ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
| Mohammad Oqail1 Ahmad and Dr.Rafiqul Zaman Khan2 |
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
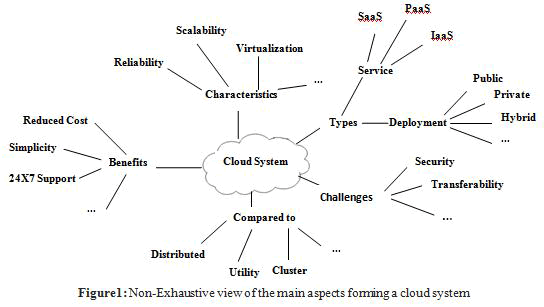
These days, the Cloud Computing is probably the most considerable technology in the IT sector. It is broadly made use to deliver services well over the internet for both low priced and technical motives. Cloud Computing support virtualization technique over the internet to meet the stretchy demand of the users with less interaction by having service provider. For that reason users are progressively engaging toward this trend. In this paper, we presented brief review of Cloud Computing; it also includes comparative study between Cloud Computing, Distributed, Utility, Cluster, and Grid Computing and also three deployment model and service model. This paper also lay out brief discussion of the main characteristics of cloud computing, benefits, challenges and its applications.
Keywords |
| Cloud Computing, SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, Distributed Computing, Utility Computing, Cluster computing, Grid Computing. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Recently, cloud computing has grown to be a key paradigm for online distribution related to computing resources and online user’s data in economically priced, where computing resources are obtained on regular basis, well over internet by using pay per use concept, it means users pay to service provider what they consume. In other term, cloud computing is network-based computing, that allows technology easy to use, the ability to be in all places, anytime and on-demand online access to shared pool of computing resources or services that can be swiftly provisioned and announced by using negligible administrator attempt or service provider connection [1]. Services may be software resources or hardware resources or physical resources such as SaaS(Software as service) or PaaS(Platform as service) or IaaS(Infrastructure as Service). |
 |
II. EVOLUTION OF CLOUD COMPUTING |
| Cloud Computing (CC) is a new terminology given to a evolution of distributed computing, utility computing and grid computing etc. Several organizations are getting to interest to use cloud computing over period of time, but CC has come into existence with the invention of ARPANET by J.C.R.Licklider in 1960's. . |
| In early 1990, cloud was actually use in commercial purpose to support large ATM Network. Beginning of the 21st century, cloud computing solutions and products had begun to seem on the market, however totally focus at this time frame was on Software as Services [27] |
| In 2002, Amazon.com performed a most important part in the formation of cloud computing if improving their data and delivering access to their personal system by method of Amazon Web Services on utility computing manner [27]. |
| It is donation of some of the scientific study to develop an explanation of the cloud computing and Youseffetal. were among the first person to deliver you understanding of cloud computing and its elements[2]. These people mentioned that cloud computing is a combination of a few innovative as well as all previous principles in a large amount of research fields like distributed, utility, cluster and grid computing and additionally virtualization. Based on Youseff et al. “cloud computing can be seen as a new computing standard which permits consumers to actually transient make use of computing facility all over the network, provided being a resource through third party provider towards probably more than one stages of abstraction” (Youseff et al. 2008) [2]. |
