e-ISSN: 2320-0812
e-ISSN: 2320-0812
L.R.D.Bhavani* and Durga aruna R
University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, A.P, India
Dept of Pharmaceutics, Vagdevi College of Pharmacy, Gurajala, Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India
Received date: 04 May 2015; Revised date: 27 May 2015; Accepted date: 02 June 2015
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis
Pharmaceutical Analysis assumes an exceptionally key part in the quality affirmation and quality control of mass medications and their plans. Pharmaceutical examination is a specific branch of scientific science, which includes isolating, recognizing and deciding the relative measures of segments in a specimen of matter. It is concerned with the substance portrayal of matter both quantitative and subjective. Pharmaceutical investigation gets its standards from different branches of sciences like physical science, microbiology, atomic science and gadgets and so forth.
Levetiracetan, Valsartan, HPLC
Almost, any physical property or normal for a specific component or compound VAL be made the premise of a strategy for its investigative determination. Eg: Spectroscopic strategy includes the retention/ emanation of brilliant vitality in all locales of the electro attractive range [1-10].
The complete investigation of a substance comprises of four principle steps [10-20].
1. Test planning/ Sampling
2. Disintegration of the example, change of the analyte into a structure suitable for estimation.
3. Estimation
4. Estimation and elucidation of the estimation.
Common techniques for analysis
The primary systems utilized for quantitative investigation are based upon,
a) Suitable concoction response taking into account either the measure of reagent expected to finish the responses or the measure of response item acquired [21-26].
E.g.: Neutralization (Acid-Base response), Complex shaping response, Precipitation response and Oxidation-decrease response.
b) Appropriate electrical estimations, which include the estimation of current, voltage or resistance in connection to the centralization of a certain animal types in arrangement [27].
E.g.: Voltametry, Potentiometry, Conductometry
Voltametry: Voltametry is a typical name for a vast gathering of instrumental methods which are in light of measuring the electric current shaped by a nonstop potential moving on the cathodes [28-30].
Potentiometry: Estimation of a potential, E, that mirrors the convergance of an analyte species in arrangement as per a Nernst-like comparison [31-38].
E = E0 + (0.059/n)log[Ox]/[Red]
c) The estimation of certain optical properties which depends either upon
- Measurement of the measure of brilliant vitality of a specific wavelength consumed by the example.
- On the emanation of brilliant vitality and estimation of the measure of vitality of a specific wavelength discharged.
Eg: Visible spectrophotometry, Ultraviolet spectrophotometry, Infrared spectrophotometry. Alongside these spectroscopic methods, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Para Magnetic Resonance (PMR) are turning out to be more famous and picking up significance in essential auxiliary examination [39-42].
A medication may be characterized as a substance implied for finding, cure, moderation, aversion, or treatment of illnesses in people or creatures or for rotating any structure or capacity of the collection of individual or creatures. Pharmaceutical science is a science that makes utilization of general laws of science to study drugs i.e., their arrangement, concoction natures, structure, structure, impact on a living being and studies the physical and compound properties of medications, the routines for quality control and the states of their stockpiling and so forth. The group of medications may be comprehensively delegated
1. Pharmacodynamic agents
2. Chemotherapeutic agents
The extent of creating and accepting a logical strategy is to guarantee a suitable system for a specific analyte more particular, precise and exact. The principle objective for that is to enhance the conditions and parameters, which ought to be followed in the improvement and approval.
A study of writing uncovers that great explanatory strategies are not accessible for the medications like Levetiracetam sodium and Levetiracetam. The current phyisico-compound routines are deficient to meet the prerequisites; henceforth it is proposed to enhance the current strategies and to grow new systems for estimation Levetiracetam sodium and Levetiracetam in pharmaceutical measurement structures receiving diverse accessible explanatory methods like HPLC [43-50].
HPLC Method Development: High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is an uncommon branch of segment chromatography in which the portable stage is constrained through the section at high velocity. Therefore the investigation time is decreased by 1-2 requests of size with respect to established section chromatography and the utilization of much littler particles of the adsorbent or backing gets to be conceivable expanding the segment productivity significantly [51,52].
Adsorption Chromatography or Normal Phase Chromatography
Reversed Phase Chromatography
HPLC Method Validation
Technique approval VAL be characterized as (ICHQ.2B) "Building up reported confirmation, which gives a high level of affirmation that a particular movement will reliably deliver a coveted result or item meeting its foreordained details and quality attributes".
