ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
Harish E.R.M1, Mahesha.K2, Sartaj Patel3
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
In Current study the stress analysis of wing-fuselage attachment bracket is considered. It is necessary to ensure the static load carrying capability of the wing-fuselage attachment bracket. Stress analysis will be carried out for the given geometry of the wing-fuselage attachment bracket of a six seater transport airframe structure. Finite element method is used for the stress analysis. Rarely an aircraft will fail due to a static overload during its service life. For the continued airworthiness of an aircraft during its entire economic service life, fatigue and damage tolerance design, analysis, testing and service experience correlation play a pivotal role. Stress analysis helps in prediction of fatigue life of structural component of airframe structure.
INTRODUCTION |
| Lugs are connector type elements widely used as structural supports for pin connections in airframe structure. For ex. For attaching engines to engines pylon support fittings, wing fuselage attachment, and landing gear links are some of the typical applications can be found. Failure of lug joints may lead to the catastrophic failure of the whole structure. Finite element analysis studies and experimental data help the designer to safeguard the structure from catastrophic failure.Attachment lugs can be some of the most fracture critical components in aircraft structure, and the consequences of structural lug failure can be very severe that sometimes the wing and fuselage get separated and result in accidents. Therefore, it is important to establish design criteria and analysis methods to ensure the damage tolerance of aircraft lug attachment. |
II. GEOMETRICAL CONFIGURATION |
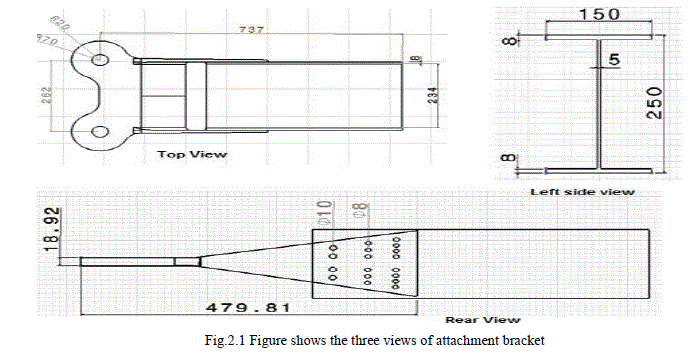 |
