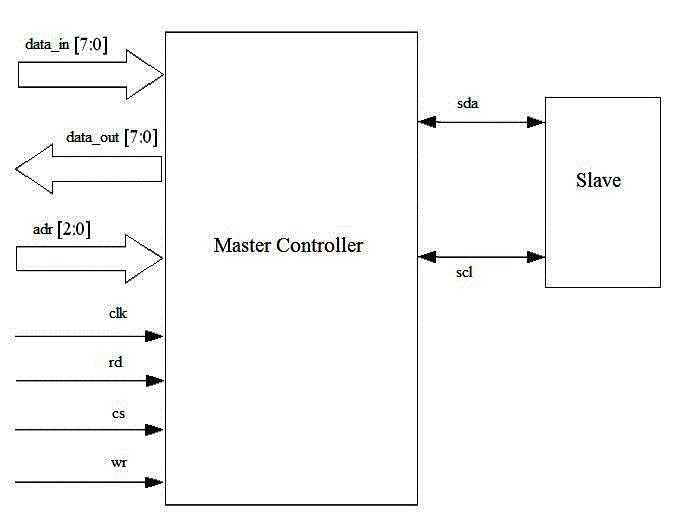
In this paper we focus on the design of I2C bus controller and the interface between the two integrated devices i.e. microcontroller and EEPROM like as a master controller and a slave for serial communication in embedded system. The components of the I2C bus controller is consist of only a bidirectional two wire and standard protocol which communicate between two integrated circuit or device. First one is serial data (SDA) line and second is serial clock (SCL) line. The I2C protocol was given by Philips Semiconductors for faster devices to communicate with slower devices and each other without data loss. The complete module is designed in VHDL and simulated in ModelSIM. The design is also synthesized in Xilinx XST 14.1.
Keywords |
| I2C Bus, microcontroller, VHDL, ModelSIM, Xilinx XST 14.1. |
INTRODUCTION |
| The design of I2C bus controller will be interface to integrate for the purpose to communicate between them i.e. the onchip
RAM (EEPROM), Oscillator (RTC), ADC. The presence of a RTC and an on chip RAM support for a data
communication between the chip and a host computer to send data on the RAM. To minimize the system-level
interconnect between integrated devices, I propose to transmit the contents of the RAM storing the results back to a
host computer via a serial bus, the I2C Interface. The interconnect integrated circuit bus commonly known as the I2C
bus which is a bi-directional, two-wire and serial communication standard protocol. The designed are simple but
difficult for efficient integrated circuit (IC) control. The system is comprised of two bus lines, SCL (Serial Clock) and
SDA (Serial Data). Each device can be identified by a unique 7 or 10 bits-address. The I2C protocol supports to
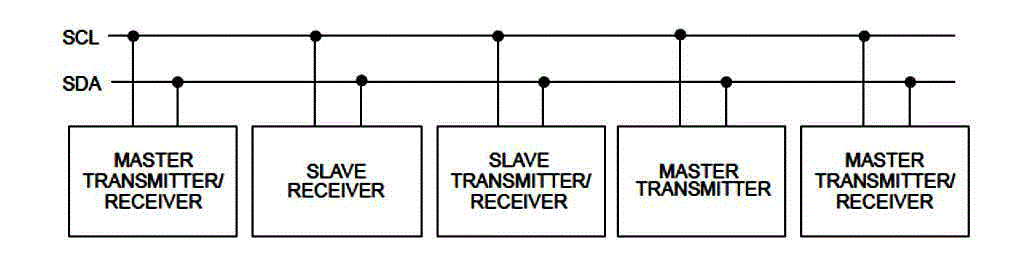
multiple master but this application discusses only a Master and a Slave system implementation. Standard I2C devices
operate up to 100Kbps, while fast-mode devices operate at up to 400Kbps. Most of the I2C devices available today
support 400Kbps operation. |
BUS SPECIFICATIONS OF I2C |
| The Philips semiconductor was introduced by I2C standard protocol for communicate with faster to various slower
devices and communicate with each other, without data loss. The I2C bus component are used, a bi-directional two
wire. First is SDA(serial data) and second is SCL(serial clock). I2C-bus supports any IC fabrication process i.e. it may
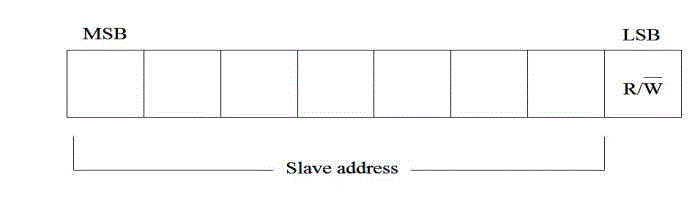
be NMOS or CMOS or bipolar. Each device recognized by a unique 7 or 10 bit address ( microcontroller, LCD driver,
EEPROM, ADC or RTC). Its can operate as either a transmitter or receiver, depending on the function of the device.
