure sine wave of fundamental frequency. In this proposed scheme, to minimize the power quality problems
at the common coupling point of the power grid, STATCOM with battery energy system storage is connected. The
STATCOM relieves the load and main supply source from the reactive power demand. The proposed scheme is simulated
in MATLAB/SIMULINK power lib. The use of permanent-magnet synchronous generator is a prime choice for variable
speed wind turbines. The advantages of variable speed wind turbines are greater annual energy capture than that of fixed
speed technology, active and reactive power control is easily achieved with the PWM inverter, there is less mechanical
stress, and no flicker problem. Variable speed turbine helps grid voltage to be controlled by varying reactive power
generation. Gearbox which couples wind turbine with generator increase losses, higher cost of the unit, and increase faults due to rotating mechanical parts. The reliability of the variable speed wind turbine can be improved significantly by using
direct drive permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG). Because of self-excitation property, PMSG provides high
power factor and high efficiency. |
| This paper investigates the application of STATCOM with PMSG based variable speed wind turbine for uninterrupted
operation during grid disturbances. Also grid synchronization of wind turbine is achieved using a rapid synchronizer by
controlling the phase angle of wind energy system output. |
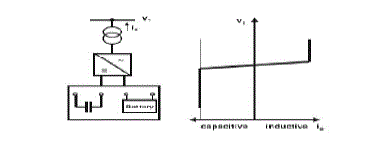
(A) STATCOM |
| The wind is variable in nature, which produces a continuous variable output power. Intermittent nature of wind introduces
voltage sags, swells, flickers and harmonics. Integrating large amount of wind power into existing power system presents
technical challenges, which requires consideration of voltage and frequency regulation, stability, power quality problems.
Shunt Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS) devices such as synchronous static compensators (STATCOMs) have
the ability to improve the voltage quality with its fast response capability, accurate reactive power compensation and
voltage control. Recent development in power electronic devices and application specific ICs and DSP system enables the
introduction of low cost and faster STATCOMs. Variable speed wind turbine with power electronic converters injects
harmonic currents in the grid. Intermittent nature of wind produces variable power and feeding this variable power to the
grid introduces voltage variation to the grid in the form of voltage sag, voltage swell and voltage flickers. These problems
have impact on system stability and quality and introduce trip to the wind turbine or damage of sensitive electronic devices
connected to the grid. STATCOM connected to the point of common coupling either supply reactive power or absorbed
reactive power, so it removes reactive power part of the grid. STATCOM injects current to the point of common coupling
in such a way that cancels out the harmonic currents. |
PMSG MODEL |
| The voltage equation of PMSG are expressed in d- and q- axis reference frame are given by |
 (1) (1) |
 (2) (2) |
| Where Vsd, Isd, Vsq and Isq are d- axis and q- axis component of stator voltages and currents, Rs is the stator resistance, ωr is
the rotor speed in radian per second Ψf is the flux linkage. |
| The electromagnetic torque is given by |
 (3) (3) |
Wind Turbine Location in Power System |
| The way of connecting the wind generating system into the power system highly influences the power quality. Thus the
operation and its influence on power system depend on the structure of the adjoining power network. |
Self Excitation of Wind Turbine Generating System |
| The self excitation of wind turbine generating system (WTGS) with an asynchronous generator takes place after
disconnection of wind turbine generating system (WTGS) with local load. The risk of self excitation arises especially when
WTGS is equipped with compensating capacitor. The capacitor connected to induction generator provides reactive power
compensation. However the voltage and frequency are determined by the balancing of the system. The disadvantages of self
excitation are the safety aspect and balance between real and reactive power. |
Consequences of the Issues |
| The voltage variation, flicker, harmonics causes the malfunction of equipments namely microprocessor based control
system, programmable logic controller; adjustable speed drives, flickering of light and screen. It may leads to tripping of
contractors, tripping of protection devices, stoppage of sensitive equipments like personal computer, programmable logic
control system and may stop the process and even can damage of sensitive equipments. Thus it degrades the power quality
in the grid. |
LITERATURE REVIEW |
| Zhonghui Zhang [1] et al. proposed Matlab based permanent magnet synchronous machine vector control simulation.
