ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
ISSN ONLINE(2319-8753)PRINT(2347-6710)
| Dr.V.Krishnasamy1 , G.Mathubala2 1 Professor of Chemistry , Bharath university ,Chennai – 73, India 2Assistant Professor of Chemistry , Bharath university ,Chennai – 73, India |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology
Simple and substituted anils were prepared and their kinetics were studied under various conditions viz., solvent ,oxidants , electrolyte , catalysts and mixture of catalysts and temperature; simple and substituted anils , pyridinium Chloro Chromate(PCC) ,Pyridinium Dichromate ( PDC) were prepared in the laboratory and kinetic study were carried out using Pyridinium dichromate , substrate , perchloric acid and osmium tetraoxide . The graphs were drawn at all relevant places and results were obtained in full satisfaction.
Keywords |
| Osmium tetraoxide chloramine [CAT], sulphonamide , oxidants , water – bath , evaporating , stirring |
INTRODUCTION |
| In 1986 , Narayanan and Balasuramaniam5 introduced Pyridinium bromochromate . This is an efficient oxidant for alcohols and a brominating agent as well .Firouzahadi and Coworkers used Zinc chromates. This is a very useful reagent for the oxidation of variety of organic compounds , including alcohols , oximes , olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons.They have also shown chromium peroxide complexes as versatile , mild and efficient oxidants in organic synthesis.Chlorotrimethyl Silone , Imidazolium dichromate , 2,2’ – Bipyridyl chlorochromate (BPCC) and the corresponding chromate (BPC) have been proposed as oxidants for the oxidation of the hydroxyl group to thr carbonyl group.4 – ( dimethyl amino ) – pyridinium chlorochromate and chromyl nitrate have been shown to be efficient and mild oxidant in aprotic media. Naphthyridium chlorochromate , Pyrazinium chlorochromate , tetrabutyl ammonium chlorochromate , dimethylpyrazole chromate , tetrabutyl ammonium dichromate , Pyridine complex of oxodiperoxochromium and the dipyridine complex of chromium trioxide are some of the Chromium (VI) oxidants introduced in the last twenty years.Quinolinium Chlorochromate was used by Bhavani et al to oxidize methyl phenyl sulphoxides.Quinolinium dichromate was introduced by Balasubramanian and Prathiba 6 as an effective oxidant under non – aqueous conditions.Pyridium Chlorochromate (PCC) is irreplaceable in the generation of functional groups in highly unsaturated carbinols and pyrols . yet mildly acidic character of Pyridinium chlorochromate precludes its use with acid sensitive substrates or products. Pyridium Chlorochromate oxidation has been investigated under various condition on different substrates .Despite the introduction of numerous oxidants based on chromium (VI) not much work has been done to investigate the mechanism of oxidation in these cases. |