Strategy approval is an indispensable piece of the system improvement; it is the procedure of exhibiting that scientific strategies are suitable for their proposed utilization and that they bolster the character, quality, immaculateness, and power of the medication substances and medication items. Essentially, technique approval is the procedure of demonstrating that a diagnostic strategy is worthy for its proposed reason.
Technique Validation, notwithstanding, is for the most part an one-time procedure performed after the strategy has been produced to exhibit that the system is experimentally solid and that it fills the planned expository need.
Validation Parameters are
(a) Recovery (b) Response function (c) Sensitivity (d) Precision
(e) Accuracy (f) Limit of detection (g) Limit of quantitation
(h) Ruggedness (i)Robustness (j) stability (k) system suitability.
Molecular Structure
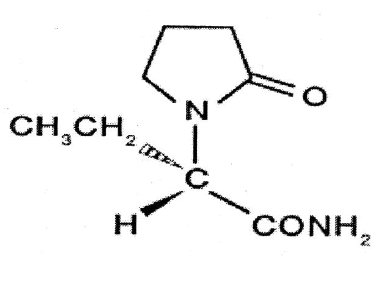
Chemical name: (-)–(S)–α–ethyl–2– oxo–1–pyrrolidine acetamide
Molecular Formula: C8H14N2O2.
Molecular Weight: 170.21
Description: fine white crystalline powder.
Category: Anticonvulsant.
Mechanism of Action
The component for anticonvulsant impact of levetiracetam is not surely knew. It is not artificially identified with different anticonvulsants and does not seem to act through the conventional systems of neuro transmitter tweak. It may act by averting hyper synchronization of epileptiform blast terminating, delivering a hindrance of the spread of seizure action [53-57].
Structure:
Chemistry of Valsartan
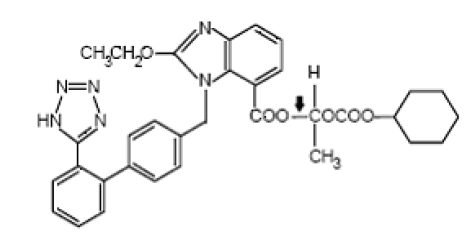
The chemical name of Valsartan is (±)-1-Hydroxyethyl 2-ethoxy-1-[p-(o-1H¬tetrazol-5-ylphenyl)benzyl]-7-benzimidazolecarboxylate, cyclohexyl carbonate (ester).
Emperical Formula : C33H34N6O6
Molecular weight : 610.67
Description : white to off-white powder
Solubility : insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in methanol.
Valsartan, a particular angiotensin II foe, is utilized alone or with other antihypertensive specialists to treat hypertension. Not at all like the angiotensin receptor enemy losartan, Valsartan does not have a dynamic metabolite or have uricosuric impacts. Valsartan rivals angiotensin II for tying at the AT1 receptor subtype. As angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor which additionally animates the blend and arrival of aldosterone, blockage of its belongings brings about reductions in systemic vascular resistance.
Mechanism of action
• It alienates angiotensin II by hindering the angiotensin sort one (AT1) receptor. Angiotensin II is the essential vasoactive hormone of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone framework with impacts that incorporate vasoconstriction, incitement of aldosterone discharge and renal reabsorption of sodium.
• It is a prodrug, is quickly changed over to the dynamic medication, amid ingestion from the gastrointestinal tract.
• It obstructs the vasoconstrictor and aldosterone emitting impacts of angiotensin II by specifically obstructing the coupling of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor in numerous tissues, for example, vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal organ. Its activity is subsequently free of the pathways for angiotensin II combination.
• Drug has more prominent partiality (> 10,000 fold) for the AT1 receptor than for the AT2 receptor.
• The solid bond in the middle of medication and the AT1 receptor is an aftereffect of tight tying to and moderate separation from the receptor.
• Drug does not restrain angiotensin changing over chemical (ACE), otherwise called kininasII, the compound that changes over angiotensin I to angiotensin II and corrupts bradykinin, nor doesit tie to or square other hormone receptors or particle channels known not critical in cardiovascular regulation.
The objective of this experiment was to develop a precise, accurate rapid economic and stable method for the analysis of Levetiracetam in the formulations.