Experiment and validate id = 0 is a good control algorithm. It provides an effective means and tools for analysis and design
of PMSM control system provides. It also provides a guideline of designing and debugging for practical PMSM system. |
| Malgorzata Bobrowska [2] et al. has presented improved voltage oriented control for converter. They proposed an
algorithm for independent control of positive and negative current sequences, which contains different controlling blocks.
They applied different voltage feed forward together with converter and proved the significance of VOC algorithm against
unbalance voltage dips. |
| Marek Stulrajter [3] et al. has proposed two techniques of PMSM control in 2007. A brief description of properties of both
methods Scalar control and vector control were presented as a control of synchronous machines. This paper shows that
scalar control is an advantage of sensor less control. A comparative study between scalar control and vector control is also
discussed. Scalar control method has some demerits such as the scalar control in an open loop does not provide a possibility
to control the currents causes different behaviors of PMSM during various operation cycles like the start-up and loading.
Vector control method gives better performance and overcome all the demerits of scalar method. It provides proper
regulation against oversaturation of the magnetic circuit and reduces the magnetizing current. |
| J-C Dai [4] et al. has proposed a practical model of direct-driven permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) wind
turbines based on neural network. A new technique of wind rotor back propagation and aerodynamic characteristic is described using four layer neural networks. Set of wind-rotor aerodynamic data is calculated with the help of combining
blade element momentum-modified theory and taken as sample data. The Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm is used for
neural network. Then, the coupling dynamic models of the wind-rotor and PMSG, and AC–DC–AC converter model are
established. |
PROPOSED MODEL |
| PMSM model, vector controller and converter which are simulated in MATLAB Simulink. The controller of machine gives
voltage reference to PWM converter to develop the same voltage. The controller provides the reference voltage to converter
from rotor field oriented vector control which is oriented in a synchronously rotating frame. The STATCOM is commonly
used for voltage sags mitigation and harmonic elimination at the point of connection. The STATCOM employs the same
blocks as the DVR, but in this application the coupling transformer is connected in shunt with the ac system, as illustrated
in Fig 5.1. The VSC generates a three-phase ac output current which is controllable in phase and magnitude. These currents
are injected into the ac distribution system in order to maintain the load voltage at the desired voltage reference. Active and
reactive power exchanges between the the VSC connected in shunt with the ac system provides a multifunctional topology
which can be used for up to three quite distinct purposes: |
| 1) Voltage regulation and compensation of reactive powe r; |
| 2) Correction of power factor; |
| 3) Elimination of current harmonics. |
SYSTEM OVERVIEW |
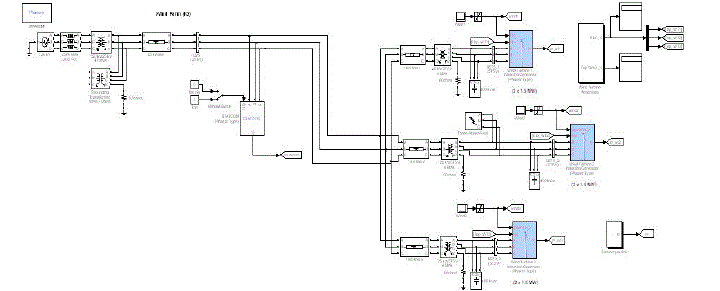
| Figure 2 shows the proposed structure of the direct drive, grid connected PMSG base variable speed wind turbine with
statcom. |
| As we can see, the statcom is connected as the central control unit to control the voltage and current over the circuit. The
controller provides the stability in case of overloaded and underload conditions. The result is driven for the bus system. |
BASIC WIND TURBINE MODEL |
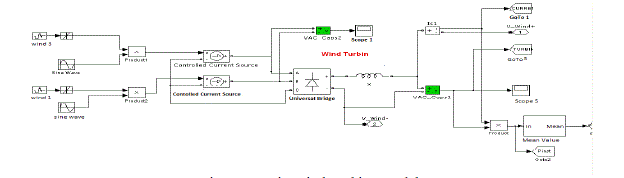
| Following figure shows the basic wnd turbine model |
| In figure 3 is showing the basic wind turbine model. As we can see, the system is connected with the wave generator as the
