Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2018
September 04-06, 2018
Page 78
conference
series
.com
September 04-06, 2018 | Zürich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Jhinhwan Lee, Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C3-019
Switching iron-based superconductivity with spin current
W
e have explored a new mechanism for switching magnetism and superconductivity in a magnetically frustrated iron-
based superconductor using spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy (SPSTM). Our SPSTM study on single crystal
Sr
2
VO
3
FeAs is made up of alternating self-assembled FeAs monolayer and Sr
2
VO
3
bilayers shows that a spin-polarized tunneling
current can switch the FeAs-layer magnetism into a non-trivial C4 (2×2) order, which cannot be achieved by thermal excitation
with unpolarized current. Our tunneling spectroscopy study shows that the induced C4 (2×2) order has characteristics of plaquette
antiferromagnetic order in the Fe layer and strongly suppresses superconductivity. Also, thermal agitation beyond the bulk Fe spin
ordering temperature erases the C4 state. These results suggest a new possibility of switching local superconductivity by changing
the symmetry of magnetic order with spin-polarized and unpolarized tunneling currents in iron-based superconductors. We have
alsoperformedhigh-resolutionquasiparticle interference (QPI)measurements, self-consistent BCS-theory-basedQPI simulations
and a detailed e-ph coupling analysis to provide direct atomic-scale proofs of enhancement of iron-based superconductivity due
to the BCS mechanism based on forward-scattering interfacial phonons.
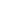
Figure-1: (a), (b)
Atomic scale evidence of plaquette antiferromagnetic order induced in FeAs layer of Sr
2
VO
3
FeAs by injection of spin-polarized tunneling
current and (c), (d) resultant local switching-off of iron-based superconductivity. (e)-(f) Quasiparticle-interference signature of enhancement of iron-based
superconductivity due to C
2
defects locally enhancing e-ph coupling with the forward-scattering interfacial phonons.
Recent Publications
1. Jin-Oh Jung, Jhinhwan Lee, et al. (2017) Versatile variable temperature and magnetic field scanning probe microscope for
advanced material research.
Review of Scientific Instruments;
88: 103702.
2. Jhinhwan Lee (2017) Real-time digital signal recovery for amulti-pole low-pass transfer function system.
Review of Scientific
Instruments;
88: 085104.
Biography
Jhinhwan Lee has completed his Bachelor’s degree from Seoul National University (1995). After obtaining his PhD degree from the same institution, he joined Professor
J C Davis’ Laboratory at Cornell University as a Postdoctoral Associate and was appointed Research Associate in 2007. He went to Korea Advanced Institute of Science
and Technology asAssistant Professor and began his life-long investigations on magnetism and unconventional superconductivity. He has received Korea Physical Society
Bombee Physics award in 2004 and the Albert Nelson Marquis lifetime achievement award in 2018. His works includes bandgap engineering of nanotube published in
nature; scanning probe microscope for advanced material research is published as a cover paper in
Review of Scientific Instruments (
2017) and switching iron-based
superconductivity using spin current published in Physical
Review Letters
with Viewpoint (2017).
jhinhwan@gmail.comJhinhwan Lee
KAIST, South Korea