E- ISSN: 2320 - 3528
P- ISSN: 2347 - 2286
E- ISSN: 2320 - 3528
P- ISSN: 2347 - 2286
The Effect of Furfural Compounds in Corncob Hydrolysate on Microbial Lipids Accumulation of Trichosporon Cutaneum for Biomass-to-Oil Bioprocessing
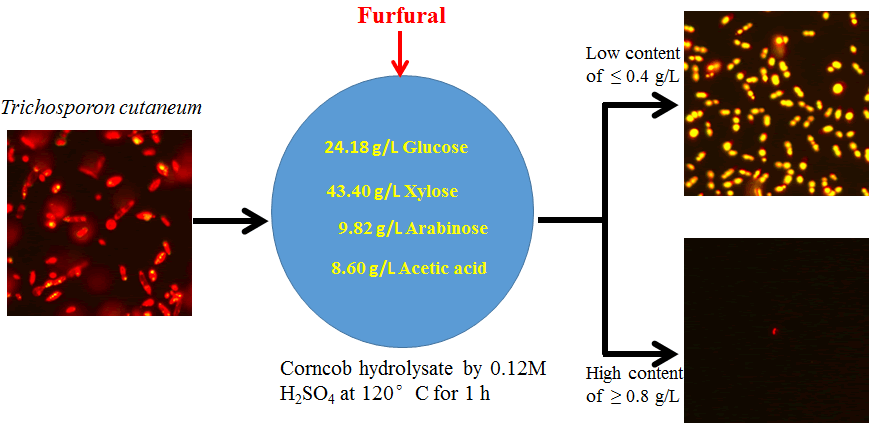
Oleaginous yeast Trichosporon cutaneum is an ideal strain to produce microbial lipids by fermentation on corncob hydrolysate. However, furfural, routinely generated during lignocellulose hydrolysis, shows detrimental effects on microbial lipids accumulation, which mechanism has not been well marked so far. In this paper, corncob biomass was hydrolyzed by 0.12 M dilute H2SO4 and directly used as the T. cutaneum fermentation medium. The different initial furfural content was obtained by adding the proportional amount of furfural into the detoxified corncob hydrolysates. To explore the furfural-mediated mechanism on microbial lipids accumulation in this work, atomic force microscopy was used for visualizing the morphology characteristics and high performance liquid chromatograph was employed for evaluating the furfural metabolism of the yeast during the furfural-detrimental process. Furthermore, flow cytometry was used to monitor the yeast growth and fluorescence spectroscopy was imaged in the dynamics process of microbial lipids accumulation. Analysis reveals that furfural at a low concentration (≤ 0.4 g/L) can be metabolized by the yeast into 2-furoic acid with little detrimental effect on microbial lipids accumulation. The furfural detriment mechanism relating to the damage of cytomembrane for preventing the yeast cell growth is proposed as the main cause of no microbial lipids accumulation of T. cutaneum in high concentration furfural situations (≥ 0.6 g/L). These results provide valuable information for developing and designing a more efficient biomass-into-lipid fermentation bioprocess.
Hongfei Yu, Liuyang Wang, Lijun Guo, Yiming Chen, Wensheng Qin and Yun Liu
To read the full article Download Full Article | Visit Full Article