primary source to the wind power system. To manage the voltage distribution, a controlled current source is attached. An
analyzer is attached with the system to monitor the voltage and to control the flow. |
GRID SYNCHRONIZATION OF WIND TURBINE |
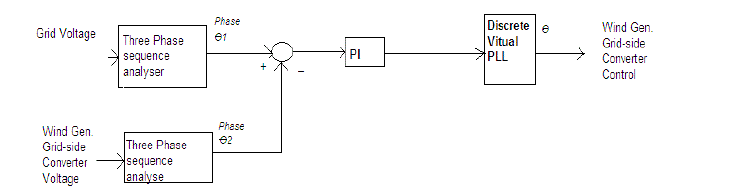
| In order to synchronize wind turbine with the grid, three measures have to be considered: the amplitude, the frequency, and
the phase angle. While the synchronisation of the voltage amplitudes and frequencies can be realised by the machine side
converter control. The phase angles between the wind energy system and grid voltage has to be addressed independently. A
rapid synchronization scheme based on controlling the phase angle of the PWM signal of the machine side converter is
used in this paper. Grid voltage and Wind turbine converter voltage were fed to the discrete three phase sequence analyzer
to produce phase angles as shown in Fig. 4. Error between these two phase angles was passed through the PI controller and
a discrete virtual PLL to produce actual phase angle θ for the PWM signal that controls the Wind turbine grid side
converter. |
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION |
| Using matlab, we develop a model of wind turbine connected to grid system with statcom, which provide protection to the
system against underload and overload problems. It reveals that, this model gives solution for removing problems and
improves power quality. |
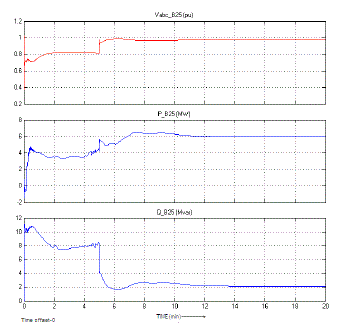
| Here figure 5 is showing the result of bus system in case of statcom based implementation. As we can see the presented
system has provided the stability in terms of voltage and current flow over the system. |
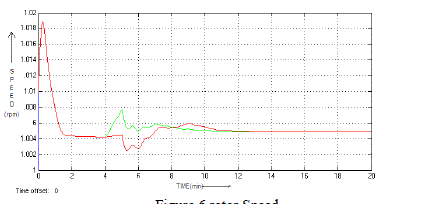
| Here figure 6 is showing the variation in rotor speed. As we can see, the presented system is a wind turbine system that
provides the variable speed of wind turbine. The rotor speed is varying to represent the underload and overload situations. |
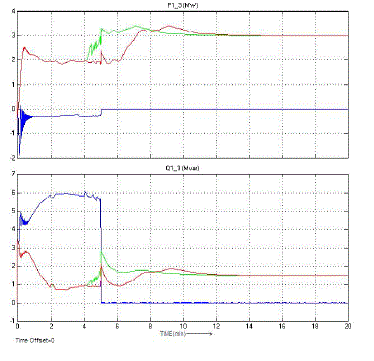
| Here figure 7 is showing the final result driven in terms of voltage and current over the system. The figure is showing the
up and down in initial stage. But the statcom provided the stability over the system. |
CONCLUSION |
| The results are found to be encouraging. In this work, a wind power system is designed using statcom based controller. The
presented system is effective enough to control the voltage and current over the system. The complete power drive train
contains generator, inverter, and statcom based controller. The system is verified under the overload and underload
conditions. The system is defined to provide the voltage and current stability over the system. The system is simulated in
MATLAB Simulink. The direct driven wind power extraction can give maximum possible efficiency because machine is
run at optimum speed. Vector control method shows better performance since lower current distortion is obtained. The
implemented control technique is suitable to drive for wind power applications. |
FUTURE SCOPE |
| In this present paper, the wind power system is defined with statcom based controller. The work can be extended in
different directions in future. |
| • In this paper, the stability of the system is achieved in case of underload and overload conditions. In future,
the system can also be implemented for different kind of faults over the system. |
| • The statcom based controller is used in this paper. In future the DSTATCOM or some other controller can be
used. |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
Figure 7 |
|
| |
References |
- M.E. Haque, M. Negnevitsky, K.M. Muttaqi, "A novel control strategy for a variable speed wind turbine with a permanent magnet synchronous generator," IEEE Trans. On Industry Applications, vol. 46, no. 1, January/February 2010.