| The wing fuselage attachment bracket considered for the study is shown in figure 2.1. The attachment bracket consists of a lug and a portion of the spar connected to each other by several bolts. The lug consists of two pin holes along with an integrated top flange and bottom flange which will be connected to the spar. The geometric dimensions of the lug attachment bracket are shown in the figure. Three views of wing fuselage lug attachment bracket are shown in the Figure 2.1. A three dimensional view of the lug attachment bracket is shown in the figure2.2. |
 |
III. MATERIAL SPECIFICATION |
| In this current study, The material considered for the lug attachment bracket of the structure is steel alloy AISI-4340, the following properties. 1. Young’s Modulus, E = 201105N/mm2 2. Poison's Ratio, μ = 0.3 3. Ultimate Strength, ÃÂñu = 1530N/mm2 |
IV. LOADS ON THE WING FUSELAGE ATTACHMENT BRACKET |
| In an aircraft the spars carry’s the most of the bending. The maximum bending moment will be at the root of the spar where wing and fuselage components will be attached to each other. A:Load calculation for the wing fuselage lug attachment bracket. 1) Aircraft category= six seater transport aircraft 2) Total weight of the aircraft=2500kg = 24525 N 3) Load factor considered in design=3g 4) Design limit load on the structure=3*24525=73575 N 5) Design ultimate load=73575*1.5=110362.5 N 6)The % of lift load acting on the wing is 80% =110362.5 * 0.8 = 88290 N 7) Load acting on the each wing= 88290/2=44145 N 8) Span wise distance of the resultant load from the root of the wing = 1400 mm 9) Total bending moment at the root = 44145*1400 = 61803000 N-mm. |
| 11) Load at each attachment: |
| Front attachment = 55% Rear attachment = 45% |
| 12) Load at front attachment =83857 * 0.55 = 4621.64 N. |
V. FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS |
| The finite element method (FEM) is a numerical technique for solving problems which are described by partial differential equations or can be formulated as functional minimization. A domain of interest is represented as an assembly of finite elements. Approximating functions in finite elements are determined in terms of nodal values of a physical field which is sought. A