ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Manoj R. Patkar1, Yogesh M. Keskar2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
This paper aims to explore the urban hybridization phenomenon as an integral part of contemporary society growth dynamics, building typologies and spatial organization. In particular, it will be examined its diffusion within newly emerging western idealized contexts due to globalization, in order to grasp the ongoing dimension of the process and outline some of its main features. It is important to notice that the peculiarity of these specific environments is due to their rapid transformation producing the almost simultaneous formation of new urban asset patterns, development models and cosmopolitan urban contexts. A core part of the work will be constituted by the analysis of some of the typical diffused city hybrid forms, paying major attention to the progressively heterogeneous landscapes and ground-scapes juxtaposition, along with the increasing urban edges uncertainty. Proliferation will be intended as a rather complex evolution process and, as a result, requiring a vaster and multilayer periphery cognition formulation. Its manifestation in urban context will be identified in some of the contemporary spatial configurations and in building typologies generally identifiable as: new public open spaces and container-like attractors, market streets, new city gates and highway-scapes, new specialized areas, downtown and super-sites urban hybrids. These evidence some of the common mechanisms and generative factors acting throughout the different social, physical, economical and territorial milieus. In this paper we are also trying to initiate the thinking process of readers about this topic, by putting some questions in front of them.
Keywords |
| Urban Hybridization, texture, fragmented spaces, development. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Emergence Of Thought |
| Initially the urban hybridization is a thought of Los Angeles (LA) school. The major shift is continued from Modern city to postmodern city. It was emerges with decentralized urban structure of the city, While Evaluating the structure and principal dynamics for such city which result is fragmentation. The pattern is noncontiguous i.e. connected collage urban patches. Segregation of urban structure is developed on demand of exclusive needs. |
| Developing a thought - process of hybridization |
| Urban hybridization is developing in the postmodern urbanism and it has certain reasons for such urban development. Following are the factors in city which are responsible for the process of hybridization. |
| a) Reform of governance |
| Fragmentation of metropolitan areas is in too much of local government, because of economic and social policie s. It is not only a barrier of effective growth management, but also a cause of racial and economic segregation, sprawl fiscal disparities within those areas. |
| b) Developing suburbs |
| Demands are of good infrastructure, private areas, exclusive needs and automobile based lifestyle by urban dwellers. It is resulting in loss of forest, wildlife in suburban areas. |
| c) Mixed functions |
| Increase of density, migrations, need of multi-functional activity at one place to have growth in economic aspect. |
| d) Diversity in lifestyle |