Chemicals and reagents
Ortho phosphoric acid : AR Grade
Methanol : HPLC Grade
Acetonitrile : HPLC Grade
Water : Milli-Q-Grade
Preparation of Buffer
Add 1 mL of orthophosphoric acid to 1000 mL of water.
Preparation of Mobile Phase
Prepare a degassed mixture of buffer, Acetonitrile and Methanol in ratio of 800:150:50% V/V
Chromatographic conditions
Column : Inertsil ph-3, 100 x 4.6mm; 3μ
Flow rate : 0.8 mL/min
Wavelength : 210 nm
Injection Vol. : 10μL
Column temp. : 500C
Run time : 30 min’s
Preparation of Diluent
Use water.
Preparation of Levetiracetam Standard Stock Solution
Accurately weigh and transfer about 50mg of Levetiracetam working standard in to a 50 mL Volumetric flask. Add about 10mL of Methanol and Sonicate to dissolve dilute to Volume with diluents and mix.
Preparation of preservatives standard stock solutions
Accurately weigh and transfer about 85mg of Methyl Paraben working standard and 10mg of propyl paraben working standard into a 200mL volumetric flask, add about 20mL of Methanol and Sonicate to dissolve. Dilute to volume with diluents and mix.
Transfer 3mL of above solution into a 50mL Volumetric flask, dilute to volume with diluents and mix.
Preparation of standard solution
Transfer 5mL of Levetiracetam standard stock solution and 3mL of preservative standard stock solution into a 25mL volumetric flask and dilute to volume with diluents and mix.
Preparation of sample solution
Accurately transfer 5mL of Levetiracetam oral solution into a 200mL volumetric flask, add about 120mL of diluents and Sonicate for 10 min’s with occasional shaking. Dilute to volume with diluents and mix. Filter a portion of the solution through 0.45μ membrane filter and Sonicate discard first few mL of the filterate.
Transfer 2mL of above solution into a 25mL volumetric flask, dilute to volume with diluents and mix.
Procedure
Separately inject 10mL of diluents standard solution (five injections) and sample solution into the Chromatographic system. Record the Chromatograms and measure the peak responses.
Evaluation of System Suitability
The Column efficiency as determined for the Levetiracetam, Methyl Paraben and Propyl Paraben peaks from standard solution is not less than 2000 theoretical plates and the tailing factor for the same peaks is not more than 2.0.
The relative standard deviation for peak area of Levetiracetam from five replicate injections of standard solution is not more than 2.0.
The relative standard deviation for peak areas of Methyl Paraben and Propyl Paraben from five replicate injections of standard solution is not more than 5.0.
The retention times for Levetiracetam, Methyl Paraben and Propyl Paraben peaks are about 2.5, 7 and 20 min’s respectively.
Calculation:
Levetiracetam (% labeled amount)
Where,
AT = Area of Levetiracetam Peak in Sample solution.
A5 = Average area of Levetiracetam Peak obtained from five replicate injections of standard solution.
W5 = Weight of Levetiracetam working standard taken, in Mg.
P = Purity of Levetiracetam working standard used (on as is basis)
L = Label claim of Levetiracetam in mg/mL.
Content of Preservatives:
Methyl Paraben (% labeled amount)
Where,
AT1 = Area of Methyl Paraben Peak in sample solution
AS1 = Average area of Methyl Paraben Peak obtained from five replicate injections of standard solution.
WS1 = Weight of Methyl Paraben working standard taken in mg.
P1 = Purity of Methyl Paraben working standard used (on as is basis)
L1 = Label claim of Methyl Paraben, in mg/mL.
Propyl Paraben (% labeled amount)
Where,
AT2 = Area of Propyl Paraben peak in sample solution.
AS2 = Average area of Propyl Paraben peak obtain from five replicate insection of standard solution.
WS2 = Weight of Propyl Paraben working standard taken, in mg.
P2 = Purity of Propyl Paraben working standard used (on as is basis).
L2 = Label claim of Propyl Paraben in mg/mL.
Method Validation Summary 1. System suitability and system precision:
A Standard solution was prepared by using Levetiracetam, working standards as per test method and was injected ten times into the HPLC system.
The system suitability parameters were evaluated from standard chromatograms by calculating the % RSD from ten replicate injections for Levetiracetam , retention times and peak areas.