continuous physical problem is transformed into a discretized finite element problem with unknown nodal values. For a linear problem, a system of linear algebraic equations should be solved. Values inside finite elements can be recovered using nodal values. The software used for the analysis of the wing fuselage attachment bracket of a six seater airframe structureis MSC.Patran & MSC. Nastran. |
VI.FINITE ELEMENT MODEL OF THE WING FUSELAGE LUG ATTACHMENT BRACKET |
| A finite element model is the complete idealization of the entire structural problem including the node location, the element, physical and material properties, loads and boundary conditions. The purpose the finite element model is to make a model that behaves mathematically as being modelled and creates appropriate input files for the different finite element solvers.In Finite Elements libraries, selected 4 Nodded QUADRILATERAL Shell Element (QUAD4). In this Geometrical model for available surface area, chosen for formulation of FE Model, reason was flow of displacement and stiffness. |
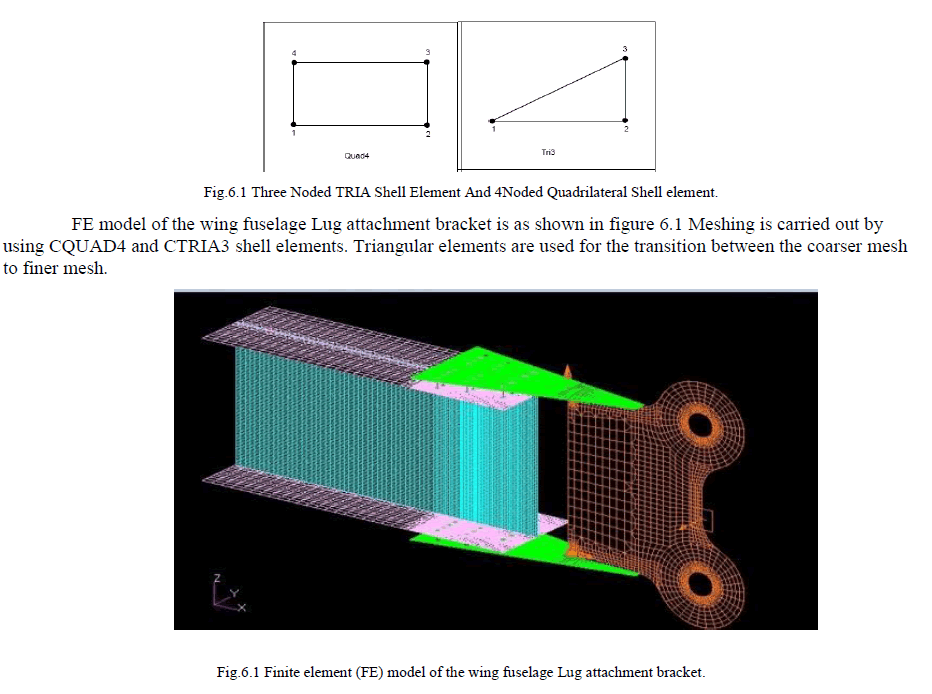 |
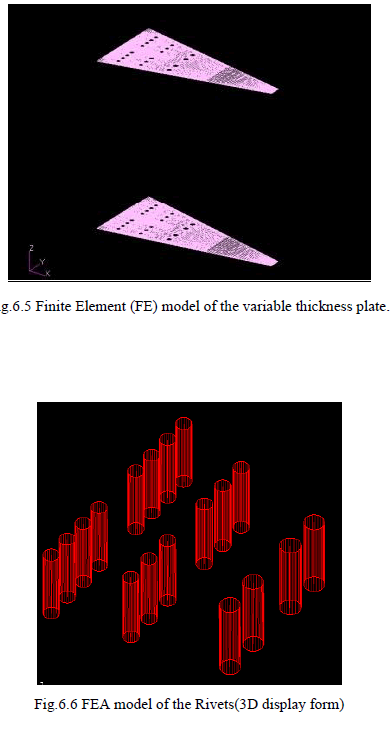
| A:Different structural members of the wing fuselage Lug attachment bracket are ïÃâ÷ Lug ïÃâ÷ I-spar ïÃâ÷ Top and bottom flanges of the lug attachment bracket ïÃâ÷ Rivets The corresponding mesh generated for each of the above mentioned members are shown in the figure below. |
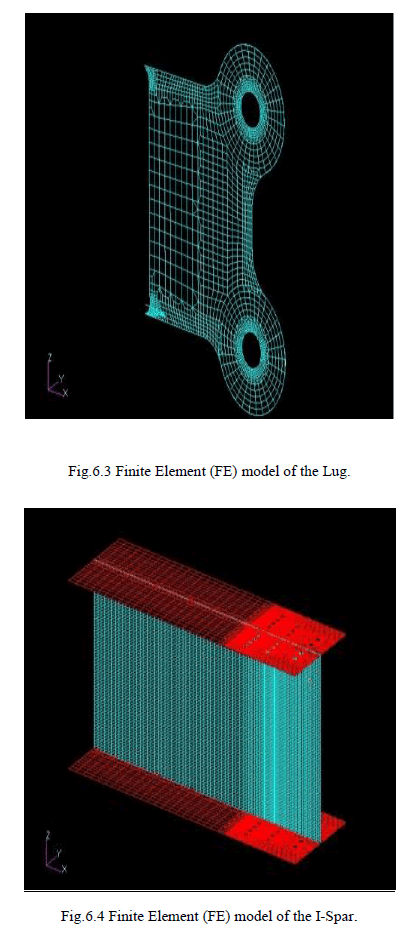 |
 |
VII.LOADS AND BOUNDARY CONDITIONS |
| The loads and boundary conditions along with the finite element model are shown in the figure 7.1. A load 46121.64 N (i.e., 86.32 N/mm) of is introduced at one end of the spar beam. This load will essentially create the required bending moment at the root. The top and bottom lug holes of the wing fuselage Lug attachment bracket are constrained with all six degrees of freedom at the semicircular circumferential region. |
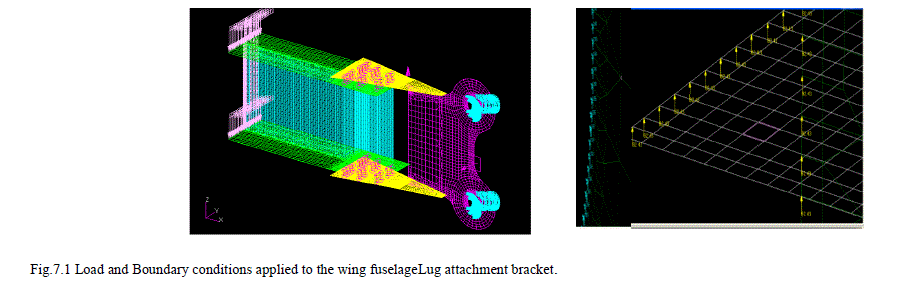 |
VIII.FINITE ELEMENT MODELLING AND STRESS ANALYSIS IN WING FUSELAGE ATTACHMENT BRACKET. |
