ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
ISSN ONLINE(2320-9801) PRINT (2320-9798)
K.Brindha, Ritika Sharma, Sapanna Saini
|
| Related article at Pubmed, Scholar Google |
Visit for more related articles at International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering
In this paper we present image encryption using symmetric algorithm (SA). Encryption is a method to protect data against destruction by involving special algorithm and keys to transform digital data into unreadable format before transmission over the network. The Decryption keys are used to get the original digital data back from the transmitted encrypted data form. Data encryption standard (DES) is one of the symmetric algorithms. This paper presents an analysis on DES algorithm for image encryption. The proposed idea will reproduce the original image with no information loss. A comparative study of the DES algorithm with the present image encryption algorithms is also done in this paper.
Keywords |
| AES, DES, decryption, encryption, symmetric algorithm. |
INTRODUCTION |
| Today security is the main concern about the transmission of data. We need a cryptosystem which ensures that our data will be secure during the transmission over the network. In secured communication the information is converted from the intelligible to unintelligible structure using certain coding operation at the transmitter. There are some techniques are used for making the data secure during conveying information over the network one of these are known as encryption and decryption. [1] The encrypted form of the information is then transmitted through the insecure channel to the destination. |
| In this paper we are using symmetric algorithm for image encryption. In Symmetric algorithm sender and receiver ends use a same cryptographic key (symmetric key) for data transformation. Symmetric key cryptography is also known as shared key cryptography. A cryptographic key is a special kind of information that helps the sender to convert original data into encrypted form and at other end it helps the receiver to access the encrypted data. At sender side the message or data is converted into a special data format called cipher text using various encryption algorithm and secret key. The receiver side performs the same operation but in reverse order. It takes cipher text as input and then converts it into the original message. There are various algorithms for image encryption such as chaotic, blowfish, AES algorithms etc. but here we are using DES. DES algorithm is a symmetric block cipher rather than stream cipher, means it processes data in blocks. [1] The algorithm is designed to encrypt and decrypt the block of data consisting of 64-bit key of which 56-bits are randomly generated and used by the algorithm. A 64-bit block of data goes in from one end of the algorithm and 64-bit block data comes out from the other end. An image is a representation of an external form of objects. Image is a set of pixels which represent as a digital value. For image encryption there are various techniques proposed. [3,4] In our method we are using DES algorithm for image encryption. Before giving image as input for DES we are converting image into byte array. |
II. INTRODUCTION |
| There are two actions are used in DES cryptography system: diffusion and confusion. DES has 16 rounds of operations. A round is a combination of diffusion and confusion. The mechanism of diffusion is to make the relationship complex between the original data and cipher code in order to reduce attempts to deduce the key. Confusion is used to make the relationship complex between the cipher code and the cryptographic key to reduce the attempts of discovering the key. The key size used in DES algorithm is 56-bits for 64-bit input data. [1,2] The remaining 8 bits are used for parity checking. The encryption process is made of two permutations, initial and final permutations, and 16 Feistel rounds. In each round a different 48 bit round key is used which is produced by the cipher key. |