| In July 2010, OpenStack is collectively launched by Rackspace Hosting and NASA, which guide to organizations present cloud computing services operating on traditional hardware [27]. |
| On March 1, 2011, IBM SmartCloud platform was introduced by IBM to help Smarter World. Cloud Computing is a crucial portion among the several elements of the Smarter Computing foundation [27]. |
| On June 7, 2012, Oracle Cloud was launched by Oracle, while its elements are continue to development phase and proposing users to became the first provider users to access combined set of IT frameworks, such as Infrastructure (IaaS), Platform (PaaS), and Software (SaaS) layers [27]. |
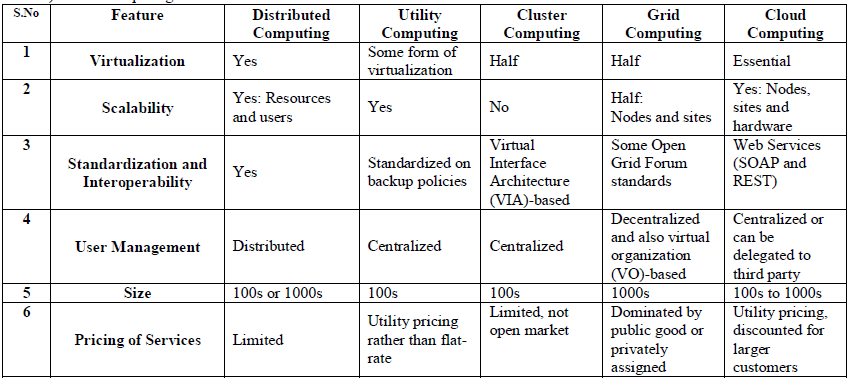
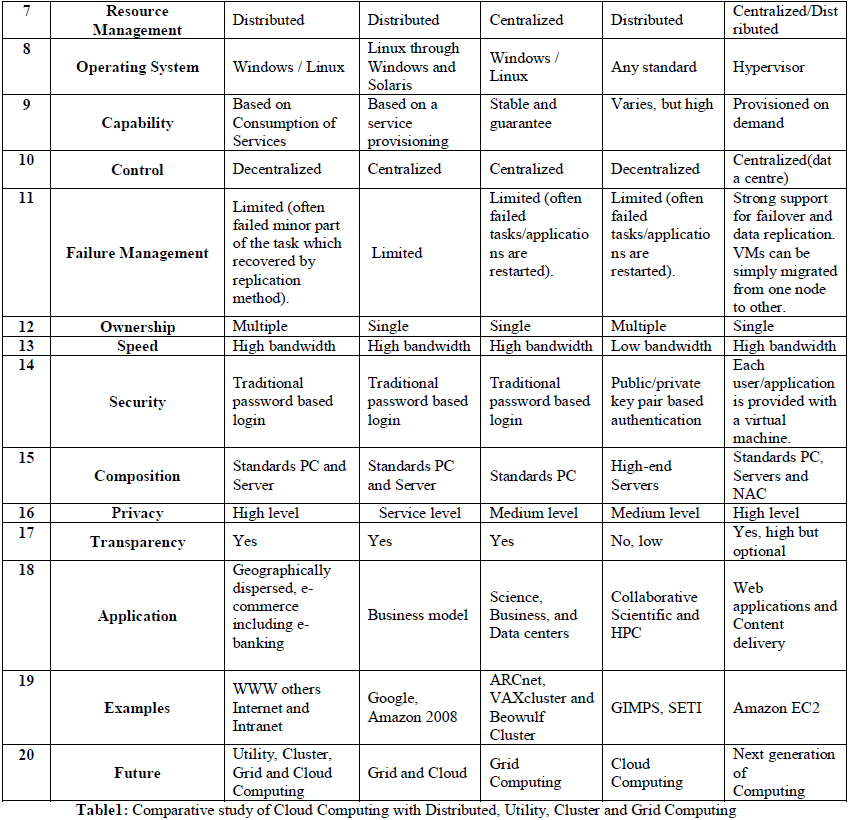
| There are various computing technologies involved in the evolution of cloud computing on which comparative study are done below: |
| 1) Distributed Computing |
| 2) Utility Computing |
| 3) Cluster Computing |
| 4) Grid Computing |
| 5) Cloud Computing |
 |
 |
III. OVERVIEW OF CLOUD COMPUTING |
| A. Definition of Cloud Computing |
| The concept of cloud relates to network of providing resources well over the internet. There resources existing in cloud can be utilized certainly by user whenever required. Customers always want service to third party provider of internet alternatively setup their personal physical infrastructure in cloud computing |
 |
| The use of the “cloud” makes references to the two essential concepts. |
âÞãAbstraction |
| The concept of abstraction in cloud computing means hide the information about the system implementation from consumers and designers. Programs and data located on physical systems that are uncertain, supervision of systems is to contact out to others, and access by consumers is everywhere [14]. |
| âÞãVirtualization |
| The concept of virtualization means to refers to something is not real but it acts as real. It is basically used to increase computing efficiency and utilize maximum hardware resources of the system. |
B. Characteristics of Cloud Computing |
| Cloud computing expose five key characteristics as stated by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). |
âÞãOn-demand self-service |
| Consumer wants computing resources from service provider without the need for human interaction then cloud service provider provides service to consumer according to required |
âÞãBroad network access |
| The resources are available over network can be allowed to globally access by using the different devices such as desktop, laptop, mobile etc. |
âÞãResource pooling |
| Cloud resources are pooled by service provider and then they are shared to serve different users. These resources are released by some consumer and can be serve to other consumer as needed. |
âÞãRapid elasticity |
| Computing capability of cloud resources can be ample flexible to provisioned, in number of cases, it allows programs automatically scale utilization in both cases rapidly scale up and rapidly scale down as need. Consumer are able easily obtained in any number at any time and often appear to be unlimited. |
âÞãMeasured service |
| Cloud system automatically measured, controlled and confirmed of utilized service by both service provider and consumer for providing transparency and accountability. Cloud computing platforms utilize a metering skill that will automatically manage as well as enhance resource utilize. All of this is executed towards some stage of abstraction commensurate to the form of service [7]. These types of services involve active user account, storage space, internet speed, processing etc. |