| 1.1Reactions of Pyridinium Dichromate |
| Pyridium dichromate (PDC) in N,N – dimethyl formamide or dichloromethane is nearly neutral non – aqueous chromium (VI) oxidant. This species probably present in the Sarret and Conferth oxidizing mixtures. Although specific reference has been made to oxidation of alcohols by Pyridium dichromate itself in a short note , there is no indication of any unusual effectiveness , utility , or advantage to be gained by the preformed pyridium dichromate as a discrete oxidizing species before Corey and Schmidt1prepared it in 1979.Solutions of Pyridium dichromate in DMF rapidly oxidize allylic alcohols44 to alpha , beta – unsaturated carbonyl compounds at O 0 C. Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of cyclic ketoximes by Pyridium dichromate and Quinolinium dichromate was investigated by Chidambaranathan et al2. Oxidation kinetics of Cyclanols by Pridiniumdichromate was studied by Padma et al 3.Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of some ortho- substituted benzyl alcohl by PDC was studied by Kabilan and Thenmozhi.4Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of some substituted phenylmethyl sulphoxide using PDC was reported by Meenakshisundaram et al. 5 Oxidation of S – phenylmercaptoacetic acid and phenoxyacetic acid by PDC was studied by Kabilan and Krishnasamy.6Gurumurthy et al 7 investigated a comparative study on the kinetics of oxidation of some secondary alcohols by 1 – chlorobenzotriazole and PDC . |
| 1.2.Reactions of Anils |
| Several oxidation of anils have been studied : |
| 1.2.1.Effect of varying PCC concentration |
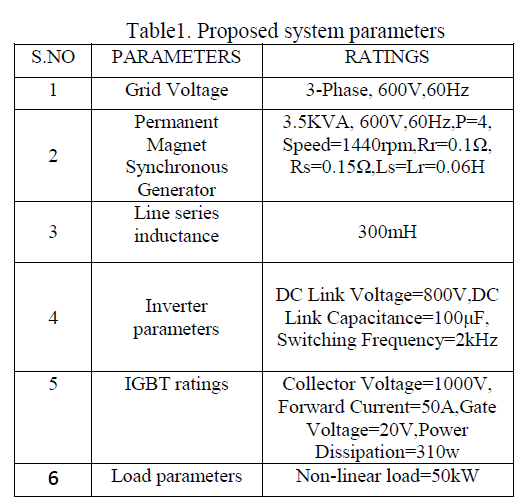
| The reaction was investigated by varying the concentration at constant substrate concentration .Th reaction was found to be first order with respect to PCC [ Table – 1.2 ] |
 |
| 1.2.2.Effect of varying the concentration of Anil |
| The reaction was carried out under pseudo – first order conditions . In this study , the concentration of PCC , Oxalic acid , Perchloric acid and percentage of oxalic acid were kept constant and the concentration of the alone varied . The reaction was found to be first order with respect to anil . [ Table – 1.3 ] |