- M. Chinchilla, S. Arnaltes, and J. C. Burgos, âÃâ¬ÃÅControl of permanent magnet generators applied to variable-speed wind-energy systems connected to the grid,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. Energy Convers., vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 130âÃâ¬Ãâ135, Mar. 2006.
- Q. Wei, Q. Liyan, H. G. Roland "Control of IPM synchronous generator for maximum wind power generation considering magnetic saturation,"IEEE Trans. On Industry Applications, vol. 45, no 3, May/June 2009.
- 4.J.M. Carrasco, , L.G. Franquelo, J.T. Bialasiewicz, E. Galvan, R.C.P. Guisado, Ma. A. M. Prats, J.I. Leon, N. Moreno-Alfonso, âÃâ¬ÃÅpower electronic systems for the grid integration of renewable energy sources: a survey,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. On Industry Applications, vol. 53, no. 4, August 2006.
- T. F. Chan and L. L. Lai, âÃâ¬ÃÅPermanent-magnet machines for distributed generation: A review,âÃâ¬Ã in Proc. IEEE Power Eng. Annu. Meeting, 2007, pp. 1âÃâ¬Ãâ6.
- Sharad W. Mohod, Mohan V. Aware "A STATCOM-Control Scheme for Grid Connected Wind Energy System for Power Quality Improvement," IEEE Trans. On Energy Conversions.vol. 4, no 3, pp. 346 âÃâ¬Ãâ 352, Mar. 2010.
- A. Kehrli and M. Ross, âÃâ¬ÃÅUnderstanding grid integration issues at wind farms and solutions using voltage source converter FACTS technology,âÃâ¬Ã in Proc. IEEE PES Gen. Meeting, vol. 3, pp. 1822âÃâ¬Ãâ1827, Jul. 2003.
- PinakiMitra, Ganesh Kumar Venayagamoorthy, Keith A. Corzine,"SmartPark as a Virtual STATCOM," IEEE Trans. On Smart Grid, vol. 2, no. 3, Sep. 2011.
- Wei Qiao, Ronald G. Harley, Ganesh Kumar Venayagamoorthy, âÃâ¬ÃÅCoordinated Reactive Power Control of a Large Wind Farm and a STATCOM Using Heuristic Dynamic Programming,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. Energy Conversions., vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 493âÃâ¬Ãâ505, Jun. 2009.
- T K. J. Astrom and T. Hagglund, PID Controllers: Theory, Design and Tuning. Research Triangle Park, NC: ISA, 1995.
- Wei Qiao, Ganesh Kumar Venayagamoorthy, âÃâ¬ÃÅReal Time Implementation of a STATCOM on a firm equipped with with Doubly Fed Induction GeneratorsâÃâ¬Ã IEEE Trans. On Industry Applications, vol. 45, no.1,pp. 98âÃâ¬Ãâ107, Jan. 2009.
- M. ÃÆÃâstman, J. M. Carrasco, L. G. Franquelo, J. T. Bialasiewicz, E. GalvÃÆán, âÃâ¬ÃÅDynamics of the low voltage ride through capabilities of generatorsâÃâ¬Ã Wartsila Technical Journal, pp. 13-16, Jan., 2010.
- R. C. Portillo Guisado, M. ÃÆÃÂ. MartÃÆÃÂn Prats, J. I. LeÃÆón, and N. M. Alfonso, âÃâ¬ÃÅPower Electronic Systems for the Grid Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: A Survey,âÃâ¬Ã IEEE Transaction on Industrial Electronics, vol. 53, no 4, Aug. 2006.
|