| The urban living is largely influenced by the globalization, due to that the social changes, adverse environmental effect, demand of premium lifestyle, imagination of external standards and transnational lifestyles, extensively seen in metropolitan areas. The attraction of the lifestyle is advertised largely, especially by the developer through advertisement. They approached to the user by showing the glorification visual of the proposed new places in city. In Bangalore one developer announces, 'live the way the world does… (We offer) international style houses… [And] exclusive locations in Asia's fastest growing city’. These factors are cased to have the hybrid structure of the city, and it is seen in the city by identifying the physical imprints of urban blocks. The city which has such structure is called Hybrid city. It can be defined as, the ubiquity of fragmentation both in material and cognitive life, including the collapse of conventional communities, and rise of new cultural categories and spaces, including especially cultural hybrids. |
| Urban hybridization - impact |
| The hybrid fragmented developing or developed city structure which impacts on environmental, physical, social and on economic factor of the city. Majorly focus on newly rapid transformation which is producing formation of new urban asset patterns and developments. It is seen in the city as emerging typical diffused city hybrid forms, the progressively heterogeneous landscapes and ground-scapes juxtaposition, along with the increasing urban edges uncertainty, Complex evolution process of proliferation of built resulting in a higher degree and multilayer periphery formation, generative factors acting throughout the different social, political and territorial milieus. |
II. AREA OF STUDY: PUNE CITY, MAHARASHTRA, INDIA |
| Introduction |
| Pune is a gamma city at global level. It is at 8th rank in Metro category. City is having the manufacturing, automobile, government & private sector research institutes, information technology (IT) and educational, management, training institutes that attract migrants, students and professionals. |
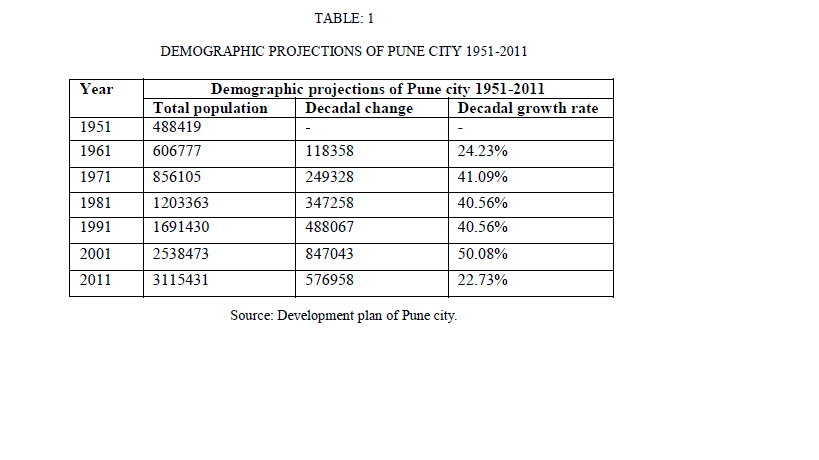 |
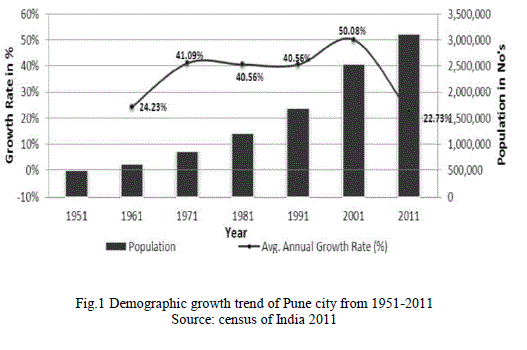 |
| Emergence stages of hybrid urban development |
 |
| Urban hybridization |
| Urban hybridization is an act due to globalization with change in of social, physical, economic, and political aspects to produce new typologies and spatial configurations in a city. Manifestation of such changing aspect creates physical distinct changes in the urban fabric. To understand the hybridization processes and their physical, social, economic, environmental impact and their causes on the city, following five categorizations of urban development pattern based on physical changes, will show the urban hybridization as a new paradigm urban development in metropolitan areas. These hybrid developments have raised the questions respective to social, physical, economic and environmental to address sustainability of the metropolitan cities. |
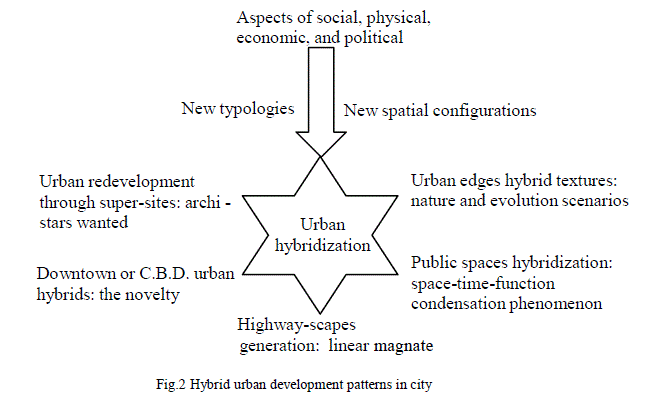 |
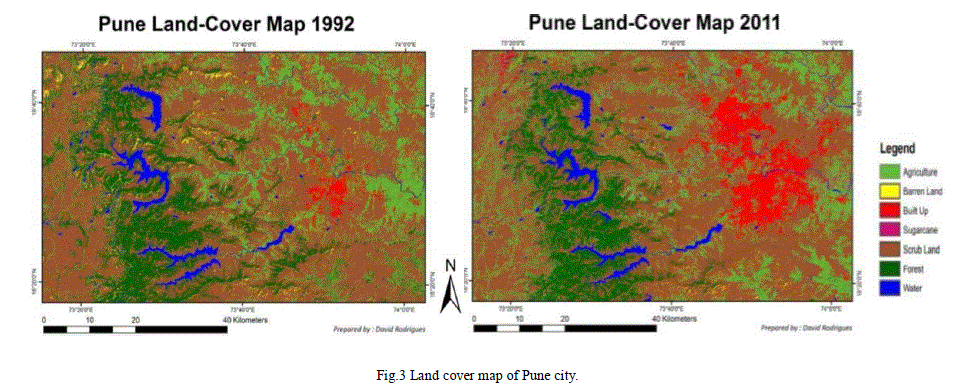 |
| Fig.3 Land cover map of Pune city. |
| Source: CDP of Pune. |
| 1. Urban edges hybrid textures: nature and evolution scenarios Development of city from the core area rapidly spreading towards hilly area i.e. started in mountain skirts from city core. • Causes and impacts: Different spatial patterns and varied building forms as fragmented planned patches in mountain skirts as well as in between agricultural pockets. Progressing as an “Educational and Cultural Centre” for the country. While this transformation, the haphazard radial development of the city created immense pressure on the provision of infrastructure. The radial development of land use pattern results into the loss the green land section of the city and Loss of wild life. Dispersion process of scattered spaces, are giving thus birth to a relatively new hybridization patterns. Many isolated and walled residential communities occurred randomly because of following mainly low market land values for the developers within the city's outskirts and the mountain-skirts quarters. It is being observed that the building of gated communities, private, high-rise condominiums with heavy security at city edges. The street pattern resulted in Grid pattern, curvilinear loop & cul-d-sac pattern and cul-d-sac pattern having patchy settlements at urban fringes. It resulted in loss of environment. Question arises due to such developments. |
