ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
ISSN ONLINE(2278-8875) PRINT (2320-3765)
S. Tara Kalyani1, Syfullah khan Md2
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
This paper presents the simulation of sensorless operation of permanent magnet brushless direct current (BLDC) motor. The position sensorless BLDC drive simulated, in this paper, is based on detection of zero crossing from the terminal voltages differences. This method relies on a difference of line voltages measured at the terminals of the motor. It is shown, in the paper, that this difference of line voltages provides an amplified version of an appropriate back EMF at its zero crossings. The commutation signals are obtained without the motor neutral voltage. The effectiveness of this method is demonstrated through simulation.
Keywords |
| BLDC motor, simulation, sensorless operation, zero crossing |
INTRODUCTION |
| In the literature there are several simulation models available for BLDC motor drives. These models employ statespace equations, Fourier series or d-q axis model. Even though these models have made a great contribution in the BLDC motor drives, there is no comprehensive model for the analysis of motor used in sensorless operation [1]. The machine models are often transformed to a rotating reference frame to simplify and to improve the computational efficiency. But, this approach will not improve the computational efficiency because the d-q transformations are suitable only for machines with sinusoidal voltage as discussed in [2]. The BLDC motors are normally powered by conventional three phase voltage source inverters (VSI) or current source inverters (CSI) which are controlled based on the rotor position information obtained from hall sensors, resolvers or absolute position sensors. But these position sensors have numerous drawbacks like increase in cost, complexity in control, temperature sensitivity requiring special arrangements. These sensors reduce the system reliability and acceptability. Therefore, sensorless techniques have become a subject of great interest in recent times. A number of sensorless techniques have been developed for BLDC motor. Some of the techniques presented [3] in the literature are based on position sensing using back emf zero detection crossing, terminal voltage sensing, sensing third harmonics of the motional emf, integration of the back emf, position sensing using inductance variation, position sensing based on flux linkage variation, Extended Kalman filter estimation or detecting the freewheeling diode conduction in open phase proposed in [4, 5]. |
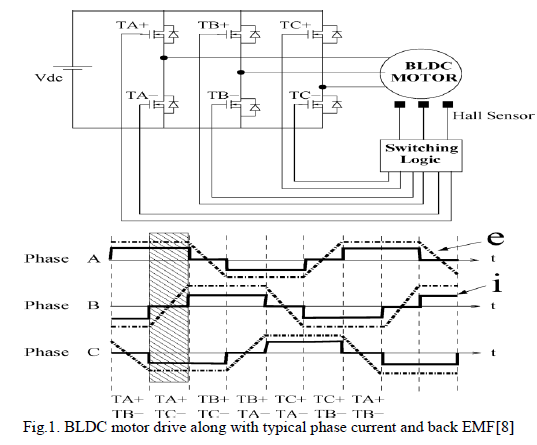
| In BLDC motors, only two out of three phases are excited at any time leaving the third winding floating. The back emf in the floating winding can be measured to determine the switching sequence for commutation of power switching devices in the 3 phase inverter. The terminal voltage of the floating winding with respect to the neutral point of motor is needed to get the zero crossing time of the back emf. The sensorless control technique based on Zero Cross Point (ZCP) of the back emf has been widely used for low cost application proposed by J. Shao [6]. In the ZCP method the back emf cannot be obtained when the BLDC motor is at standstill or operating nearly zero speed as discussed by Yen- Shin Lai and Yongkai Lin [7]. Therefore, a special control is needed for smooth and reliable sensorless control operation of BLDC motor [8]. |
