e-ISSN:2320-1215 p-ISSN: 2322-0112
e-ISSN:2320-1215 p-ISSN: 2322-0112
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Bapuji Pharmacy College, Davanagere-577 004 Karnataka, India. Vinayaka Mission’s University, Salem, Tamil Nadu, India.
2Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, R.R. College of Pharmacy, Bengaluru,-560 090, Karnataka, India.
Received: 18 October 2013 Accepted: 16 December 2013
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews in Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
2-amino-6-fluoro-7-chloro (1,3) benzothiazoles are treated with aldehydes to get Schiff’s base (Azomethine) in presence of ethanol and HCl, then all the Schiff’s bases are separately refluxed with thioglycolic acid in presence of the solvent 1,4-dioxane and triturated with NaHCO3 solution results to give parent oxothiazolidine.The resulted azomethine (Schiff’s base) are treated with chloro acetyl chloride, triethylamine in presence of dioxane results gives the parent compounds of azetidinone. The identities of compounds were confirmed on the basis of their spectral (IR, 1HNMR and MASS) data further, they have been screened for their antifungal and anti-inflammatory activities.
Azetidinone, Benzothiazole, Fluorine, Schiff’s base, Thiazolidinone
The rapid progress of organic Fluorine chemistry [1-5] since 1950 has been translated as a pathfinder to invent useful biodynamic agents in Medicinal and Biochemistry.The new generation antibiotics like Norfloxacin, Ciproflaxacin, Flufloxacin, Sporfloxacin and Ofloxacin which were incorporated with fluorobenzene moiety proved their efficacy as potent bio active molecules.
Thiazolidinones [6-8] are the derivatives of thiazolidine, which belongs to an important group of heterocyclic compounds. Thiazolidinones, with carbonyl group at 2, 4 or 5 have been subjected to extensive study in the recent past.
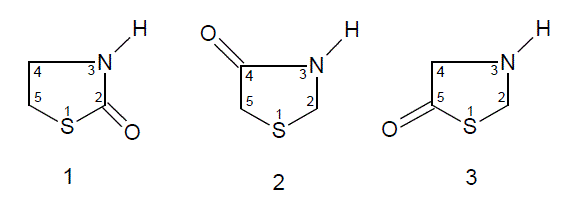
Numerous reports have appeared in the literature, which highlight their chemistry and use. Diverse biological activities such as bactericidal, pesticidal, fungicidal, insecticidal, anticonvulsant, anti-tuberculosis, antiinflammatory, antithyroidal, potentiation of pentobarbital induced of sleeping time, etc., have been found to be associated with thiazolidinone derivatives. In recent years several new methods for the preparation of thiazolidinone derivatives and reactions have been reported in the literature. Thiazolidinones, in the presence of various reagents, undergo different types of reactions to yield other heterocyclic compounds, e.g., thiazole, benzothiophenes, triazinones etc. These advances warrant reviewing the chemistry and biological properties of various 4-thiazolidinones Azetidinone [9-11] is a 4 membered cyclic amide, which is present in the clinically useful penicillins and cephalosporins.
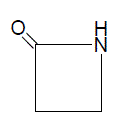
2-Azetidinones, commonly known as β-lactams, are well-known heterocyclic compounds among the organic and medicinal chemists.The activity of the famous antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams and carbapenems are attributed to the presence of 2-azetidinone ring in them. Recently, some other types of biological activity besides the antibacterial activity have been reported in compounds containing 2-azetidinone ring. Such biological activities include antimicrobial, anti-tubercular, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, local anesthetics, anti inflammatory, anthelmintic, anticonvulsant, hypoglycemic activity.
Based on the above observations we have synthesized some Fluoro-Benzothiazole incorporated with Thiazolidinones and Azetidinone derivatives starting with fluoro-chloro-aniline, in hope of getting pharmacological agents with broad spectrum of clinical activity.
Melting points were determined by open capillary tube method and are uncorrected. T.L.C. was run on silica gel G plates using butanol, ethyl acetate and chloroform (1:2:1) as developing solvent for the purity of the compounds. I.R. Spectra were recorded on Shimadzu FTIR Spectrophotometer by using NUJOL MULL technique.
An equimolar (0.01 mole) each mixture of 2-[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-1,3 benzothiazole-2-yl) amino] aceto hydrazide (VI) and appropriate aromatic aldehyde (VII) in ethanol (25 ml) containing 2-3 drops of acetic acid was heated under reflux on a water bath for 3 – 4 hrs. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to a possible extent and residue was poured into ice cold water to get the product. It was filtered, washed with portion of a cold water and dried. The crude product was purified by recrystallisation from ethanol.
A mixture of 2[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-1,3-benzothiazol-2yl)amino]-N-[arylidine] acetohydrazides (VIII; 0.001 mole) and mercaptoacetic acid (0.001 mole) was dissolved in dioxane (20 ml) and pinch of anhydrous zinc chloride was added. The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 12 hrs. and the solvent was removed as far as possible. The residue was cooled triturated with crushed ice (50 gm). The solid separated was filtered, washed with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution until no effervescence were observed and than with portion of a cold water. The crude product was purified by recrystallisation from ethanol to get a crystalline compound
To a mixture of 2[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-benzothiazol-2yl)amino]-N-[arylidene] acetohydrazides (VIII; 0.001 mole), triethylamine (0.003 mole) dissolved in dioxane (25 ml) and chloroacetylchloride (0.0012 mole) was added drop wise while cooling and stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred for 14 hrs. at room temperature and solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was cooled and triturated with crushed ice (50 gm). The solid separated was filtered, washed with small portion of cold water and dried. The product was purified by recrystallisation from aqueous ethanol to get a pure crystalline compound.
