Keywords
|
| OFDMA, BER, CRN, RAN |
I. INTRODUCTION
|
| Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is regarded as one of the prime multiple schemes for wireless networks. Spectral efficiency plays an important role in achieving high data rate in wireless communication. Efficient usage of energy is important for wire communication as well as wireless communications.Radio resource management schemes are mainly concentrating on maximizing the spectral efficiency of OFDMA systems rather than maximizing total throughput of the system. In wireless Communication, it is important to minimize the total transmit power consumption [1] in RANâÃâ¬ÃŸs.It is important to find out the tradeoff between minimum power consumption and energy efficiency. Radio resource allocation in OFDMA based systems mainly depends on total transmit power and data rate. So we are formulating the energy efficient resource allocation schemes with reduced complexity.OFDMA plays an important role in future cognitive radio networks. It also allows changing the spectral environments dynamically by allocating unused spectrum to the secondary users. Spectrum utilization can also be improved by using OFDMA to overcome the frequency selective fading. Energy efficient power allocation [2][3] algorithms are necessary to optimize bit error rate, transmission channel capacity, and transmit power in OFDMA based cognitive radio networks. |
| Our ultimate aim is to increase the channel capacity and energy efficiency of CR users by limiting the interference [6] introduced to the primary user system. From the simulation results we can conclude that the proposed optimal algorithms offer better energy efficiency and channel capacity which is very close to the uniform optimal algorithms. |
II. SYSTEM MODEL
|
| Energy efficiency and Spectral efficiency are plays an important role in wireless communication systems. The increase in demand for frequency bands with high data rate requirements, we are in a need to efficiently utilize the available spectrum with better energy efficiency. So cognitive radio (CR) networks are plays vital role in utilizing the available unused spectrum efficiently with better energy efficiency. |
| A. System Model of OFDMA based CR systems |
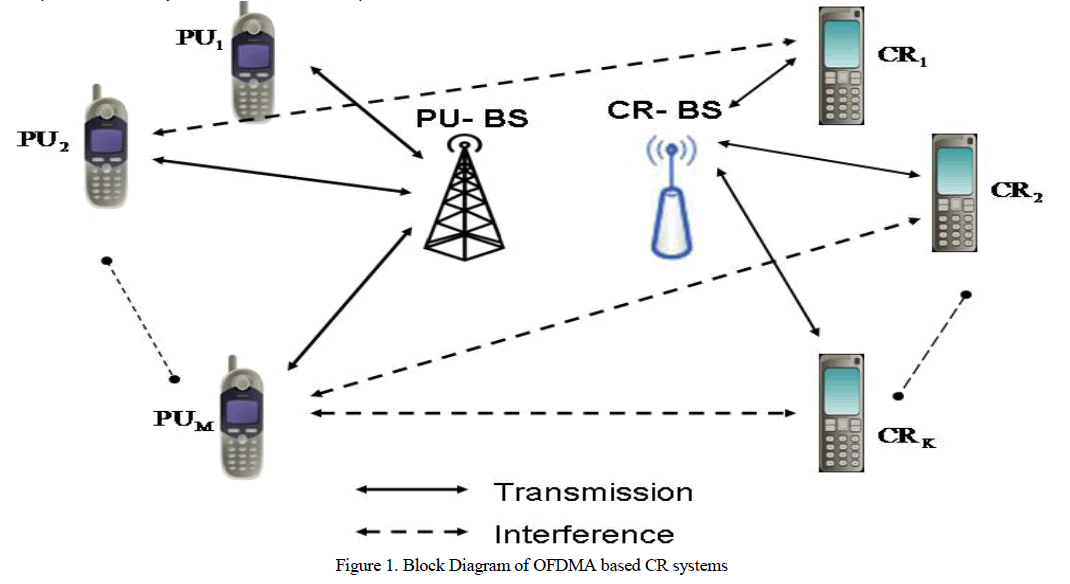 |