Obviously an LCD driver is only a receiver whereas a memory can both receive and transmit data. In addition to
transmitters and receivers, devices can also be considered as masters or slaves when performing data transfers. |
I2C Bus Terminology: |
| Transmitter: The device which sends the data or message to the receiver. |
| Receiver: The device which receives the data or message from the bus. |
| Master:-The device which generates clock signals, initiates a transfer i.e. start condition and terminates a transfer i.e.
stop condition. It may also act as a transmitter/receiver. |
| Slave:-The device addressed by a master. Also it may act as a transmitter/receiver. |
| Multi master: More than one master can attempt control the bus at the same time without demeaning the
data/message. |
| Arbitration: It is a procedure to ensure that, if more than one master simultaneously tries to control the bus, only one
is allowed to do so and the data is not corrupted. |
| Synchronization: It is a procedure to synchronize the clock signals of two or more devices. |
I2C BUS CONTROLLER DESIGN |
| The design of the master controller for I2C bus is following some step:- |
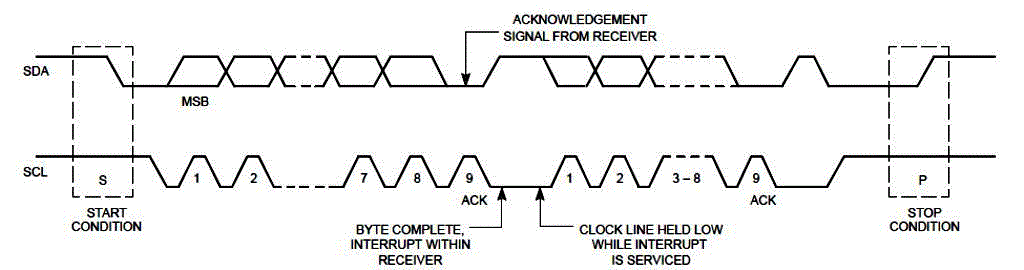
| (a) START and STOP condition: all transactions begin form START(S) and can be terminated by a STOP (P).
A HIGH to LOW transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH defines a START condition. A LOW to
HIGH transition on the SDA line while SCL is HIGH defines a STOP condition. |
| (b) Byte format Data Transfer: every byte must be 8 bit long put on the SDA line. Each byte followed by
Acknowledge bit. Which show in figure 2. |
| (c) Device Addressing: the device addressing of the I2C bus are using 8 bit word within one W/R bit which
depend on the clock like as if clock is low then write and high then read. |
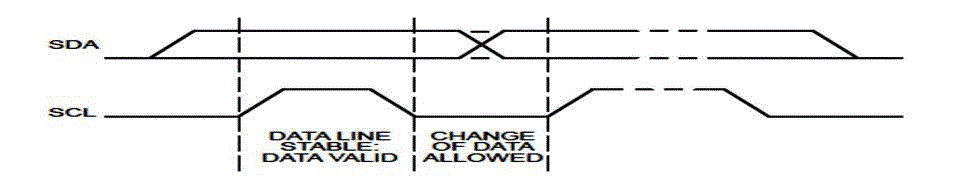
| (d) Data Validity: The data on the SDA line are valid for during high period of clock pulse. |
I2C BUS ARCHITECTURE |
| The I2C bus architecture consists of Master and Slave and there is only one master. The master controller for I2C bus is
design on the verilog Hardware Description Language (HDL). I2C is a two-wire, bi-directional serial bus that provides
a simple and efficient method of data exchange between devices. |
I2C PROTOCOL AND DESIGN STEP |
| Normally, a standard communication protocol consists of four parts: (a) START signal generation,(b) Slave address
transfer,(c) Data transfer,(d) STOP signal generation. |
| The functional description of I2C master has to be described in the Verilog HDL. That is called design module / core.
The test bench program has to be developed to test the design module. The test bench gives the input to the design
module & verifies the outputs. The test bench has to be written in such way to check the design module in all possible
conditions. Verilog simulator tool is used to verify the design functioning (Simulation). |
CONCLUSION |
| We can be interface of between two or more device using a I2C bus and data are serially communicate. Two device as
microcontroller (master) and EEPROM (slave) using a I2C bus can be interface of each other. The master controller is
design on the verilog HDL, simplifies the design process. It is similar to device address and a unique bits-address on
the master and slave device which each device can be identified. The design of master controller is easy but slave
design is difficult. The designer can write his design description without choosing any specific fabrication technology.
If a new technology emerges, designers do not need to redesign the circuit. He simply input the design program to the
logic synthesis tool and creates a new gate level netlist using the new fabrication technology. The logic synthesis tool
will optimize the circuit in area and timing for the new technology. |
ACKNOWLEDGMENT |
| The correspondence author is thankful to all the faculty members of department of Electronics & Communication, IES
College of Technology Bhopal, M.P. and India for continuous support and encouragement. This is an opportunity to
prove our technical skill for the benefit of social civilization. |
Figures at a glance |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
|
References |
- D. Paret: Le bus I2C, de la thÃÆéorie ÃÆàla pratique, ISBN2100017179, ed. DUNOD, Paris 1993.
- R. Herveille. I2C-Master Core Specification, Rev. 0.9,
- I2C bus Inter Integrated Circuits bus by Philips Semiconductors.
- O. Romain, T.Cuenin & P.Garda: âÃâ¬ÃÅDesign &modeling of an I2c Bus ControllerâÃâ¬ÃÂ, FDL 0âÃâ¬Ãâ¢3,Frankfurt, Deutschland, Sept 23-26,2003.
- Muhammed Ali Mazidi, Janice Gillispie Mazidi &Rolin D. Mckinlay, The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems, using Assembly andC , secondEdition, Pearson Education.
- http://www.engineersgarage.com/microcontroller/8051projects/interface-serial-eeprom-24c02-AT89C51-circuit.
- http://www.charmedlabs.com/index.php?option=com_smf&Itemid=36&topic=640.0.
- IEEE Computer Society. IEEE StandardVerilog̨̉ HD Language, IEEE Std 1364-2001, TheInstitute of Electrical and ElectronicsEngineers,Inc,28 September 2001.
- R. Herveille. I2C-Master Core Specification,Rev. 0.9, 2003.7.
- A Novel Architecture of I2C Slave using One-Hot Encoding Technique,Devashree Mahato, Sulipta Das, Durga Prasad Das.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I2C.
- A.R.M. Khan, A.P.Thakare, A.R.M. Khan,FPGA based design and implementation of serial datatransmission controller, et. al. / InternationalJournalof Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 2(10),2010, 5526-5533.
|