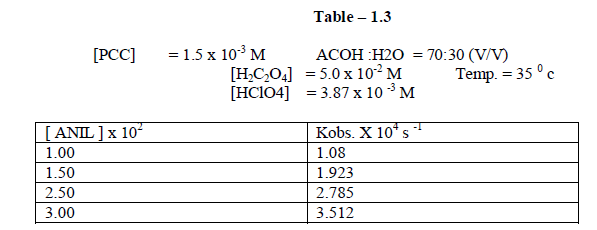 |
| 1.2.3.Effect of varying solvent Composition |
| The reaction was studied by the different composition of acetic acid under constant [Reactants ]. It was found that as the percentage of acetic acid increased , the rate decreased. [ Table – 1.4 ] |
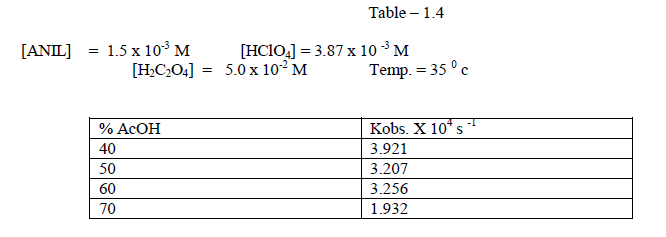 |
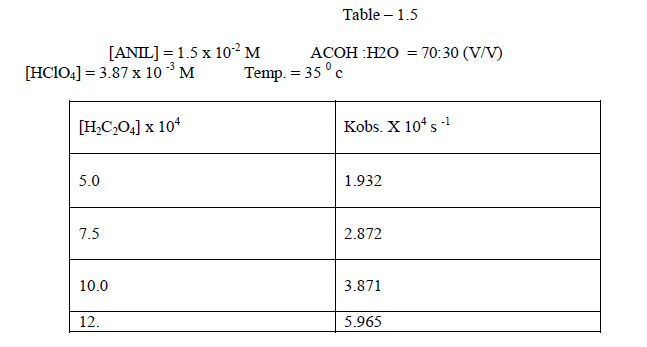
| It was found that the rate deccreases with increase of percentage of acetic acid 1.2.4Effect of varying Oxalic acid The reaction was carried out under by varying , the concentration of , Oxalic acid and by keeping other [reactans] constant.Theresult indicate that as the concentration of oxalic acid increased , the rate constant also increased[ Table – 1.5 ]. |
 |
| 1.2.5.Effect of varying Perchloric acid |
| The reaction was studied by varying , the concentration of perchloric acid and by keeping other [reactans] constant. . The result indicate that as the concentration of Perchloric acid increased , the rate constant also increased. [ Table – 1.6 ] |
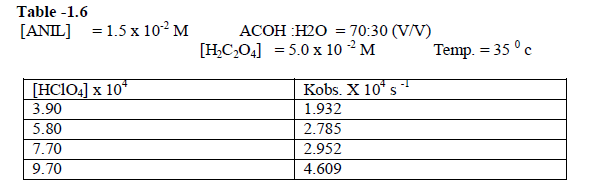 |
| 1.2.6.Effect of varying Sodium Perchlorate |
| To follow the Primary Salt effect , the reaction was studied with varying concentration of Sodium Perchlorate by keeping other [reactants] constant. It was found that as the concentration of Sodium Perchlorate increased , the rate constant also increased. This shows that the participation of ions which are similar in their sign or dipole –ion interaction in the rate determining step. [ Table 1.7 ] |
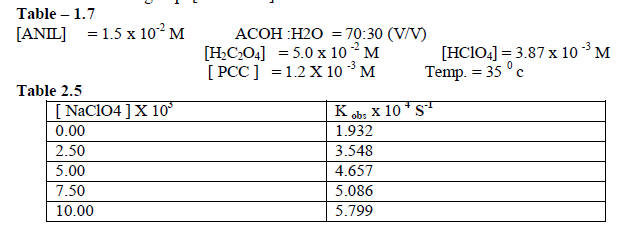 |
| 1.2.7.Effect of MnSO4 |
| The reaction rate decreases tremendously with the increase in the concentration of MnSO4 [ Table - 1.8 ] This may be due to the formation of Cr(VI) in the rate determining step. |
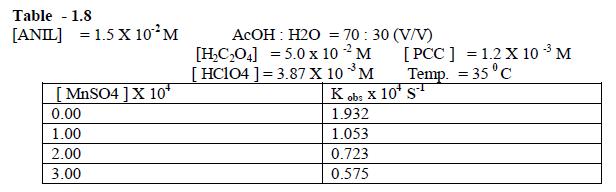 |
| 1.2.8 Effect of temperature The rate of oxidation of some meta and para substituted anils had been studied at four different temperatures viz., 350 c , 400 c, 450 c and 50 0 c . It was observed , as we expected ,that the rate increases very much with increase of temperature .[ Table – 1.9 ] |
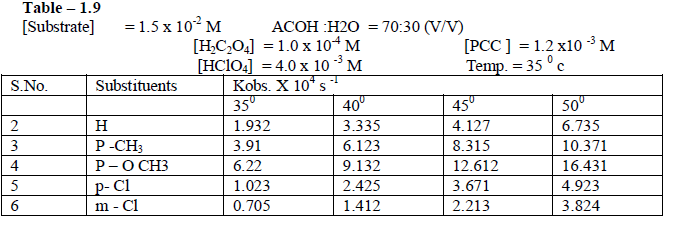 |
II.EXPERIMENTAL |
| 2.1. General method of preparation of Anils |
 |
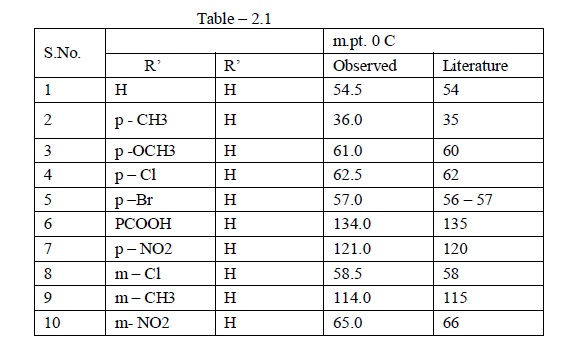
| The anils were prepared 87a by refluxing equimolar quantities of benzaldehyde and aniline or substituted anilines in alcohol for about 2 to 3 hrs. The resulting solution was cooled and poured into the cold water . The precipitated anil was filtered , washed , dried and recrystallised from alcohol. The purity of anils were checked by determining their melting points ( Table 2.1). |