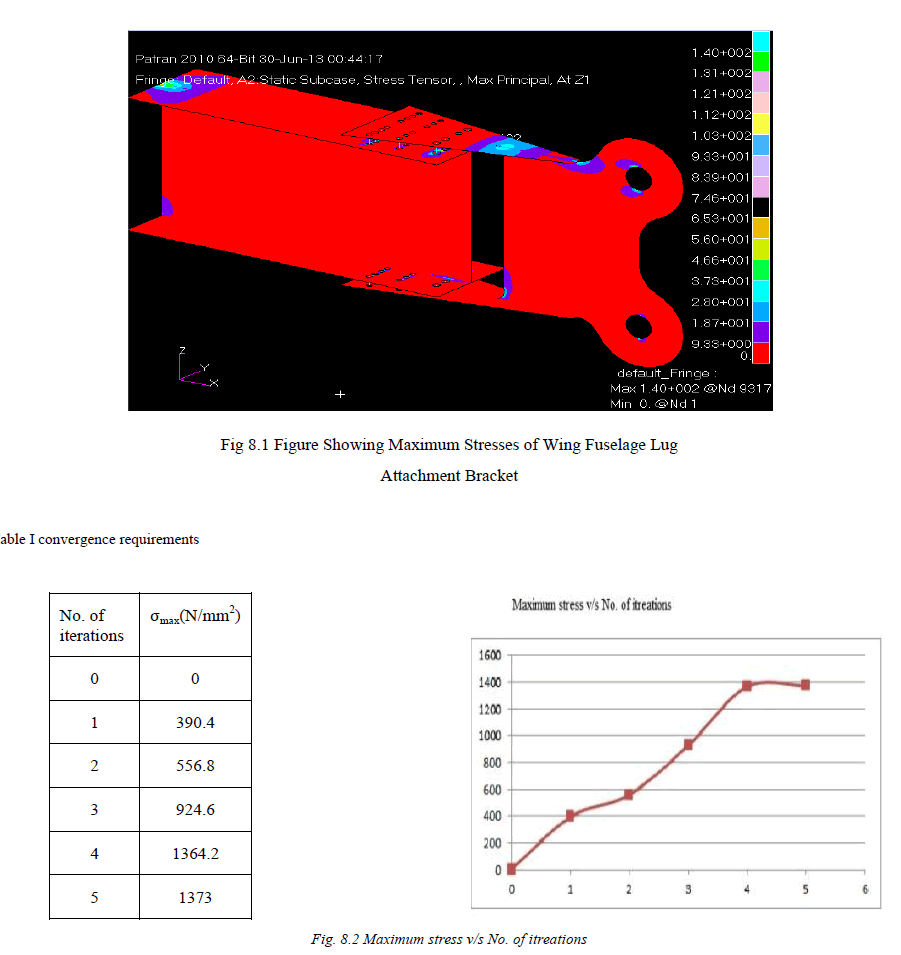
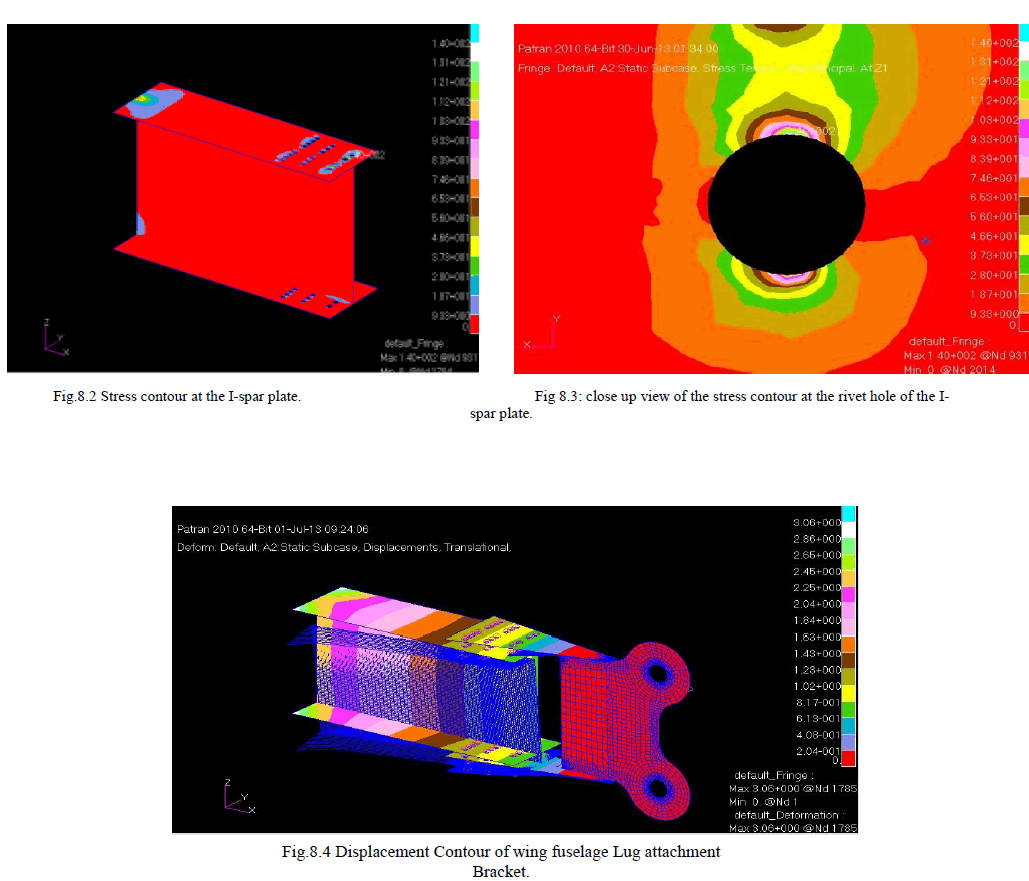
| The stress values at the I-spar rivet hole and the displacement contours are shown in the figures 8.1 and 8.4. A maximum stress of 1373 N/mm2 (140 kg/mm2) is observed at the rivet hole of I-spar section. |
| A maximum displacement of 3.06 mm at the free end of the cantilever structure can be observed from the displacement contour in the figure 8.4. |
 |
 |
VIII. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS |
| The stress contour indicates a maximum stress of 1373 N/mm2 at one of the rivet hole of the I-spar. The maximum stress value obtained is within the yield strength of the material. The point of maximum stress is the possible location of crack initiation in the structure due to fatigue loading. |
IX. CONCLUSIONS |
| Stress analysis of the wing fuselage lug attachment bracket is carried out and maximum tensile stress is identified at one of the rivet hole of I-spar plate.FEM approach is followed for the stress analysis of the wing fuselage lug attachment bracket.)A validation for FEM approach is carried out by considering a plate with a circular hole.Maximum tensile stress of 1373N/mm2 (i.e., 140 kg/mm2) is observed in the I-spar plate.Several iterations are carried out to obtain a mesh independent value for the maximum stress.A fatigue crack normally initiates from the location maximum tensile stress in the structure, further fatigue life estimation can be carried out to predict the life of the airframe component. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT |
| The analytical work was conducted Bangalore Aircraft Industries Private Limited, the author gratefully acknowledge their support The author also would like to thank K E Girish(DIRECTOR, BAIL) for providing expert guidance and advice for the analytical work.addition the author would like to thank theto Dr. Mahesha.K. Professor and Head of the Department, Mechanical Engineering, Acharya Institute of Technology, Bangalore. |
References |
|