Keywords
|
| MPPT, Incremental Conductance, PV cell, Algorithm, simulation. |
I.INTRODUCTION
|
| Photovoltaic (PV) systems have been used for many decades. Today, with the focus on greener sources of power, PV has become an important source of power for a wide range of applications. Improvements in converting light energy into electrical energy as well as the cost reductions have helped create this growth. Even with higher efficiency and lower cost, the goal remains to maximize the power from the PV system under various lighting conditions.[2] |
| Unfortunately, PV generation systems have two major problems: the conversion efficiency of electric power generation is very low (9÷17%), especially under low irradiation conditions, and the amount of electric power generated by solar arrays changes continuously with weather conditions. |
| Moreover, the solar cell V-I characteristic is nonlinear and varies with irradiation and temperature. In general, there is a unique point on the V-I or V-P curve, called the Maximum Power Point (MPP), at which the entire PV system (array, converter, etc…) operates with maximum efficiency and produces its maximum output power. The location of the MPP is not known, but can be located, either through calculation models or by search algorithms. Therefore Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) techniques are needed to maintain the PV arrayâÃâ¬ÃŸs operating point at its MPP[1]. |
| MPPT:- Maximum Power Point Tracking, frequently referred to as MPPT, is an electronic system that operates the Photovoltaic (PV) modules in a manner that allows the modules to produce all the power they are capable of. MPPT is not a mechanical tracking system that “physically moves” the modules to make them point more directly at the sun. MPPT is a fully electronic system that varies the electrical operating point of the modules so that the modules are able to deliver maximum available power. Additional power harvested from the modules is then made available as increased battery charge current. MPPT can be used in conjunction with a mechanical tracking system, but the two systems are completely different. |
| The P&O and IC techniques are the most widely used. |
II. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
|
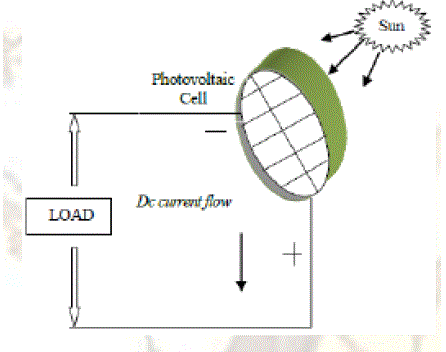
| Solar cell convert sunlight directly to dc power. Photovoltaic cell generates electricity from the sun. PV panel works under the phenomenon of photoelectric effect. When solar cell are exposed to sunlight , it converts solar energy into electrical energy |
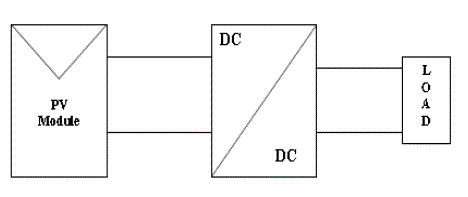
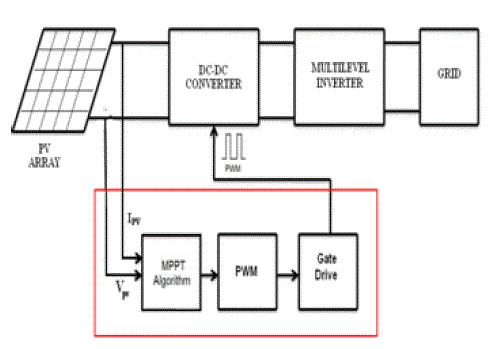
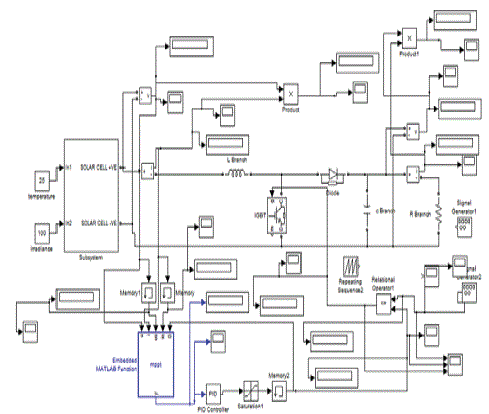
| The system configuration for the topic is as shown figure 2. Here the PV array is a combination of series and parallel solar cells. This array develops the power from the solar energy directly and it will be changes by depending up on the temperature and solar irradiances. |
| So we are controlling this to maintain maximum power at output side we are boosting the voltage by controlling the current of array with the use of PI controller. By depending upon the boost converter output voltage this AC voltage may be changes and finally it connects to the utility grid that is nothing but of a load for various applications. Here we are using Five-level H-Bridge Cascade multilevel inverter to obtain AC output voltage from the DC boost output voltage. |
III. ROLE OF MPPT IN SPV SYSTEM
|