III. DES ALGORITHM |
| An initial and final permutation, each of the permutation takes 64-bit input and applies permutation techniques. In these two processes no key is used hence they are straight or keyless permutations which are opposite to each other. |
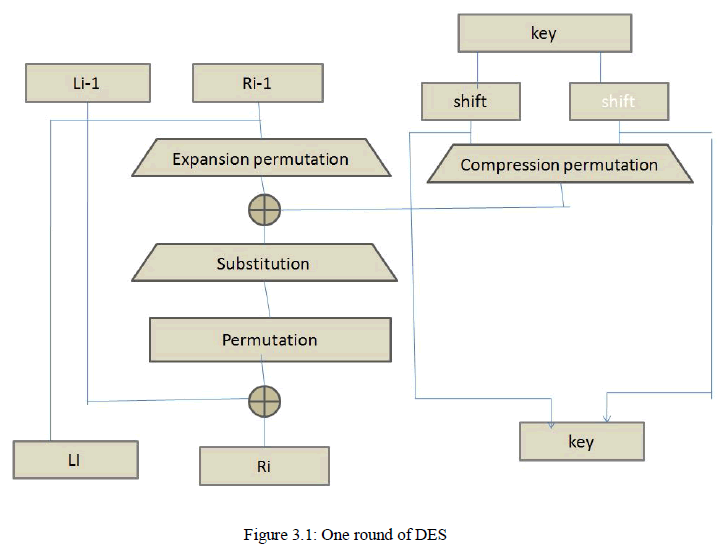 ] ] |
| The first operation in DES algorithm is initial permutation. Initial permutation reorders the input data as, odd bits to right hand side and even bits to left hand side. After initial permutation, the block is divided in two halves, right and left, each of which is 32 bit long. The halves are denoted by L and R. After this split up of data, 16 rounds of identical operation, called function f, are performed. In this function data are merged with the key. [1] DES algorithm is performed on these two halves, L and R. A round takes Li-1 and Ri-1 from previous round or the initial permutation box and after operation creates Li and Ri, which goes to the next round or final permutation box. |
IV. FUNCTIONS OF DES |
| The 64 bit DES key is reduced to 56 bit key by ignoring every 8 bit. These left out bits are used for parity checking to ensure the key is bugs free. After obtaining the 56 bit key a different 48 bit sub key is generated for each round of the DES function. The next step in DES algorithm is computation of the DES function. This function is applied on a 48 bit key to the rightmost 32 bits (Ri-1) to produce a 32 bit output. [1] This function is made up of four sections. Expansion P-box operation is used to expands the size of right half from 32 bit to 48 bit. Expansion permutation is performed by duplication of certain bits. In a 4 bit input block produces the output of 6 bit by repeating first and fourth bit. This provides longer result which is compressed during substitution operation. S-box permutation is performed on the compressed key with the expanded block, moves the 48 bit result to a substitution operation. The S boxes are nonlinear and the critical giving the DES algorithm maximum security. In P-box permutation each input bit is mapped using a straight permutation (each bit is used only once and none is left out). Final permutation is same as initial permutation but it works in reverse order. [1, 3, 4] |
| The Decryption process in DES algorithm is same as encryption but the only difference is that it performs all the operations in reverse order. [4] To get the original data receiver uses the same secret key to decrypt the code and the keys are used in reverse order. If the encryption keys are subkey1, subkey2, subkey3….subkey16, then the decryption keys are subkey16, subkey15, and subkey14… subkey1. |
V.IMAGE ENCRYPTION AND DECRYPTION ANALYSIS |
| Encryption process: |
| Encryption process has two inputs one image which is already converted into plain text and one encryption key. |
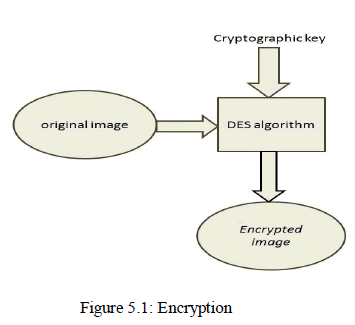 |
| The encryption key is selected randomly in this algorithm using method generateSecret() of the class SecretKeyFactor which are defined in javax. Size of image is larger than text data. The storage unit for an image is BLOB, so the direct encryption of an image is complicated. To reduce the complexity we have proposed this idea in which we are encrypting an image in three steps as following: |