| In this paper, Figure 1 shows the block diagram of OFDMA based CR Systems for uplink [5] as well as downlink. It shows the signal transmission between PU and Primary User (PU)-Base Station (BS), SU and Cognitive Radio (CR)-Base Station (BS).It also sows the interference between PUâÃâ¬ÃŸs and SUâÃâ¬ÃŸs. In this each Primary radio networks (PRN) cell has one PU-BS and multiple Primary Users. Each Cognitive radio network (CRN) cell has one CR-BS and multiple SUâÃâ¬ÃŸs. The primary cell system coexists with the CR cell system in the same geographical location.CRN cell system control the interference to the PUâÃâ¬ÃŸs as well as the intercell interference and signal transmission to SUâÃâ¬ÃŸs.The secondary users (SUâÃâ¬ÃŸs) can be able to access the available CR Bands without causing harmful interference to the primary users. |
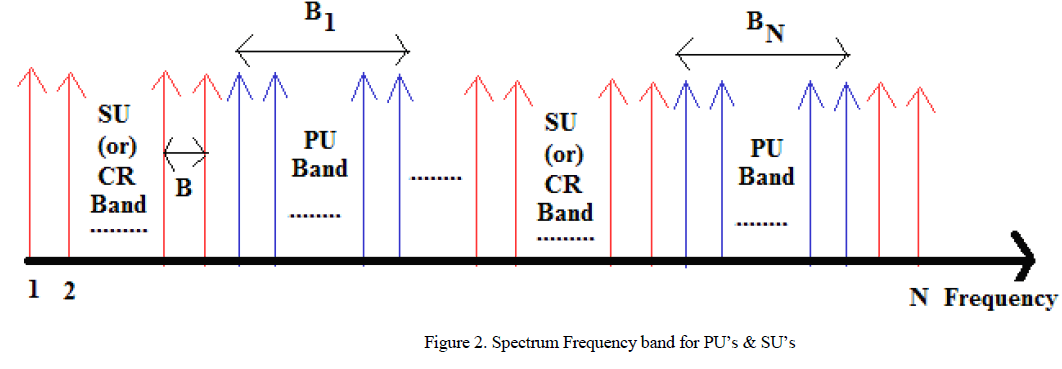 |
| Figure 2 shows the spectrum frequency band for PUâÃâ¬ÃŸs and SUâÃâ¬ÃŸs. The CR frequency spectrum band is divided into N subcarriers which are applied to OFDMA system having a bandwidth of „BâÃâ¬ÃŸ.The side by side distribution of spectrum frequency band for PU bands and the CR bands will be assumed by showing in figure 2. The frequency bands B1,B2 ,ãÃÆûãÃÆûãÃÆû ,BN has been occupied by the PUâÃâ¬ÃŸs are called as PU bands while the other bands are called as SU bands (CR bands). It is assumed that the CR system can use the inactive PU bands provided that the total interference introduced to the Mth PU band [10] does not exceed remaining all the bands. We also achieve a tolerable interference power and interference temperature limit. |
| We can use Cognitive Radio networks, to establish communication among unauthorized users without affecting the use of spectrum. Energy efficient power allocation [8] is necessary for OFDMA based Cognitive Radio networks to achieve the maximum energy efficiency and less interference. |
III. DESIGN METHODOLOGIES
|
| Effective energy efficient power allocation algorithms [7] are needed in order to maximize the channel capacity of CR networks by considering the two factors channel state Information and maximum tolerable interference limitation. The interferences introduced into the primary userâÃâ¬ÃŸs band must not exceed from a tolerable level. |