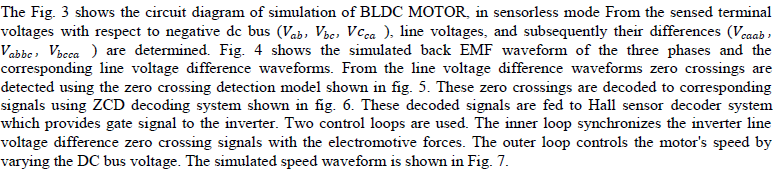
| In this paper a Matlab/Simulink sensorless operation is developed. This paper simulates a simple and reliable method for the detection of back EMF zero-crossings for sensorless operation using MATLAB/SIMULINK as discussed and simulated using SABER software in [8] . In this paper, the zero crossings of the back EMF are estimated indirectly from the terminal voltages measured with respect to dc negative terminal. The method does not involve any integrations. Further, since line voltages are used, the requirement of neutral potential has been eliminated. This also eliminates the common mode noise. Device drops and their variations would also not play a part since line voltages are used. Using this model of BLDC motor suitable for the dynamic behavior of the motor is studied. Also simulation has been carried out to study the effectiveness of the sensorless control based on detection of zero crossing from the terminal voltages differences. The organization of this paper is as follows. Section II describes the proposed back EMF zero-crossing estimation method. Section III presents the simulation results of the proposed method. Section IV presents the conclusion. |
PROPOSED BACK EMF ZERO-CROSSING ESTIMATION METHOD |
| Consider a BLDC motor having three stator phase windings connected in star[8]. Permanent magnets are mounted on the rotor. The BLDC motor is driven by a three phase inverter in which the devices are triggered with respect to the rotor position as shown in Fig. 1. The phase A terminal voltage with respect to the star point of the stator ïÿýïÿýïÿýïÿýïÿýïÿý , is given as |
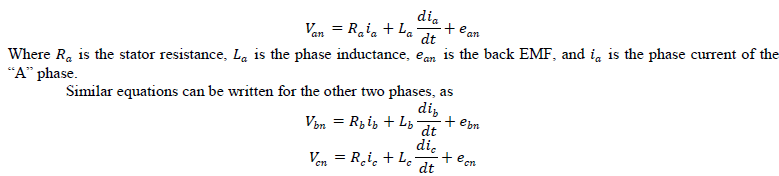 |
| Where symbols have their obvious meanings. |
 |
| From above equations, the line voltage vab may be determined as |
 |
 |
SIMULATION AND RESULTS |
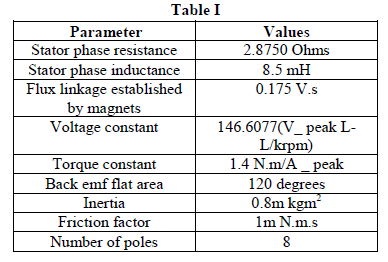
| This section presents the aspects of continuous sensorless operation. This sensorless method is simulated in MATLAB/SIMULINK. The motor parameters are given in Table I. |
 |
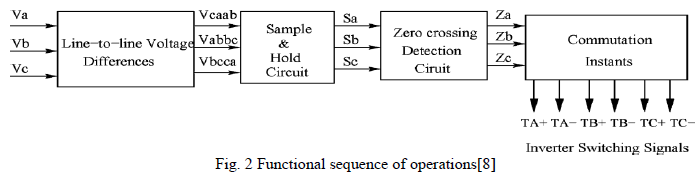
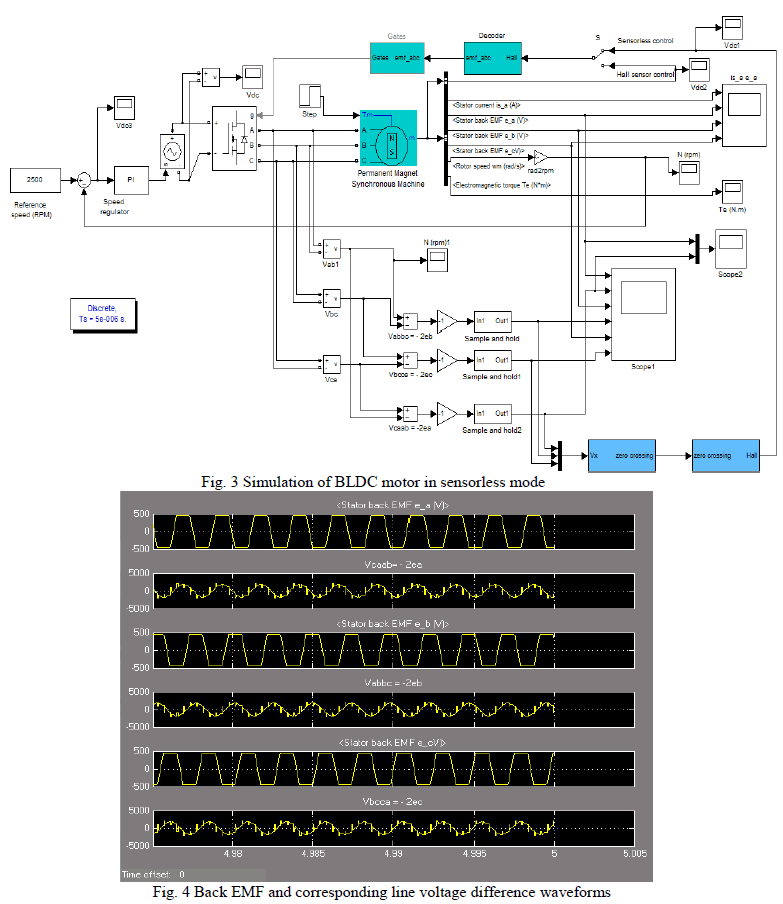
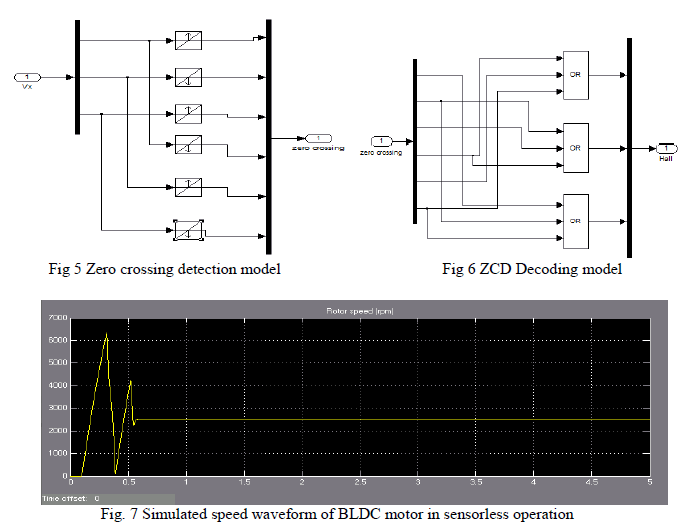
| The functional sequence of operations of the simulated back EMF zero-crossing detection for sensorless operation is shown in Fig. 2, and is further explained in the following. |
 |
 |
 |
CONCLUSION |
| A simple technique to detect back EMF zero crossings for a BLDC motor using the line voltages is simulated using MATLAB/SIMULINK. It is shown that the method provides an amplified version of the back EMF. Only three motor terminal voltages need to be measured thus eliminating the need for motor neutral voltage. Running the machine in sensorless mode is then simulated, in this paper. Hardware model can be developed based on the proposed simulation method of sensorless control of BLDC motor. Thus this primitive model can be extended as an industrial module, by incorporating the safety features, such as over current, over-voltage protection. This can be achieved by monitoring the inverter input voltage and also the inverter input current. . It is also required to monitor the temperature of the semiconductor power-devices, as these devices are very sensitive to temperature. |
References |
|