| Photovoltaic systems normally use a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) technique to continuously deliver the highest possible power to the load when variations in the isolation and temperature occur, Photovoltaic (PV) generation is becoming increasingly important as a renewable source since it offers many advantages such as incurring no fuel costs, not being polluting, requiring little maintenance, and emitting no noise, among others. PV modules still have relatively low conversion efficiency; therefore, controlling maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for the solar array is essential in a PV system. The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is a technique used in power electronic circuits to extract maximum energy from the Photovoltaic (PV) Systems. In the recent days, PV power generation has gained more importance due its numerous advantages such as fuel free, requires very little maintenance and environmental benefits. To improve the energy efficiency, it is important to operate PV system always at its maximum power point. Many maximum power point Tracking (MPPT) techniques are available and proposed various methods for obtaining maximum power point. But, among the available techniques sufficient comparative study particularly with variable environmental conditions is not done. This paper is an attempt to study and evaluate s60e main types of MPPT techniques namely, Open-circuit voltage and Short-circuit current, P&O, IC etc. [4] |
| A solar cell basically is a p-n semiconductor junction. When exposed to light, a dc current is generated. The generated current varies linearly with the solar irradiance. The standard equivalent circuit of the PV cell is shown in Fig.1. |
| The basic equation that describes the I-V Characteristics of the PV model is given by the following equation: |
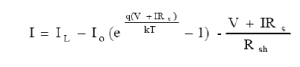 |
| This equation shows the dependence of PV current on temperature and hence the dependence of power drawn from the PV array. |
IV. IC MPPT TECHNIQUE
|
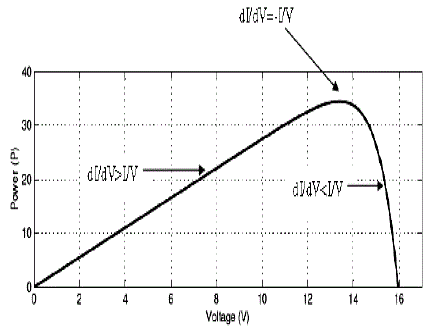
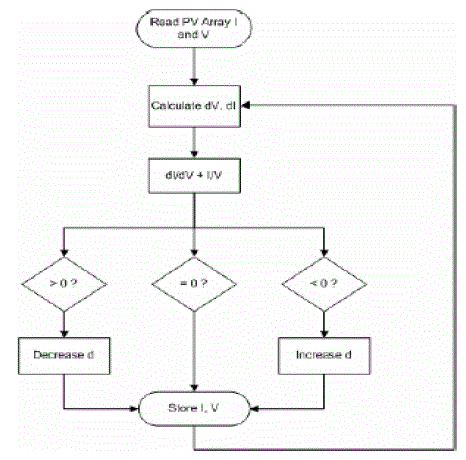
| The disadvantage of the perturb and observe method to track the peak power under fast varying atmospheric condition is overcome by IC method . The IC can determine that the MPPT has reached the MPP and stop perturbing the operating point. If this condition is not met, the direction in which the MPPT operating point must be perturbed can be calculated using the relationship between dl/dV and –I/V This relationship is derived from the fact that dP/dV is negative when the MPPT is to the right of the MPP and positive when it is to the left of the MPP. This algorithm has advantages over P&O in that it can determine when the MPPT has reached the MPP, where P&O oscillates around the MPP. Also, incremental conductance can track rapidly increasing and decreasing irradiance conditions with higher accuracy than P and O |
| Fig-4 shows that the slope of the P-V array power curve is zero at The MPP, increasing on the left of the MPP and decreasing on the Right hand side of the MPP. The basic equations of this method are as follows.[11] |
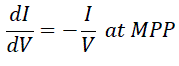 |
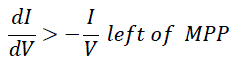 |
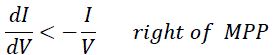 |
V. INCRIMENTAL CONDUCTANCE MPPT ALGORITHM
|
| This method exploits the assumption of the ratio of change in output conductance is equal to the negative output Conductance Instantaneous conductance. We have, |
| P = V I |
| Applying the chain rule for the derivative of products yields to |
| ∂P/∂V = [∂(VI)]/ ∂V |
| At MPP, as ∂P/∂V=0 |
| The above equation could be written in terms of array voltage V and array current I as |
| ∂I/∂V = - I/V |