| We can write the optimization problem by mathematically |
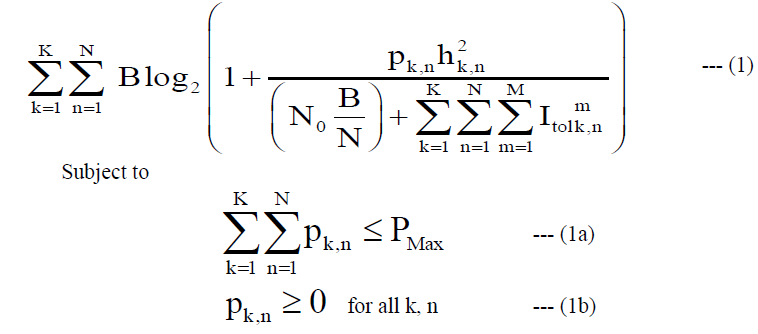 |
| Where |
| N - Total number of subcarriers |
| M - Total number of Primary Users |
| K - Total number of CR users |
| N0 - Power spectral density of additive white Gaussian noise |
| B - Bandwidth of particular frequency band |
| pk,n - Transmit Power allocated for kth CR user of nth subcarrier |
| hk,n - Channel gain for kth CR user of nth subcarrier |
| I tot k,n- Interference introduced into mth primary user of kth CR user of nth subcarrier |
| Pmax - Maximum power |
IV. PROPOSED ALGORITHMS
|
| The proposed algorithm for Power allocation is compared with existing algorithms how close they come to the optimum allocation. |
| A. Proposed Optimal Power Allocation |
| After assigning subchannels to the users by using subcarrier allocation algorithm, we can allocate the power according to channel state information from all the users to achieve maximum transmission capacity to CR users by allowing the interference introduced into the primary users below the threshold value. Transmit power may vary according to data rate for the number of users. |
| The optimal power allocated to kth CR user of nth subcarrier is given by the following equation |
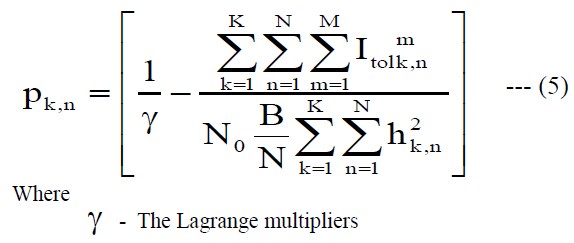 |
V. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
|
| The performance of proposed algorithm can be shown in the simulation results by using MATLAB 7.9.The simulation parameters are Total number of subcarriers N=256, Total number of Primary Users M=20, Total number of CR users K=15, Itol=1x10-6,Pmax=1x10-4, BER=1x10 - 1.5, Bandwidth B= 100 MHz . |
| A. Simulation Results |
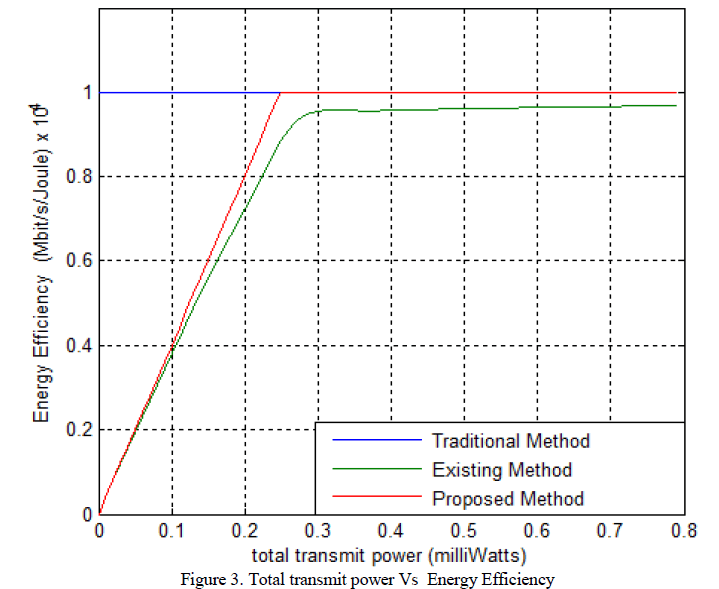 |
| Figure 2 shows the simulation result of total transmit power versus Energy efficiency. |
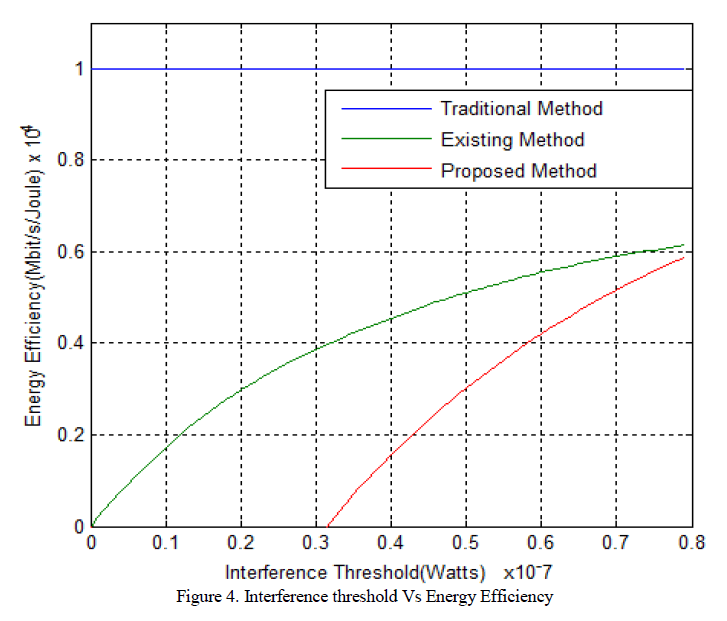 |
| Figure 3 shows the simulation result of interference threshold versus energy efficiency. |
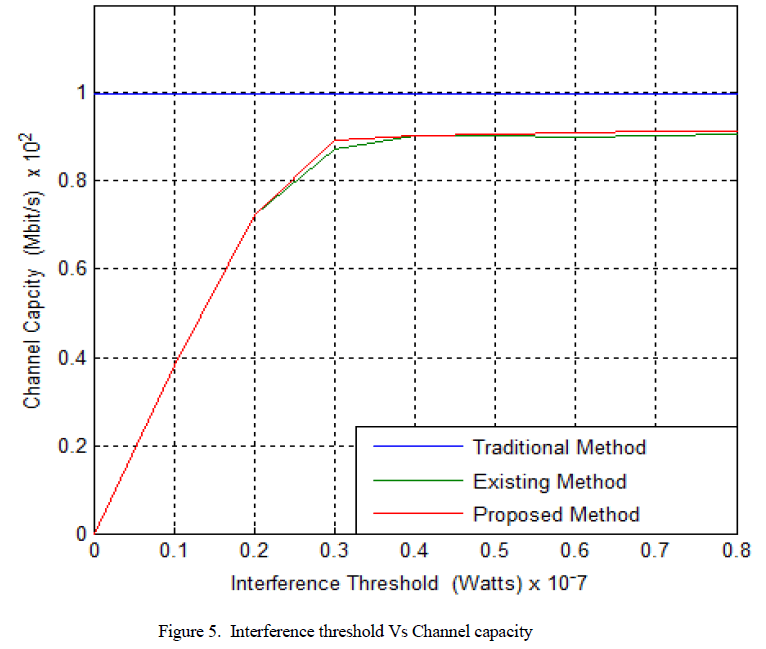 |
| Figure 4 shows the simulation result of interference threshold versus channel capacity. |
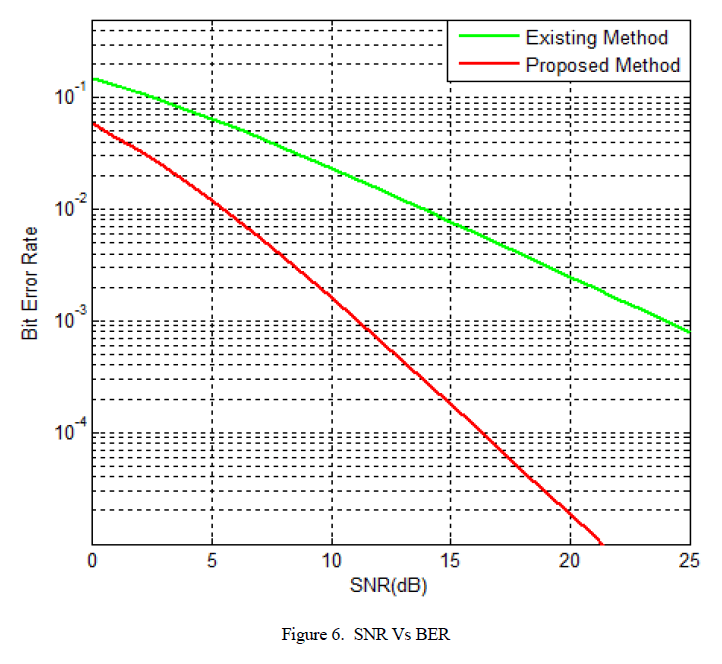 |
| Figure 4 shows the simulation result of signal to noise ratio (SNR) versus bit error rate (BER). |
VI. CONCLUSION
|
