ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
Dalvir Singh1, Dr. Charanjit Singh2, Amandeep Singh3
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
For high rate data transmission in wireless communication, OFDM system is one which attracts every researcher towards it. Because it has several advantages such as high number of orthogonal sub-carriers, no inter-symbol interference, high spectral efficiency, tolerance in multipath delay spread, power efficiency, frequency selective fading immunity etc. Among all above advantage it has one major flaw of peak-to-average-power ratio (PAPR). In fact, PAPR in OFDM system is the most detrimental aspect which degrades power and spectral spreading [1]. In this paper, we review and analyze various PAPR reduction techniques and compare their results which describes that some technique mitigate PAPR to a specific extent but at the cost of BER degradation whereas some improve BER but with little amount of PAPR reduction.
Keywords |
| Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), Peak to-average-power ratio (PAPR), Bit error rate (BER). Selective mapping (SLM), Complementary cumulative distribution function (CCDF). |
INTRODUCTION |
| Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is combination of modulation and multiplexing technique. Due to its several advantages it becomes most luring technique for 4G wireless mobile communication. OFDM is vastly used in digital audio broadcasting (DAB), digital video broadcasting-terrestrial (DVB-T), mobile multimedia access communication (MMAC), IEEE802.11a, IEEE802.16 and IEEE802.20 [2]. |
| OFDM is bandwidth efficient technique that decomposes the high rate data stream which has bandwidth (w) into n number of lower rate data streams and then transmit them over large number of individual subcarriers. These individual subcarriers have bandwidth (w/n) which is narrower than the coherence bandwidth of channel (Bc). |
| Peak value of independently modulated sub-carriers in OFDM system is very high compared to average value. The ratio of this value is called peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) [3]. Though OFDM has many advantages like high spectral efficiency, robustness to channel fading, immunity to impulse interference, capacity to handle very strong echoes and less non-linear distortion it also has disadvantage of high PAPR [4]. It becomes very necessary to mitigate high PAPR otherwise it limits the system performance and require high power amplifier with large dynamic range which is bulky and costlier. There are various techniques to overcome above mentioned major problem. These techniques can be categorized into signal scrambling and signal distortion techniques. |
| This paper is organized as follows. Section II describes, PAPR in OFDM system. Section III describes PAPR reduction techniques. Section IV describes overall analysis of different techniques. Section V describes conclusion. |
PAPR IN OFDM SIGNAL |
| OFDM System suffers from serious problem of high PAPR which arises as a consequence of the coherent addition of Multiple Sub-carrier Amplitudes & Phases from the System. A large PAPR limits the range of Linear Operation of power amplifier in transmitter this reduces the efficiency of the system. Let data block of length N be represented by vector |
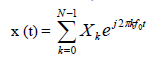 (1) (1) |
 |
PAPR REDUCTION TECHNIQUES |
| Various PAPR reduction techniques are proposed in literature. Which are categorized in following two type. |
| Signal scrambling techniques |
| Block Coding Techniques, Selected mapping (SLM) [2][5][8], Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS) [5][6], Tone Reservation (TR) etc are Signal Scrambling Techniques. |
PARTIAL TRANSMIT SEQUENCE |
| Partial Transmit Sequence (PTS) is one of the most efficient techniques to diminish PAPR. In this scheme original OFDM signal is divided into number of sub-blocks. Then phase rotation is added to develop number of candidate signal and choose one with lowest PAPR [6]. |
 |
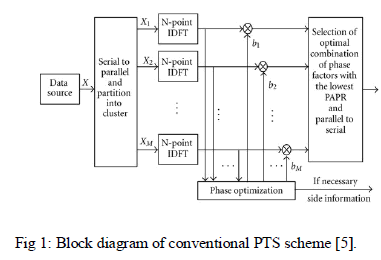 |
| Get M candidates’ time domains using IDFT |
| All the candidates have same information x provide different PAPRs. One with smallest PAPR in XïÃÂø is selected for transmission [6]. |
BLOCK CODING TECHNIQUE |
| Block coding is the simple technique to diminish PAPR. Basic idea behind it is to select code words with low peak power after coding from all probable symbols. With N sub-carrier QPSK modulation provides 2N bits and thus 22N messages [7]. |