Are these developments continuing to develop exclusive Private spaces and resulting in a loss of Public interactive spaces as well as environmental assets? |
 |
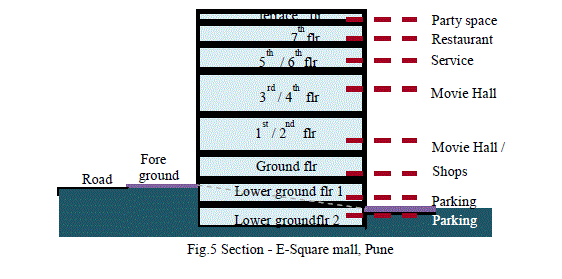
2. Public spaces hybridization: space-time-function condensation phenomenon |
| The case represents an in-between condition: it appears to be a well-integrated hybrid, taking advantage of the available resources in place and completing the existing functions. • Causes and impacts: In post-1989 cities were welcoming of the new multifunctional and multi-storey containers, i.e. malls. Insertion process of these 'hybrid machines' (Boeri, Lanzani and Marini, 1993: 50) is not the one of integration, rather the one of implantation throughout the 'street advertisement architecture' glorification. Influence of branding largely on commercial world. It is preferably used by specific group of people due to brands. There is adaptation of western concept with respect to change in lifestyle and time-saving convenience, but above all - the 'novelty' factor. Question arises due to such developments. |
Is this typological change creating equitable public place for city, in case of diverse contexts? |
 |
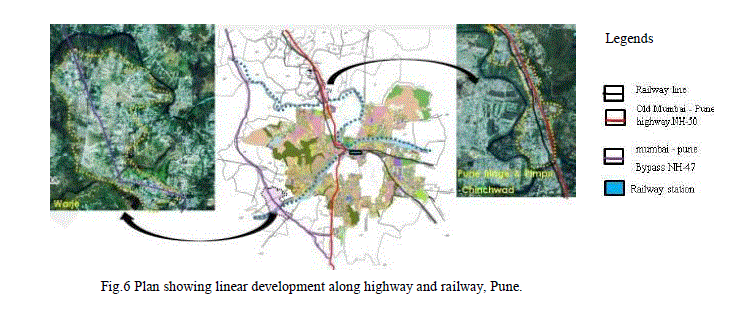
3. Highway-scapes generation: linear magnate |
| In between cities (Pune & Pimpari-Chinchwad) the railway and road highway are important for residential commercial, industrial and recreational activities. • Causes and impacts: It represents a powerful urban element that participates intensively in the urban spaces breaking up, generating new tensions and accumulative processes along these linkages that bind it with the city. The highway-scape, triggered by its enormous magnetic power, demonstrates the 'gates' importance for the contemporary globalized cities‟. Big advertising posters, bright colors and forms, are the arrangement of this new hybrid space, half high-speed street/half city. Malls, hotels, industries, offices, institutions, residential apartments are emerging along the railway line and highway this is developing as an economic growth corridor for the city. City people uses Private vehicle to access these functions extensively. The construction of multilayer streets formation starts, resulting in flyovers, grade separators. They become necessary to maintain road hierarchy and the separations of traffic modes. Question arises due to such developments. |
Are these growth corridors being responsible discouraging future livable streets environments? |
 |
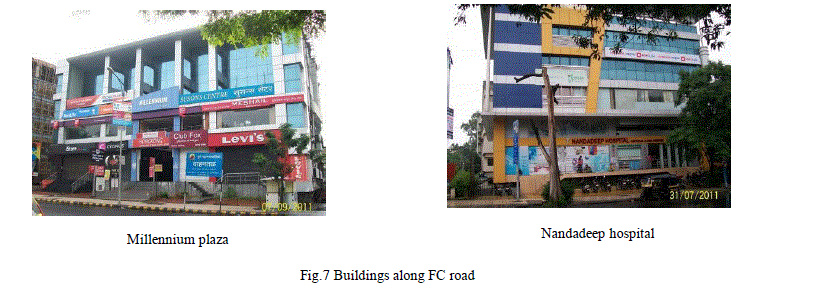
4. Downtown or C.B.D. urban hybrids: the novelty |
| Emergence of modern characters is contrast to traditional character in the city. Hybrids signs in the city central areas: demolishing and rebuilding practices are always in favor of office buildings - old residential ones are thus disappearing. It is quite obvious that the local administration is unanimously part of the process, but a question that may occur is 'why'. Aspects (which are still evolving) of the hybridization phenomenon is the high-tech metamorphosis of preexisting buildings, operated through additions, amplifications and juxtapositions. In