| In first step an image is converted into byte array and this byte array is changed into a string object. In second step we have define a method for encryption or decryption and key generation by defining the objects of some awt classes. In third step we are converting the byte array of image in a string for des algorithm’s input for encryption. DES takes 64 bit length of data at a time as input. String conversion of an image has length in lacs so this will be passed in a loop for encryption. |
| The header is excluded from the encryption and only the byte elements of the array which start from the next to the header are encrypted. Then by the compression of the key image has been encrypted and pass to the other end. |
Decryption process: |
| The encrypted image is divided into same block length of DES algorithm. First block of 64 bit is entered into the function and same cryptographic key is used for decryption but this is used in the reverse order. |
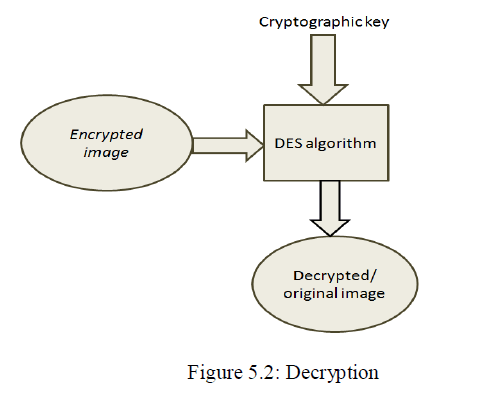 |
| After the decryption of the encrypted text the output is obtained as the same string which was passed at encryption time. Then this string is again changed into the byte array and this byte array is transformed into the original image. |
VI. IMPLEMENTATION AND RESULT |
| In this paper we showed the image processing using MATLAB and encryption, decryption part in the java language. We take a color image with size of 339*450 (49 KB). Firstly we generate a byte array and translate in to string of chosen image, and then encrypt it using DES algorithm. |
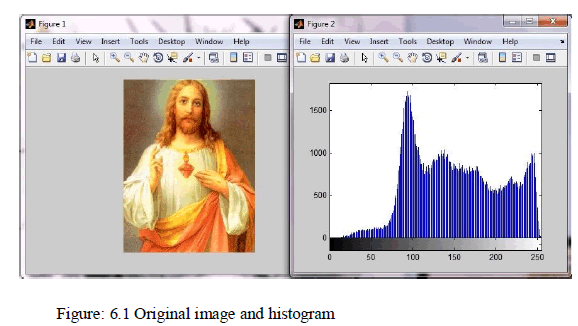 |
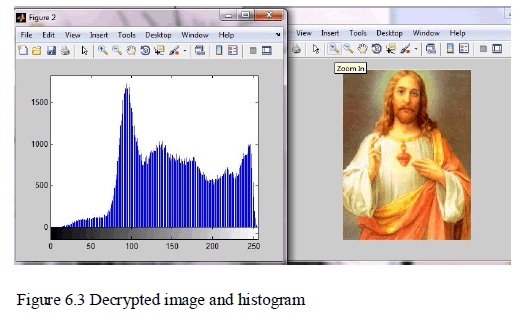
| In the result we showed an original image’s histogram and final image’s histogram where it is clearly visible that original image is same as input image. |
| The result shows the cipher code for the image which is in string form using DES algorithm. Here the results are displayed on command prompt. The given output is of 64 bit of data. |
| Encryption: |
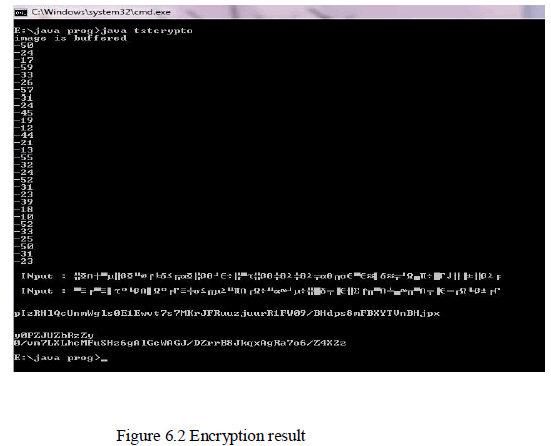 |
| This encrypted text transfer to the sender. And there decryption part is done. |
| The decrypted image is same as the given input image. The corresponding histogram is also same. |
 |
| Decryption: |
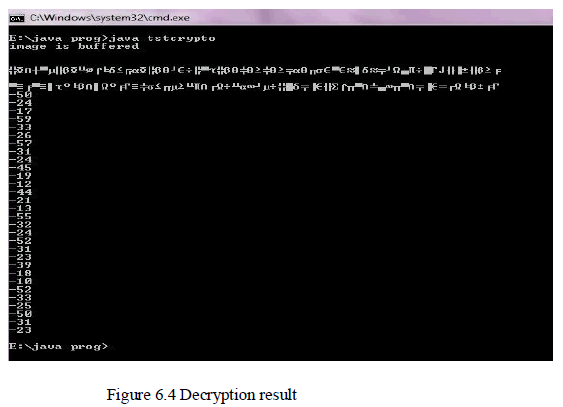 |
| After decryption we are getting the same byte array and string values. This confirms that there is no data loss. |
VI.COMPARISON WITH AES |
| DES algorithm and AES algorithm both is symmetric key algorithm and both are used as a block cipher. It uses 128,192 or 256 bits key where as the DES algorithm encrypts 64 bit data using 56 bit key. But here we are using DES algorithm for image encryption. The image is already transformed into two forms before encryption; this makes it difficult to access the image in unauthorized manner. DES cryptography is a much faster algorithm than other cryptography algorithms. And it is easier to implement and generally require less processing power than AES. If we concern about key size we can say that it is more difficult to recover AES key as compare to DES key. [8] |
VII .CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK |
| In this paper we have done the image encryption with DES algorithm which provides more security during the transmission. We used three different steps such as first we converted image into byte array and then byte array to string then this string is passed for encryption in DES. The resultant final decrypted image is same as input image. We have discussed the compared study of DES with AES. Our future work involves encryption of text data embedded in image. |
References |
|