Page 73
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2018
September 04-06, 2018
September 04-06, 2018 | Zürich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Functionalized track-etched PVDF membrane electrodes for heavy metal analysis in water
Uliana Pinaeva
1
, Marie-Claude Clochard
1
, Emanuel Balanzat
2
, Travis-Lee Wade
1
, Travis-Cameron Dietz
3
and
Mohamad Al-Sheikhly
3
1
Ecole Polytechnique-Université Paris Saclay, France
2
CIMAP, France
3
University of Maryland, USA
B
eing a greatest earth’s resource, water should be preserved. Its pollution effects on all living beings due to accumulation of
toxic elements. Therefore, the needs of water quality monitoring are necessary to prevent potential contamination disasters.
Currently, tolerable limits are in a few μg/L that requires sensitive, environmentally friendly, fast and on site instruments, which are
able to analyze heavy metal concentrations in water. To fit the requirements, we are developing a portable electrochemical device
based on the functionalized membrane electrodes. These membrane electrodes are made of track-etched functionalized nanoporous
poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes of 9 μm thickness covered with gold layers of 35 nm thickness on each side. To create
nanoporous membranes, PVDF films were irradiated by swift heavy ions. Chemical etching reveals ion tracks into nanopores. For
sub-micron pore diameters, the reactivity of remaining radicals formed during irradiation was found sufficient to initiate free-
radical polymerization of vinyl (or allyl) monomers. This method allows any selective polymer issued from radical polymerization
to be grafted onto pore walls of PVDF membranes. For instance, poly (acrylic acid) has shown a high selectivity toward Pb
2+
and
Cu
2+
ions, poly (4-vinylpyridine) toward Hg
2+
. Recently developed bis [2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl] phosphate (B2MP) grafted inside
the nanopores of PVDF membranes were found efficient for pre-concentration of UO
2
2+
from aqueous solutions. EPR, FESEM, FTIR
were used to study radical content, morphology of the surface and presence of functional groups inside the nanopores. Voltammetry
was used to demonstrate the sensitivity of such functionalized membrane electrodes in trace level. A first generation prototype
exhibiting its own potentiostat, software and set of membrane electrode pads have been developed.
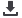
Figure:
FESEM photo of cross section of B2MP functionalized track-etched PVDF membrane, fluence 10
9
cm
-2
(right),
and proposed configuration of UO
2+
trapping by phosphate groups of B2MP (left)
Recent Publications
1. U Pinaeva, MC Clochard, E Balanzat, T LWade, T CDietz andMAl–Sheikhly Bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate
radiografted onto track-etched PVDF for uranium (VI) determination by means of cathodic stripping voltammetry Haz.
Mat. 2018 (submitted) .
Biography
Uliana Pinaeva has completed her Master’s degree in Applied Physics at the ENS de Cachan. Currently, she is pursuing her PhD in the Laboratoire des Solides Irradiés
at the Ecole Polytechnique. Her research interest focuses on “Functionalization of polymers by means of radiation grafting technique for heavy-metal ions extraction and
their following analysis by voltammetry”.
uliana.pinaeva@polytechnique.eduUliana Pinaeva et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C3-020