ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| Abdul Rasheed Md1, Ravi Kumar Kola2, Prameela Devi Yalavarthy3 |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical used to make polycarbonate plastics, epoxy resins, thermal paper. BPA-based products also include DVDs, computers, home appliances, spectacles and optical lenses, reusable water bottles, food storage containers, sports safety equipment, medical equipment, construction materials, paints and coatings. BPA contamination may occur from many different sources, but the most common way of BPA contamination is through packaged foods or beverages where the packing material contains BPA. The objective of this research paper is to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of Bisphenol A (4,4’-Isopropylidenebisphenol) against four different strains of bacteria i.e., Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus substilis, Proteus valgaris and Escherichia coli, using agar diffusion method. BPA is completely soluble in organic solvents and partially soluble in water. The results showed the zone of inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus 23mm, Bacillus substilis 22mm, Proteus vulgaris 21mm and Escherichia coli 20mm. From the results it can be concluded that BPA may show the cytotoxic effects and these studies are also under way.
Keywords |
| BPA, Bacillus substilis, Proteus vulgaris, Salmonella aureus, Escherichia coli, zone of inhibition and agar diffusion. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Bisphenol A (BPA) is the molecular building block for polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. U.S. production of BPA grew rapidly from 16 million pounds in 1991 to about 2.3 billion pounds in 2004, making it one of the most produced chemicals in the world [3]. BPA is a chemical recorded in the CAS (Chemical Abstract Service), number 00080-05-7 and its chemical name as used in Europe is 2, 2-Bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane [23]. There are a large number of synonyms to BPA like Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)dimethyl methane; 4,4′-dihydroxydiphenyl propane; 4,4′-dihydroxy-2,2-diphenyl propane; Diphenylolpropane; 4,4′-isopropylidenediphenol. BPA is produced by the condensation of phenol and acetone in the presence of catalysts and catalyst promoters. Its molecular formula is C15H16O2 and molecular mass is 228.29 g / mol, and melting point is 155 °C (311 °F). The decomposition temperature is > 200°C (392°F) and it is completely soluble in organic solvents and partially soluble in water. It exists at room temperature in the form of a white solid flake or crystal [25]. BPA has been used in a wide variety of consumer products for several decades and continues to be manufactured in large quantities around the world. Humans are exposed to BPA through consumption of food and beverages contaminated with BPA, as well as environmental contamination. Polycarbonate plastic can become unstable over time and with use, allowing BPA to leach into material in contact with the plastics. Other consumer items, such as carbonless paper, computers, home appliances, spectacles and optical lenses, reusable water bottles, food storage containers, sports safety equipment, medical equipment, construction materials, paints, coatings and DVDs, also contain BPA. Additionally, BPA is now found nearly everywhere in the environment and commonly found in dust particles, surface water and drinking water, as over 6 billion pounds are produced worldwide each year [26]. Production of BPA releases approximately two hundred thousand pounds of the chemical into the atmosphere annually [19]. BPA in the rise of multiple diseases including prostate [5] and breast cancer [9], urino-genital abnormalities in male babies, a decline in semen quality in men [10], early onset of puberty in girls, metabolic disorders including insulin resistant (type 2) diabetes and obesity, neurobehavioral problems [1] such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and bisphenol-A also can change endogenous hormone synthesis, hormone metabolism and hormone concentrations in blood [27]. There are many reports on the contamination of BPA in the environment especially in water [28], air and soil [22, 17]. |