Acceptance Criteria:
1. The % RSD for the retention times of principal peak from 10 replicate injections of each Standard solution should be not more than 1.0 %
2. The % RSD for the peak area responses of principal peak from 10 replicate injections of each standard Solution of Levetiracetam should be not more than 2.0% and for Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben not more than 5%.
3. The number of theoretical plates (N) for the Levetiracetam, Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben, peaks is NLT 2000.
4. The Tailing factor (T) for the Levetiracetam, Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben, peaks is NMT 2.0
Observation:
The %RSD for retention times and peak areas were found to be within the limits.
2. SpecificityB) Interference from degradation products:
A study was conducted to demonstrate the effective separation of degradants from Levetiracetam. Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben Separate portions of Drug product exposed to following stress conditions to induce degradation.
a) Water degradation
b) Acid degradation
c) Base degradation
d) Peroxide degradation
e) Thermal degradation
f) UV degradation
g) Humidity degradation
Stressed samples were injected into the HPLC system with photo diode array detector by following test method conditions. All degradant peaks were resolved from Levetiracetam, Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben peaks in the chromatograms of all samples and placebo did not shown any considerable peaks under the above conditions.
The chromatograms of stressed samples were evaluated for peak purity of Levetiracetam, Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben using water’s Empower software.
For all forced degradation samples the degradants should not interference in quantitating the Levetiracetam Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben.
Acceptance criteria:
Purity angle should be less than Purity Threshold. Levetiracetam, Methy Paraben & Propyl Paraben and its degraded substances should not have any flag in purity results table.
Observation:
Purity angle was found to be less than threshold angle in all forced degradation studies with out having signs of purity flags. Thus, this method is considered to be "Stability Indicating".
3. Precision
a. System precision: Standard solution prepared as per test method and injected five times.
b. Method precision: Prepared six sample preparations individually using single as per test method and injected each solution.
Acceptance criteria:
The % relative standard deviation from the five injections should be not more than 2.0% and methyl paraben and propyl paraben not more than 2%
The assay of Levetiracetam, should be not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0%.
Test results are showing that the test method is precise. Refer tables 7.3a for system precision and 7.3b for method precision.
Accuracy (recovery)
A study of Accuracy was conducted. Drug Assay was performed in triplicate as per test method with equivalent amount of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben into each volumetric flask for each spike level to get the concentration equivalent to 50% to 150% of the labeled amount as per the test method. The average % recovery of was calculated.
Separately inject the blank, placebo, Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben in to the chromatograph.
Acceptance criteria
The mean % recovery of the Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben at each level should be not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0%.
Observation
The recovery results indicating that the test method has an acceptable level of accuracy.
5. Linearity of test method
A Series of solutions are prepared using Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben working standard at concentration levels from 50% to 150% of target concentration (50%, 60%, 80%, 100%, 120% and 150%).Measure the peak area response of solution at Level 1 and Level 6 six times and Level 2 to Level 5 two times.
Acceptance criteria
Correlation Coefficient should be not less than 0.9990.
% of y- Intercept should be ±2.0.
% of RSD for level 1 and Level 6 should be not more than 2.0%.
Observation:
The correlation coefficient was found to be 0.99958.
From the above study it was established that the linearity of test method is from 50% to 150% of the target concentration.
6. Ruggedness of Test Method
i) System to system /Analyst to Analyst/column to Column variability:
System to system /Analyst to Analyst/column to Column variability study was conducted on different HPLC systems, different columns and different analysts under similar conditions at different times. Six samples were prepared and each were analysed as per test method.
The relative standard deviation for Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben were found to be below 2 % on the columns, systems and Analysts.
Comparison of both the results obtained on two different HPLC systems, different column and different analysts shows that the assay test method is rugged for System to system /Analyst to Analyst/column to Column variability.
Acceptance criteria:
The % relative standard deviation of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben from the six sample preparations should be not more than 2.0%
The % of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben should be between
95.0%-105.0%.
Observation:
The % RSD was found within the limits.
ii) Bench top stability of standard and Test preparation:
A study to establish stability of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben standards and test preparations on bench top was conducted over period of two days. Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben test preparation spiked to target concentration are injected initial, 6.0Hr, 12Hr and 18Hr. The difference in % of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben from initial to 18 hours is within the limits. In the similar way standard preparations were injected initial, 6.0Hr, 12Hr and 18Hr.
From the above study, it was established that the standard and test preparations were stable for a period of 18 hours on bench top.