 |
| 2.2.PREPARATION OF PYRIDINIUM DICHROMATE [ PDC] |
| Pyridine ( 80.6 ml ) was gradually added to a cooled solution of 100 gm ( 1 mol ) of Cr2O3 in 100 ml water at 30 C . The solution was distilled with 400 ml of acetic acetone and cooled to 20 c . After 3 hrs. the orange crystals were collected , washed with acetone and dried in vacuuo. |
| 2.3.PRODUCT ANALYSIS |
| The reactants in the ratio anil : PDC ( 1 : 10 ) in the 70 % acetic acid were mixed under kinetic conditions . The products of oxidation were identified as the corresponding benzaldehyde and nitrosobenzene . benzaldehyde was characterized as the 2, 4 – dinitropheynyl hydrozone derivative . The remaining solution on evaporation yielded nitrzobenzene , which was identified by its characteristic UV spectrum |
| 2.4. STOICHIOMETRY |
| The stoichiometry of the reaction was detrmined by carrying out several sets of experiments with varying amounts of [PDC] largely in excess over [anil]. The estimation of unreacted PCC showed that one mole of anil reacts with two mole of PDC [ ie.1 :1) |
III.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION |
| Kinetics and mechanism of several organic substrates by PDC were documented ; but there are no systematic kinetics reports of the oxidation of Osmium (VIII ). Catalysed oxidation of benzaldehyde anils by Cr (VI) Complexes. This prompted us to undertake the title for investigation. |
| 3.1.Effect of varying the concentration of PDC |
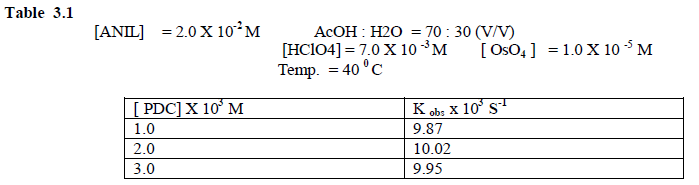
| The kinetics of the above reaction was investigated with [ PDC ] = 1.0 - 3.0 / 10-3 M and [ Anil] = 2.0 / 10-3 M respectively . Plot of log [ PDC ] versus time were linear , indicating a first order dependence on [ PDC]. The pseudo – first order rate constants kobs. calculated from the slopes of the above plots are found to be independent of the initial concentration of PDC . ( Table 3.1) |
 |
| 3.2.Effect of varying the of substrate |
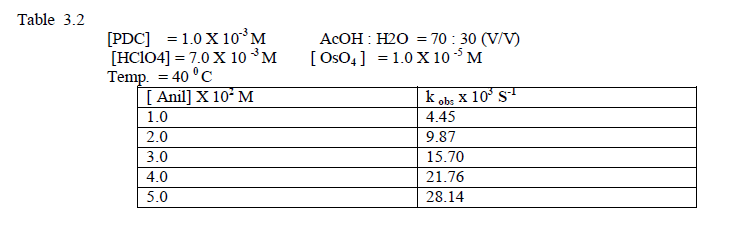
| The concentration of Anil was varied 1.0 – 5.0 /10-2 M at fixed concentrations other reaction components. The rate of oxidation increases with increase of [ Anil] [Table 3.2 ] Plots of log k obs versus log [ Anil ] gave straight line withslope equal to 1.09 [ Fig.1]. hence the order with respect to [substrate ] is uity. |
 |
 |
References |
|