C. Service Model of Cloud Computing |
| It is made of the specific groups of services that you can access on a cloud computing system. NIST offered three services models and they are: |
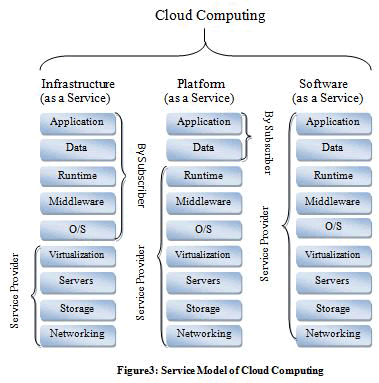 |
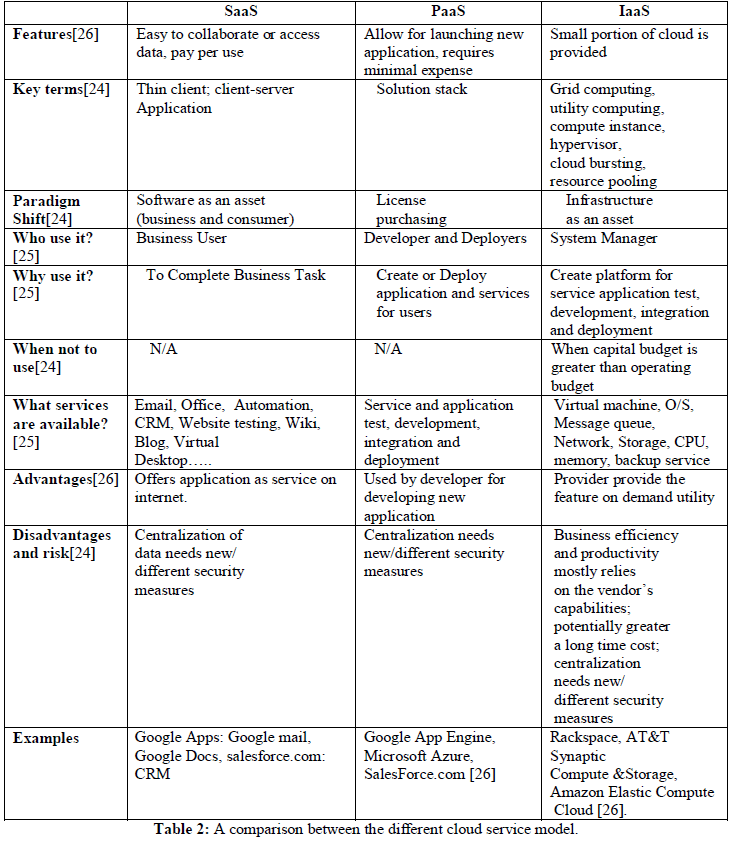
âÞãCloud Software as a Service(SaaS) |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) is a service model, in which software application is made for customers and hosted by the vendor are accessible for clients on demand over the network. Customers do not have necessary to installed copy of software on the desktop, laptop or any other client devices |
Pros of IaaS are as follow [2]: |
| ïÃâ÷ Provides products for documenting online such as Microsoft office. |
| ïÃâ÷ Software available in for short term manner. |
| ïÃâ÷ Technique available for fast delivering the technology. |
| ïÃâ÷ Broad application of services available online such as face book, twitter, Hotmail etc. |
| ïÃâ÷ It uses programming interfaces which provide implementation between different Tools of software. |
âÞãCloud Platform as a Service (PaaS) |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) make it possible for customer to established computing platform to develop and host application. Customers can establish their own small scale organization than larger scale can be able to handle. The cloud provider provides the underlying cloud infrastructure such as operating system, servers, or storage which is not accessible by the customer. |
| Pros of PaaS are as follow [2]: |
| ïÃâ÷ Pay per use |
| ïÃâ÷ No need of installing or downloading software for users. |
| ïÃâ÷ Concurrent users can access the application due to shared architecture. |
| ïÃâ÷ Provide same integrated platform for develop, deploy and test so it reduce development and maintenance cost. |
| ïÃâ÷ Provides reliability and security. |
âÞãCloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) |
| It offers cloud infrastructure, client using this infrastructure for established their own operating system and cloud provider manage the system's CPU, memory and processing. Client can configure and maintain all what it takes in cloud. IaaS is combination of both public and private infrastructure or can be obtained as individual. For IT resources IaaS will provide a new consumption model as compare to SaaS and PaaS the IaaS is growing rapidly [8]. |
| Pros of IaaS are as follow [2]: |
| ïÃâ÷ Multiple customers can access on a same hardware resources. |
| ïÃâ÷ Fully scalable |
| ïÃâ÷ Cost varies on depend on service. |
| ïÃâ÷ It provides the resources as a service. |
| ïÃâ÷ It allows dynamic scaling. |
 |
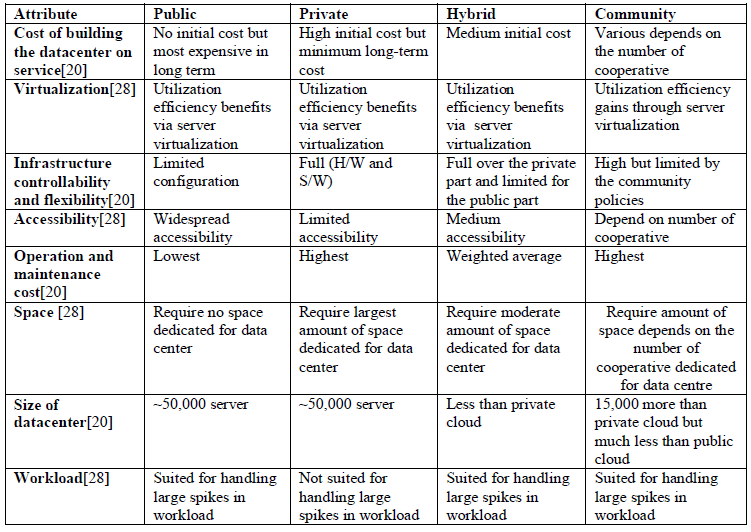
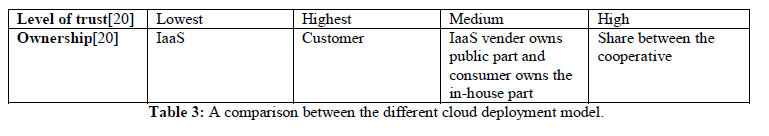
D. Deployment Model of Cloud Computing |
| It is related to the location and management of cloud system. NIST recognize four kinds of deployment models in cloud computing and they are |
âÞãPublic Cloud |
| The infrastructure of public cloud is made available for the general public where the resources are provided over internet and any users can access from the cloud, it is owned by the cloud vendor [18]. The public cloud infrastructure is not visible for the customer where the infrastructure is hosted. |
âÞãPrivate Cloud |
