Keywords
|
| Inverter, Sinusoidal-PWM, Modified Reference, Harmonic Reduction, Ripple, Fast Fourier Transform. |
INTRODUCTION
|
| The objective of the dc/ac inverter is to produce a sinusoidal ac voltage with controllable magnitude and frequency. Inverters are widely used in many applications such as in the UPS and ac motor drives. There are many types of inverters. The pulse-width-modulated (PWM) inverter[1] is the most favoured one for industrial applications. The control schemes of PWM inverters are broadly classified as programmed PWM inverters and sinusoidal PWM inverters. The sinusoidal PWM method is very popular in many applications. |
| One of the major issues with PWM is the presence of harmonics. The higher order harmonics around the carrier frequency are relatively easier to filter out, but the lower order harmonics smaller in magnitude and cause problems in certain applications for the PWM inverters. To reduce these lower order harmonics a variety of techniques have been proposed. Sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) technique is used to generate gate pulses. SPWM technique is widely used in industries. |
| SPWM is a very simple technique for harmonic reduction. In this technique pulse magnitude will be constant and only pulse time (width) can be changed.[2] In this pure sine wave is compared with carrier (triangular) wave and producing gate pulses. Sine wave has fundamental frequency and carrier wave can be taken more than fundamental frequency. |
| Advantages of SPWM: |
| 1. The output voltage control is easier with PWM than other schemes and can be achieved without any additional components. |
| 2. The lower order harmonics are either minimized or eliminated altogether. |
| 3. The filtering requirements are minimized as lower order harmonics are eliminated and higher order harmonics are easier to filter out. |
| 4.It has very low power consumption. |
TEST SYSTEM
|
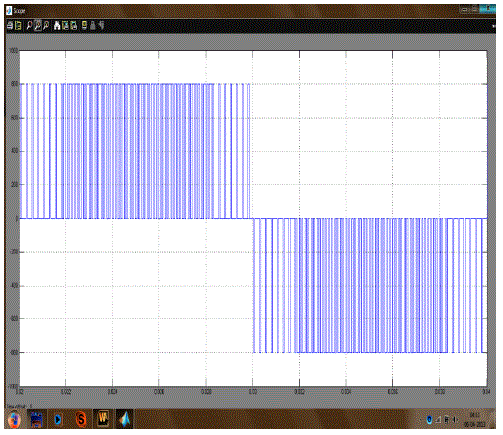
| Basically, a full-bridge single-phase inverter is known as H-bridge inverter as shown in Figure 1.The full bridge inverter can provide either Bipolar or Unipolar output voltage switching. The Unipolar inverter is optimum for harmonic elimination more than Bipolar inverter. The H-Bridge inverter circuit consists of four main switches and four freewheeling diodes.[3] According to four-switch combination, three output voltage levels, +Vdc , -Vdc and 0 can be synthesized for the voltage across Vab in Figure 2. |
| The various parameters used for studies done in this paper are listed in Table I. |
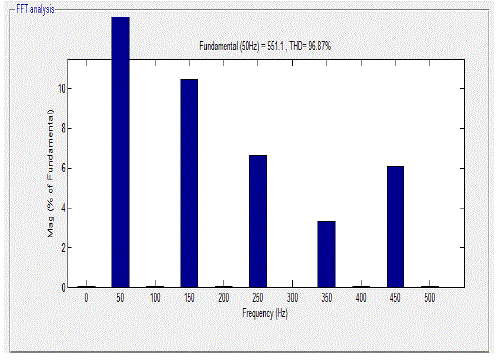
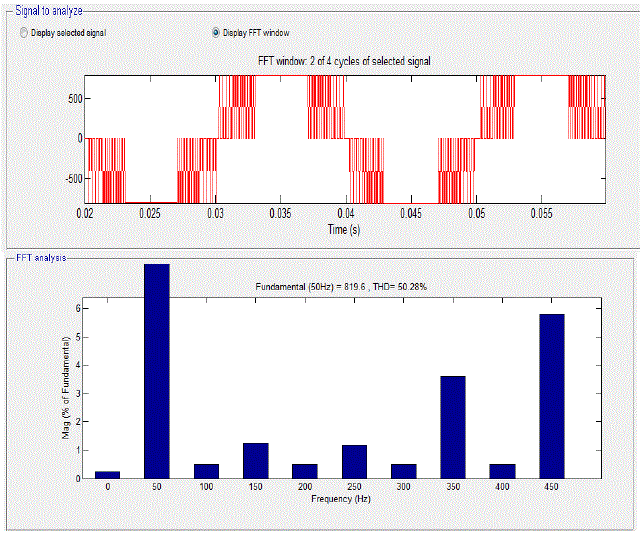
| The inverter output voltage is as shown in Figure 2. The output voltage has fundamental and some harmonics superimposed due to switching. Figure 3 shows the harmonic content of Vab by using FFT analysis |
| The ratio of fc to fmaffects the output voltage harmonic content of the PWM inverter. The effect of this ratio is practically seen only when this ratio is small. A sufficiently high ratio, i.e., ïÿýïÿýïÿýïÿý ïÿýïÿýïÿýïÿý > 9, than the effect of this ratio on harmonics is negligible. |
CIRCUIT TOPOLOGY
|