| The MPPT regulates the PWM control signal of the dc – to – dc boost converter until the condition: (∂I/∂V) + (I/V) = 0 is satisfied. In this method the peak power of the module lies at above 98% of its incremental conductance. The Flow chart of incremental conductance MPPT is shown below.[8] |
VII. SIMULATION RESULTS
|
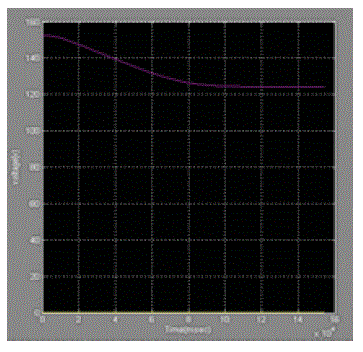
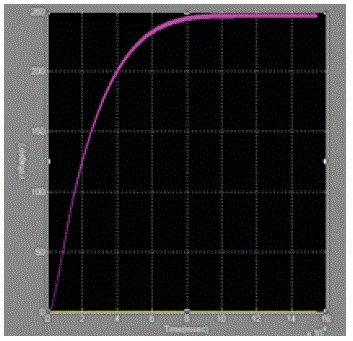
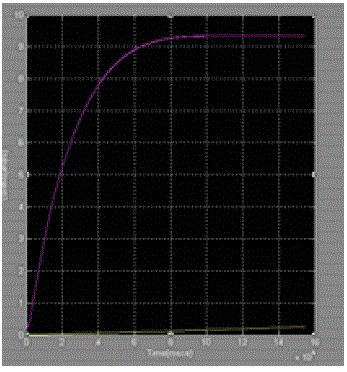
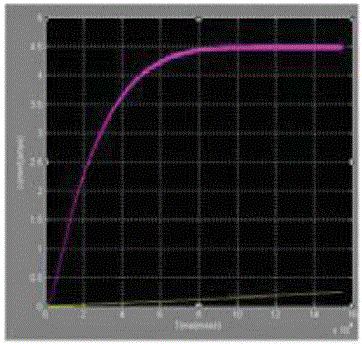
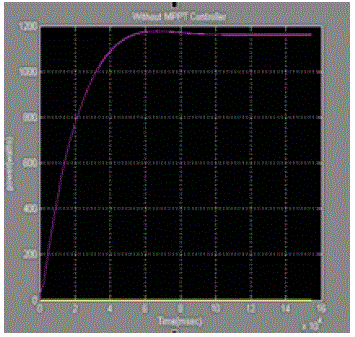
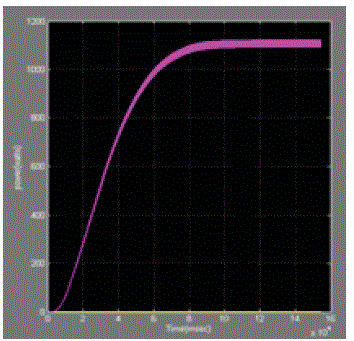
| Let us consider photovoltaic cell with Irradiance is 1000w/m2 And Temperature is 25oc and Simulated the Circuit without maximum power point tracking controller and with maximum power point tracking and the results are showin the below[12] |
VIII. CONCLUSION
|
| The paper proposes a simple MPPT algorithm is called Incremental conductance Method. This method computes the maximum power and controls directly the extracted power from the PV. The proposed method offers different advantages which are: good tracking efficiency, response is high and well control for the extracted power. |
| |
Figures at a glance
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Figure 5 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Figure 6 |
Figure 7 |
Figure 8 |
Figure 9 |
Figure 10 |
 |
 |
| Figure 11 |
Figure 12 |
|
| |
References
|
- . ROBERTO FARANDA, SONIA LEVA,“ Energy comparison of MPPT techniques for PV Systems”, Department of Energy Politecnico diMilano Piazza Leonardo da Vinci, 32 – 20133 Milano ITALY
- Dave Fre ,“Introduction to Photovoltaic Systems Maximum Power Point Tracking”
- N. Femia, G. Petrone, G. Spagnuolo and M. Vitelli, “Optimization of Perturb and Observe Maximum Power Point Tracking Method”, IEEEsTransactions On Power Electronic s, Vol.20, No. 4, pp. 16-19, Mar. 2004.
- “COMPARISON OF MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING ALGORITHMS FOR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM” International Journalof Advances in Engineering & Technology, Nov 2011
- “A Survey of Maximum PPT techniques of PV Systems” Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University, Alexandria, EGYPT
- “Comparison Study of Maximum Power Point Tracker Techniques for PV Systems” Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East PowerSystems Conference (MEPCON?10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 278.
- Johan H. R. Enslin, Senior Member, IEEE, Mario S. Wolf, Dani¨el B. Snyman, and WernherSwiegers,” Integrated Photovoltaic MaximumPower Point Tracking Converter”, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 44, NO. 6, DECEMBER 1997
- M.Lokanadham,PG Student, K.VijayaBhaskar,Asst. Professor,” Incremental Conductance Based Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)for Photovoltaic System” M.Lokanadham, K.VijayaBhaskar / International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) ISSN:2248-9622
- F. Liu, S. Duan, F. Liu, B. Liu, and Y. Kang, ?A variable step size INC MPPT method for PV systems,? IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 55,no. 7, pp. 2622–2628, Jul. 2008.
- 10.DivyaTeja Reddy Challa1, I. Raghavendar, „ Implementation of Incremental Conductance MPPT with Direct Control Method Using CukConverter’
- Azadeh Safari and SaadMekhilef, Member, IEEE ,? Simulation and Hardware Implementation of Incremental Conductance MPPT With DirectControl Method Using Cuk Converter’
- BurriAnkaiah&JalakanuruNageswararao,? MPPT Algorithm for Solar Photovotaic Cell by Incremental Conductance Method? InternationalJournal of Innovations in Engineering and Technology (IJIET)
|