| The infrastructure of private cloud is made available only for specific organization and not for other organization. It means resources available in private cloud can be access by internal users, anyone within the organization but users outside of that organization cannot access. Commercial data are fully maintained as well as infrastructures of private cloud are entirely taking care by the organization itself [18]. Private cloud a lot more protected when we compare with the public cloud. |
âÞãHybrid Cloud |
| The infrastructure of hybrid cloud is combination of more than one cloud such as public, private or community cloud. Critical data can hosted by organization on private cloud and data by having pretty less security relates to public cloud [7]. |
âÞãCommunity Cloud |
| The infrastructure of public cloud is deployed for several organizations and not for specific organization but support specific community or interested group. It means organizations that have similar policies, objectives and targets or belongs to specific community, build a shared cloud datacenter that can be used by all of the members [19][20]. It is based on the faith between all the members in community cloud, which can walked through their mutual benefits [20]. |
 |
 |
E. Benefits of Cloud Computing |
âÞãReduced Cost |
| Organizations want to reduce the cost of managing and maintaining has to shift toward the resources of cloud computing vendor. Using cloud provider services, organization keep their applications up to date on their systems free without having to purchase and install[9][11]. |
âÞãFlexibility |
| The main reason of popularity of cloud computing is flexibility, due to this users have ability to access data anywhere and anytime such as from home, on holiday in the world. If user is off-line want to access data, user can connect through virtual office, quickly and easily. The devices which are applicable include laptop, desktop, smart phone etc. with internet connection [9][10]. |
âÞãAvailability and Reliability |
| Availability of cloud resources is high because it is up to vender available on 24x7 and more reliable chances of failure are minimal and immediate response to disaster recovery. From anywhere one can login and access the information. |
âÞãSimplicity |
| Simplicity offers a user does not require training or have technical sound to work on a cloud, with little knowledge of hardware and software can use the cloud resources [13]. |
âÞãGreener |
| The cloud computing is naturally a green technology since it enable resource sharing among users thus not requiring large data centers that consumes a large amount of power[19].Users can get anything from cloud at anytime and anywhere[11]. |
âÞãCentralized |
| Because the system is centralized, you can easily apply patches and upgrades. This means your users always have access to the latest software versions [12]. |
âÞãMobility |
| Users of cloud do not require to carry their personal computer, because they can access own documents anytime anywhere[19]. |
âÞãUnlimited Storage Capacity |
| Cloud computing support unlimited data storage capacity, so it offers virtually unlimited storage of data. Users can store approximately hundreds of petabytes ( a million gigabytes) compared to own computer's current capacity can be 500 GB or 1 TB, so do not require to panic about your data[10][15]. |
F. Challenges of Cloud Computing |
âÞãSecurity |
| There is in reality that security challenge has been a major obstruction in the influencing cloud computing acceptance[16]. Without hesitation, moving your records, running your software on someone else's hard disk using someone else's CPU appears daunting to many[17]. Well-known security challenges in the cloud computing are: confidentiality, integrity, privacy, accountability, phishing and so on [7]. Regarding to a 2009 IDC Survey, security was graded as the greatest aspect for retaining back organizations from implementing it[16]. |