 |
MATERIALS AND METHOD |
| The technical grade quality of Bisphenol A is procured from HiMedia Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., (23 Vadhani Ind. Est., LBS Marg, Mumbai, India) for the study of antibacterial activity. The bacterial strains used in this study are Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus substilis, which are gram positive bacteria and Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli which are gram negative bacteria. The bacterial strains were obtained from Microbial Type Culture Collection (MTCC), Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH), Chandigarh – India and maintained in the Microbiology Department of Kakatiya University. Two gram positive bacteria i.e.,Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus substilis and two gram negative bacteria i.e.,Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli were used for assessing and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of the BPA. The method followed is agar well diffusion method [18, 24]. The test organisms were sub cultured using nutrient agar medium. The tubes containing sterilized medium were inoculated with respective bacterial strain. After incubation at 37±10C for 24 hrs they were stored in refrigerator. The stock culture was maintained. Bacterial inoculums were prepared by transferring a loop full of stock culture to nutrient broth. The flasks were incubated at 37±10C for 48 hrs before the experimentation. |
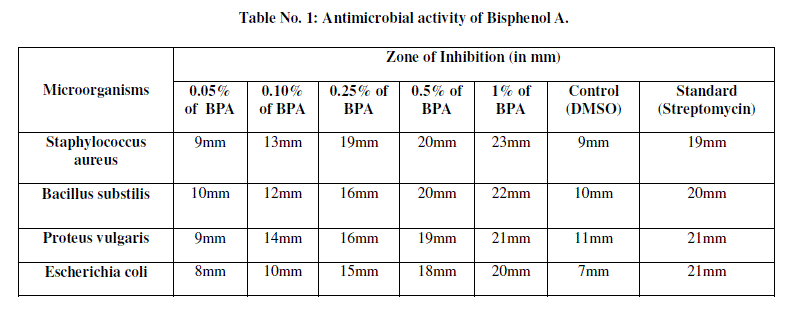
| Stock solution of the test compound was prepared by dissolving10mg/ml of DMSO and was used for testing at different concentrations. Streptomycin is used as standard drug for both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The nutrient agar medium was sterilized by autoclaving at 1210C(12lbs/sq..inch) for 12 min. Petri-plates, tubes and flaks were sterilized in hot air oven at 1600C for an hour. In each sterilized petriplate (10cm diameter) about 27ml of molten nutrient agar medium which is inoculated with the respective strain of bacteria was poured. The plates were left at room temperature to allow solidification. In each plate seven discs of 6mm diameter were made with a sterile borer. The test compound, BPA at concentration 50μg/ml, 100μg/ml, 250μg/ml, 500μg/ml and 1000μg/ml was added to respective disc aseptically and labeled accordingly. The plates were kept undisturbed for 1 hour at room temperature to allow the diffusion of the solution properly in the nutrient agar medium. After incubation of the plates at 37±10C for 24 hours, the diameter of zone of inhibition surrounding each disc was measured with the help of an antibiotic zone reader. All the experiments carried out in triplicate. Simultaneously controls were maintained employing 0.1 ml of DMSO to observe the solvent effects and the results were represented in Table No.1. |
RESULT AND DISCUSSION |
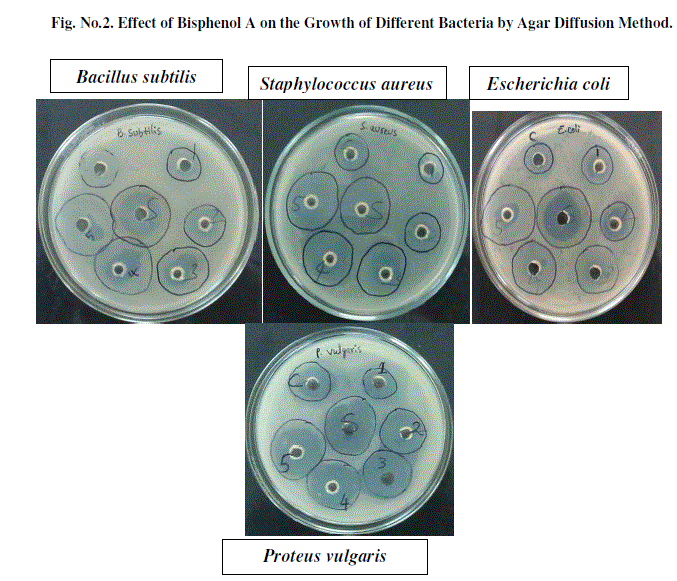
| As BPA is one of the highest volume chemicals produced worldwide, with over 6 million pounds produced each year [3] and is used for the production DVDs, computers, home appliances, spectacles and optical lenses, reusable water bottles, food storage containers, sports safety equipment, toys, water pipes, optical lenses, medical equipment, construction materials, paints and coatings, polycarbonate plastics, epoxy resins and thermal paper [5, 2]. Epoxy resins are used as protective linings for a variety of canned foods and beverages and as a coating on metal lids for glass jars and bottles. These uses result in consumer exposure to BPA via the diet [16]. Residues of BPA are also found in different environments such as rivers and wastewater effluents [14, 11]. Xenoestrogens are chemical with potent estrogenic properties [7]. BPA is classified as a xenobiotic disturbing hormonal balance in humans and other animals and it is an endocrine disruptor [20, 4] The exposure during early development to xenoestrogens such as BPA may be the underlying cause of the increased incidence of infertility, genital tract abnormalities, and breast cancer observed in European and US human populations [21]. Numerous toxicological and biochemical studies have confirmed that BPA has estrogenic properties and an agonistic effect towards the estrogenic receptor. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the National Toxicology Program (NTP) have “some concern” for effects on the brain, behavior, and prostate gland in fetuses, infants, and children at current human exposures to BPA. Number of studies has examined BPA levels in other body fluids such as follicular fluid [12], urine [5] and semen [13, 15,]. BPA is found in milk due to contact with plastic materials during food processing and storage [6]. The Scientific Committee on Food (SCF), an advisory body of the European Commission on the safety of food, after comprehensive analysis of all aspects of BPA toxicity, has specified the tolerable daily intake (TDI) of BPA as 0.01 mg/ kg body mass per day [8]. Recent studies have shown that BPA can alter the gene expression (i.e. turned on or off) and the low-dose BPA exposure during pregnancy has multigenerational consequences and it may increase the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in F2 generation [26]. To test the effect of BPA as antibacterial agent, concentrations ranging from 0.05% to 1% were observed and the results are presented in [Table No.1] The antibacteriall activity of the BPA was studied by agar well diffusion method [18,24]. BPA is completely soluble in organic solvents and partially soluble in water [25]. DMSO scored as better solvent followed by methanol and ethanol, in terms of their compatibility with MIC determination. Hence it is dissolved in DMSO [29]. Among the different concentrations chosen i.e., 0.05%, 0.10%, 0.25%, 0.5% and 1%, BPA has shown strong antibacterial activity against all the bacterial strains that were tested [Fig.No.2]. It is found that the effect of BPA on the bacterial growth show the zone of inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus 23mm, Bacillus substilis 22mm, Proteus vulgaris 21mm and Escherichia coli 20mm [Table No.1]. BPA showed a maximum zone of inhibition in Staphylococcus aureus. and has antimicrobial activity against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. It has greater activity against gram-positive species over gram-negative species. It is evident from the study that the BPA is more effective in killing gram positive bacteria. The death of bacteria may be because it blocks lipid synthesis in them and has been shown to intercalate into bacterial cell membranes and disrupt membrane activities without causing leakage of intracellular components [30]. Since BPA is acting as xenoestrogen its usage should be limited in consumer products and especially the usage in child care products should be restricted. As there is a controversy and public concern in the use of BPA in consumer products as it possess hazardous health effects, methods should be developed for production of alternate compounds. |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| `From the above study it can concluded that the antibacterial activity increased with the increased concentrations of BPA It is evident from the study that the BPA is more effective in killing gram negative bacteria when compared to gram positive bacteria. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS |
| The authors wish to thank the Head, Department of Zoology, Kakatiya University, Warangal, for providing laboratory facilities. We thank to Department Microbiology, Kakatiya University., for providing bacterial strains to carry out this work. |
 |
References |
|