| If k bit data block is encoded by (n.k) block code with generation matrix G at transmitter and a phase rotator vector b is used to produce encoded output. By separating large information sequence into different sub-blocks and encode these subblocks with system on programmable chips (SOPC) large PAPR reduction can be achieved [7]. |
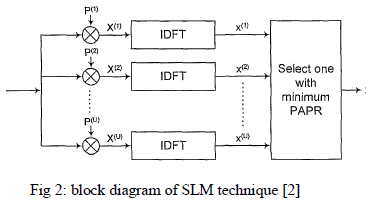
SELECTIVE MAPPING |
| Selective Mapping is promising technique to mitigate PAPR in OFDM system. Fundamental idea behind scheme is phase rotation. Signal with low PAPR is selected from different independent phase sequences that have same information at transmitter [2]. |
 |
 |
| To get simulation result we set N to 64, 16QAM modulation used , for different phases U (4, 16, 32) and compare with unmodified signal U=1, we also compare results with and without oversampling factor. If number of sub-carrier is N and 32-point IFFT used then the ratio of α = NIFFT/N is called oversampling factor [9]. |
TONE RESERVATION |
| This is an accurate method for PAPR mitigation. Amount of PAPR mitigation relies on some factor such as number of reserved tones, location of reserved tones, and amount of complexity and allow power on reserved tones. |
| Method shows that reserving a small fraction of tones leads to large mitigation of PAPR with simple operation at transmitter and no complexity at receiver end. There is no need for additional operation and no side information to receiver. It based on summing a data block and time domain signal. A data block is dependent block signal to the original multicarrier signal to minimize high peak. This time domain signal can be calculated simply at the transmitter of system and stripped off at receiver [7]. This scheme takes an edge as no need of side information to send along with message, less complexity. BER is improved to a little extent with tone reservation. One of the advantages with this technique is reduction in complexity. |
SIGNAL DISTORTION TECHNIQUES |
| Clipping and Filtering [2][9][10], Peak Windowing [11], Envelope Scaling etc. are signal distortion techniques. |
CLIPPING AND FILTERING |
| The simplest technique of PAPR reduction is clipping whose fundamental process to clip the part of signal which is out of allowed region with high peak [9]. Clipping is expressed as |
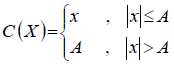 (9) (9) |
| A = Positive real number represent clip level |
| This is the simple algorithm to mitigate PAPR by removing the signal component that exceeds some unchanging amplitude called clip level. It is a non-linear process which causes in-band noise, which demotes performance of BER and out of band noise which further reduces the spectral efficiency. Filtering after clipping can demote out of band radiation but cause peak re-growth which may exceed clip level. To avoid peak re-growth iterative clipping and frequency domain filtering can be used. |
PEAK WINDOWING |
| With this technique it is possible to remove larger peaks at the rate of a little amount of interference when large peaks arise infrequently. It mitigates PAPR at cost of increases BER (bit-error-rate) and out-of-bands radiation. It provides better PAPR mitigation with better spectral properties. [11] |
| In this method multiply large signal peak with a specific window such as Gaussian shaped window, Kaiser, cosine, and hamming window which results a spectrum of convolution of original OFDM spectrum with spectrum of window. |
| The window size should be narrow otherwise it affects number of signal sample which cause increasing BER. PAPR level will decrease to 4db with this technique from number of independent subcarrier [7]. SNR limited to 0.3db due to signal distortion. Back off Pmax of about 5.5 dB require to keep in band spectral density to at-least 30db below. |
ENVELOPE SCALING |
| Objective of this algorithm is to mitigate PAPR by scaling. Input envelope for few subcarrier before IFFT operation. Here 256 subcarriers with QPSK modulation technique are used to make sure envelope for all subcarrier are equal. According to algorithm input envelope in some sub-carrier is scaled to attain the smallest amount of PAPR at IFFT output. Thus, at receiver there is no need of side information for decoding purpose. PAPR reduces to 4db with same algorithm. If QAM is used number of sub-carrier will large then need to send excessive side information otherwise BER demote in large amount. |
OVERALL ANALYSIS OF VARIOUS TECHNIQUES |
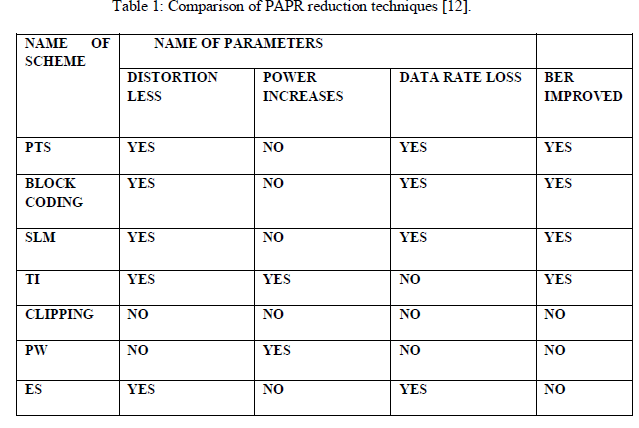 |
CONCLUSION |
| In this paper, we have analyzed various PAPR reduction techniques and also compared these techniques for different parameters. We observe that SLM is most effective technique to mitigate PAPR to great extent and also improve BER performance of the system. |
References |
|