âÞãServices Delivery and Billing |
| Cloud computing having on demand nature of the service, so it is challenging task to figure out the costs of delivery. Planning and study relating to cost would be very challenging until the provider has a few good and identical benchmarks to present [22]. |
âÞãLoad balancing |
| Load balancing is challenging task, when the failure some of its parts during the service providing. Load balancing would be put in action duration of the service when the failure some of its parts. Its component would be regularly watched and often one will became nonresponsive, at that time load balancer is up on and balance the load of that nonresponsive part and do not send traffic to it. |
âÞãTransferability |
| If cloud customers want to migrate from one cloud to another cloud that is from one hosting provider to another have to face more problems. It's not easy to migrate to other hosting provider because of migration process will take time to transfer files, which indirectly your business in off line for some time/days. |
âÞãOwnership |
| Once data has been moved to the cloud, some people panic that they might lose some of their rights or are unable to protect the rights of their users. A large number of cloud providers are dealing this challenge along with well created user-sided agreements. That said, users would be wise to seek advice from their favorite legal representative. Users never claim to service provider who use in their provision of service and forms any kind of ownership over your data [19]. |
IV. APPLICATION OF CLOUD COMPUTING |
A. Development & Test |
| The cloud customer can develop and test their complete production on demand in the cloud. Developers can save their time and expanse over traditional development and testing scenarios, that allows developers to quicker handoff from design to function. It also provide the patterns towards about iterative active development, the opportunity to trial and able to move out quick competitive differentiator with the cloud [12]. |
B. Cloud-Based Anti-Spam and Anti-Virus Services |
| A number of organizations utilize cloud services which typically perform anti-spam sorting and deliver you antivirus services. Even if majority of services are hosted by the organization inwardly, they can be easily positioned in your organization based on cloud situation. |
C. IT Education and Research |
| IT field is swiftly heading in the direction of Cloud Computing, because it supports multiple types of cloud deployment (public, private hybrid, or community), multiple models of application programming and extensible framework enabling educators/researchers to develop their own programming model and application schedule [23].Due to above platform provided by cloud computing, software industry also concentrating in shifting from developing applications for PCs to Data centers |
V. CONCLUSION |
| In this paper, we have surveyed of cloud computing, discussed its vital principles, non-exhaustive vision of the main aspects forming a cloud system, evolution and comparative study with distributed, utility, cluster and grid computing, outstanding characteristics as well as pros and cons. Cloud computing technology is still evolving, we desire these work may give a much better knowledge of the design challenges of cloud computing, and mark the way for more research in this realm. |
References |
|