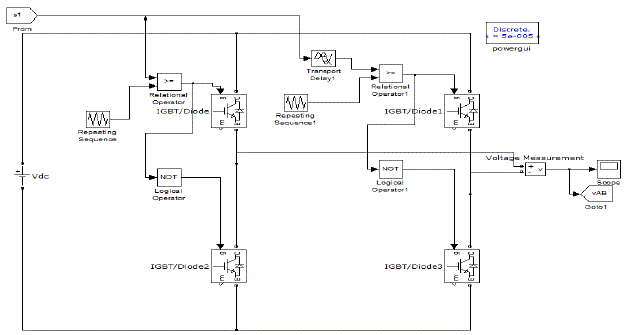
| Fig 4 shows the circuit configuration of a basic single phase inverter referred to as the H- Bridge. The H- Bridge inverter consists of 4 IGBT switches as shown . |
CONTROL SCHEME
|
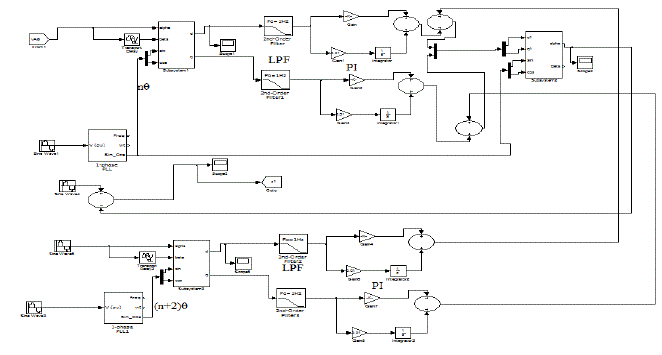
| According to the elimination of harmonics a control scheme is proposed for modifying reference sine wave to the inverter. Figure 5 shows the block diagram model of the scheme for nth and (n+2)th harmonics elimination at a time i.e., 3rd and 5th harmonics or 5th and 7th harmonics and so on will be eliminated at a time. |
| The output voltage of the inverter Vab istaken as α – component and is delayed by 90o to get the ïÿýïÿý – component . A phase locked loop is applied to the reference sine wave to get the angle information nθ and (n+2)θ, where n is the harmonic order to be eliminated. The transform shown in Eq. 1 converts the α – ïÿýïÿý to de – qe quantities whereby the harmonic of interest becomes DC quantities. |
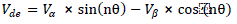 |
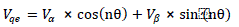 |
| The low pass filters (LPF) having cut off frequency 1 Hz, is applied to extract the DC quantities. After passing through a suitable PI controllers, a reverse transformation as shown in Eq. 2 is done to get the α component of voltage. |
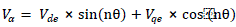 |
| This signal is subtracted from the reference and compared with the carrier to generate the switching pulses (S1). This block diagram shows elimination of two harmonics (3rd and 5th) at a time. This scheme can be extended to include other harmonics also in a similar fashion. |
SIMULATION RESULTS
|
| The system shown in Fig 4 was simulated in MATLAB with the control scheme shown in Fig 5. The results for elimination of 3rd and 5th dominant harmonics at a time with FFT analysis are shown in Fig.6 below |
CONCLUSION
|
| In this paper, the popular sinusoidal PWM technique with a control scheme, which can reduce any two dominant lower order harmonics at a time, is proposed. Since there is no hardware requirement here, the scheme is reliable and economical. Furthermore, by using the multilevel inverters we can improve the THD in future. |
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
|
| We take this opportunity to express our deepest gratitudeand appreciation to all those who have helped us directly or indirectly towards the successful completion of this paper. |
Tables at a glance
|
 |
| Table 1 |
|
Figures at a glance
|
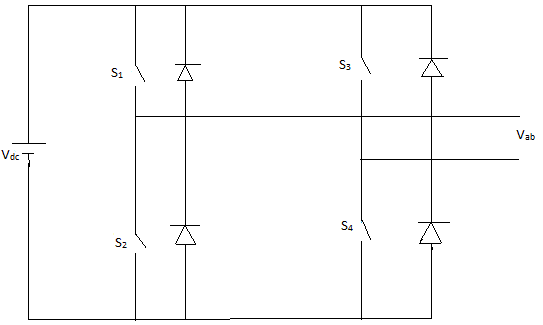 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
Figure 6 |
|
References
|
- 1.MUHAMMAD H. RASHID,“Power Electronics-Circuits, Devices and Applications”.
- 2.L.UMANAND, “Power Electronics-Essentials and Applications”.
- P.S.BHIMBRA, “Power Electronics”.
- R.N. RAY, D. Chatterjee and S.K. Goswami, “An application of PSO technique for harmonic elimination in a PWM inverter”, Applied Soft Computing Journal, Vol. 9, No. 4, Sept. 2009, pp. 1315-1320.
- D.G.Holmes and T.A.Lippo, “Pulse Width Modulation for Power Converters-Principles and Practice”, IEEE press series on power engineering,Wiley Interscience Publication, 2003.
|