Acceptance criteria:
The difference between initial and bench top stability sample for % of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben should be not more than 3.0.
The % assay of standard kept on bench top should not differ from initial value by more than 2.0.
Observation:
The % assay was found within the limits.
7. Robustnessi) Effect of variation in mobile phase composition:
A study was conducted to determine the effect of variation in Organic phase composition in mobile phase. Standard solution prepared as per the test method was injected into the HPLC system using two mobile phases. The system suitability parameters were evaluated and found to be within the limits for mobile phase having 95% and 110% of method highest organic phase. Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben blend solution at target concentration was chromatographed using mobile phase having 95% and 110% of the method organic phase.
Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben were resolved from all other peaks and the retention times were comparable with those obtained for mobile phase having 100% of the organic phase.
From the study it was established that the allowable variation in mobile phase composition is 95% to 110% of the method highest organic phase of mobile phase.
Acceptance criteria:
The Tailing Factor of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben standards should be NMT 2.0 for Variation in Organic Phase.
Observation:
The tailing factor for Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben are found to be within the limits.
ii) Effect of variation of flow rate:
A study was conducted to determine the effect of variation in flow rate. Standard solution prepared as per the test method was injected into the HPLC system using flow rates, 0.9ml/min and 1.1ml/min. The system suitability parameters were evaluated and found to be within the limits for 0.9ml/min and 1.1ml/min flow.
Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben were resolved from all other peaks and the retention times were comparable with those obtained for mobile phase having flow rates 1.0ml/min.
From the above study it was established that the allowable variation in flow rates is 0.9ml/min and 1.1ml/min.
Acceptance criteria:
The Tailing Factor of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben standards should be NMT 2.0 for Variation in Flow.
Observation:
The tailing factor for are found to be within the limits.
iii) Effect of variation of temperature:
A study was conducted to determine the effect of variation in temperature. Standard solution prepared as per the test method was injected into the HPLC system at 30ºC temperature. The system suitability parameters were evaluated and found to be within the limits for a temperature change of 30ºc.
Similarly sample solution was chromatographed at 30ºC temperature. Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben were resolved from all other peaks and the retention times were comparable with those
Acceptance criteria:
The Tailing Factor of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben standard and sample solutions should be NMT 2.0 for Variation in temperature.
Observation:
The tailing factor for Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben are found to be within the limits.
iv) Effect of variation of pH:
A study was conducted to determine the effect of variation in pH. Standard and sample solutions were prepared as per the test method and injected into the HPLC system using pH 2.4 and 2.8. The system suitability parameters were evaluated and found to be within the limits for pH 2.4 and 2.8.
Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben were resolved from all other peaks and the retention times were comparable with those obtained for mobile phase having pH 2.5.
From the above study it was established that the allowable variation in pH 2.4 and 2.8.
Acceptance criteria:
The Tailing Factor of Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben standard should be NMT 2.0 for Variation in pH.
Observation:
The tailing factor for Levetiracetam, Methyl paraben, Propyl paraben are found to be within the limits. Refer table-7.7.
Conclusion:
From the above results it is concluded that the method is robust.
More quick, exact, particular, delicate, financial and reproducible, isocratic converse stage HPLC technique was created and approved for quantitative determination of VALSARTAN in pharmaceutical measurements frames. The system was approved for specificity, linearity, exactness, accuracy, roughness and power according to ICH rules. Strength studies were additionally led to determination of dependability for both test and standard arrangements.
The adjustment bend was developed at six fixation levels and the technique was discovered to be straight over focus range from 18-36. The relationship coefficient was discovered to be ≥0.9999. The precision of system was performed at 50, 70, 90, 100, 110 and 200% to analyte fixation and %recovery was discovered to be 100.2, 102.2, 101.4, 101.4, 101.1 and 101.2% separately.
Framework suitability parameters were performed by planned test changes like portable stage stream rate, cradle pH, organization and section temperature to the created technique. The outcomes were well in tolerating breaking points. Test and standard arrangements were stable up to 5 days at room temperature and in cooler. The outcomes were gotten in this period was dependable.
In this way the proposed explanatory technique was straightforward, quick, specific, exact, precise, and monetary. The created expository HPLC system was powerful, rough, and effective and speaks to particular technique for quantitative determination of VALSARTAN in pharmaceutical dose structures and this HPLC strategy effectively relevant for customary investigation of VALSARTAN in quality control lab.