The synthesized compounds are screened against fungi like Candida albicans and Aspergillus niger to know their antimicrobial activity (by cup plate method) [12-18].
The synthesized compounds are screened for anti-inflammatory activity by using inhibition of albumin denaturation technique which was studied according to Jayachandran E. and G.M. sreenivasa with slight modification.
The standard drug and test compounds were dissolved in minimum amount of dimethyl formamide (DMF) and diluted with phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 7.4). Final concentration of DMF in all solutions was less than 2.0%. Test solution (1 ml) containing different concentrations of drug was mixed with 1 ml of 1% mM Bovine albumin solution in phosphate buffer and incubated at 270±10C in incubator for 15 min. Denaturation was induced by keeping the reaction mixture at 600±10C in water bath for 10 min. After cooling the turbidity was measured at 660 nm (UVVisible Spectrophotometer SL-159, Elico India Ltd.). Percentage of inhibition of denaturation was calculated from control where no drug was added. Each experiment was done in triplicate and average was taken. The Ibuprofen was used as standard drug [19-23].
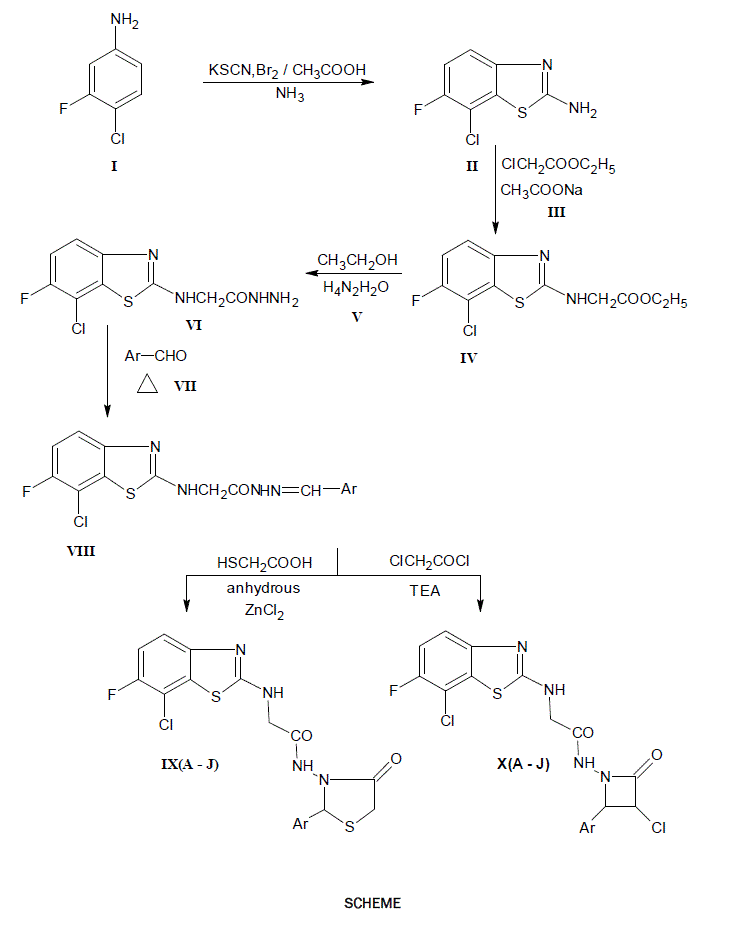
Synthesized compounds of 2-[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-benzothiazol-2-yl)amino]-N-[2-aryl-4-oxothiazolidin-3-yl] acetamide and 2-[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-benzothiazol-2-yl)amino]-N-[4-aryl-3-chloro-2-oxoazetidene-1-yl) acetamide have been screened for following.
The same types of compounds were subjected to antifungal activity. For these activities Candida albicans and Aspergillus flavus fungal organisms were used. The Griseofulvin were used as a standard. Standard and synthesized compound were tested at two conc. viz., 50 ug/ml and 100 ug/ml.
The compounds have shown activity but non of them have shown better activity than the standard. Some of the compounds like XB, XH and XJ have shown activity almost equal to standard against Aspergillus flavus organism at 100 ug/ml conc. and XB, XH, XJ have shown activity near to standard at 50 ug/ml conc. And the compounds IXI, XA, XB have shown activity near to standard against Candida albicans organisms at 100 ug/ml conc. and at 50 ug/ml conc. The remaining compounds have shown very low activity. From this it is concluded that the synthesized compounds have shown better activity against Aspergillus flavus than Candida albicans.
Synthesized compounds of 2-[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-benzothiazol-2-yl)amino]-N-[2-aryl-4-oxathiazolidin-3-yl] acetamide and 2-[(7-chloro-6-fluoro-benzothiazol-2-yl)amino]-N-[4-aryl-3-chloro-2-oxoazetidene-1-yl) acetamide have been evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity (in-vitro). The results are presented in table reveals that some of compound promisingly inhibit albumin denaturation in comparison with standard drugs, ibuprofen exhibited 80% and diclofenac sodium exhibited 88% inhibition of albumin denaturation.
Azetidinone series showed 5 compounds and thiazolidinone series 5 compounds having more than 25% inhibition of albumin denaturation. Out of that IXJ and XD showed 53% and 45% inhibition of albumin denaturation.
The authors are thankful to The Principal Bapuji Pharmacy collage, Davangere for providing necessary facilities to carryout this work.