| From the simulation results we can conclude that, the proposed optimal algorithm provides better performance compared to conventional algorithms which can achieve higher energy efficiency, less bit error rate (BER) and also achieve a good tradeoff between rate channel capacity and interference threshold in cognitive radio networks with low computational complexity. In future work we can extend the same work for increasing Total number of subcarriers N, Total number of Primary Users M, Total number of CR users K and reduced tolerable interference Itol, transmit power Pmax, and bit error rate with necessary conditions to provide almost near to optimal solutions. |
References
|
- ZiaulHasan, GauravBansal, EkramHossain and Vijay K. Bhargava, “Energy-Efficient Power Allocation in OFDM-Based Cognitive RadioSystems: A Risk-Return Model”, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 8, No. 12, pp.6078-6088, 2009.
- Qilin Qi, Andrew Minturn and Yaoqing Yang, “An Efficient Water-Filling Algorithm for Power Allocation in OFDM-Based Cognitive RadioSystems”, International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI 2012), 2012.
- JiaGuo, ShenGu, Xinbing Wang, Hui Yu and Mohsen Guizani, “Subchannel and Power Allocation in OFDMA- Based Cognitive RadioNetworks”, 2009.
- Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Ernest S. Lo, Member and Robert Schober, “Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for Secure OFDMA Systems”,IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, Vol. 61, No. 6, pp.2572-2585,2012.
- Wei Wang, Wenbo Wang, Qianxi Lu and Tao Peng, “An uplink resource allocation Scheme for OFDMA-based cognitive radio networks”International Journal of Communication Systems, Volume 22 Issue 5, Pp. 603-623,2009.
- Errong Pei, Sheng Wang and ZhiZhong Zhang, “Energy-Efficient Power Allocation for OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Systems with ImperfectSpectrum Sensing”, 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, pp.1-3, 2011.
- Zhihua Tang, Guo Wei, “An efficient subcarrier and power allocation algorithm for uplink OFDMA-based cognitive radio systems”, IEEEconference on Wireless Communications & Networking Conference, pp. 1526-1531, 2009.
- Aissa, InèsFrikha, Mounir and Tabbane Sami, “Radio resource allocation for OFDMA-based Cognitive systems”, Wireless Days (WD), IFIP,pp.1-3, 2011.
|