a similar way 'strategies at the urban and architectural level, were developed to wipe out the past and join the 'civilized texture‟ and propositions of glass buildings, aluminum cladding, and multicolored facades. Well visible the insertion of the high-tech facades in the preexisting residential buildings Causes and impacts: The novelty (equal to different from past, equal to coming from western cultures) character of the new glassbuildings is making of them symbols of the new capitalist political era success and thus widely accepted if not even encouraged. Thus, being anchored on a political ground, the values and reasons for promoting them are stronger than harmony and local context design criteria. Urban fabric is presents diverse architectural characters and material. The contemporary buildings are with more focusing on material aesthetics. Question arises due to such developments. |
Are these evolved and evolving contemporary trends of architectural characters or only material aesthetics for the building façade? |
 |
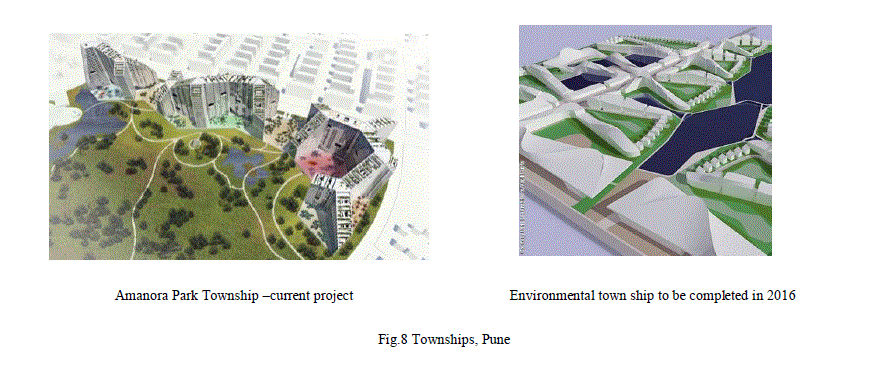
5. Urban redevelopment through super-sites: architects fashion and trends. |
| The importance of the image, the flash sensation, the 'eye-catching' impression, in the strategizing for the contemporary cities future is intrinsically bound to a fundamental shift in the cities role itself. Images of their future or ongoing realizations are circulating all over the global net by the advertisements. Causes and impacts: Distribution of work places (IT‟s), industries, educational institutes etc. in city is scattered. New development rules are caused to have such developments. Influence of global economy on the city growth become large due to the international connections and communication of the businesses. Become tourist destinations that, buildings are of attractive forms. As an Investment for the future people are buying the property in city fringe areas. Second home concept is becoming popular – in case of bungalows, demanding the separate houses for the exclusive facilities and luxurious living style. They are expensive ones. Living in the mega housing project and township is becoming Status symbol. Question arises due to such developments. |
Such townships and housing projects are responsible for city growth so, are these developments creating inclusive or exclusive community urban spaces? |
 |
III. CONCLUSION |
| Urban hybridization is becoming integral part of contemporary society growth dynamics and spatial organization due to globalization. |
Are there possibilities to achieve social, physical and economical sustainability and active public realm with hybrid urban structure? |
| „Lack of close knowledge of the different actors and social group‟s behaviours and of their reasons' involved in the whole urban evolution process results in hybrid structure of the city. Hybridization is become a part of today‟s society growth because, cities recently entered in the progressively globalized international networks. It is generating cosmopolitan urban context and transcultural spaces. Concern with spatial organization of the city a great attention is to be focused on broadening the urban knowledge and discipline horizons. Overcoming on the negative process of the designing/ planning/ policies process is to be considered. Social integration purpose misses in overall project phases. Necessary for avoid the 'individual projects to be developed‟ and more ambitious projects to be encouraged. |
ACKNOWLEDGMENT |
| We are very much thankful to Prof. Piyush Hajela and Ar.Nupoor Saran Saboo in School of Planning and Architecture Bhopal, for their valuable guidance for this paper. |