Page 88
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2018
September 04-06, 2018
September 04-06, 2018 | Zürich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Solution deposition of Cu doped Co
3
O
4
for electrooxidation of glucose
Mahabubur Chowdhury
1
, Micaela Harry
1
, Franscious Cummings
2
and
Christopher Arendse
2
1
Cape Peninsula University of Technology, South Africa
2
University of the Western Cape, South Africa
O
ne of the major causes of death and disability in the world is due to diabetes mellitus. The frequent testing of physiological
blood glucose levels to avoid grave emergencies is vital for the confirmation of effective diabetic treatment. The current
glucose sensors that are being used by diabetic patients are glucose oxidase sensors. However, due to problems associated
with fabrication of enzymatic glucose sensors, non-enzymatic glucose sensors have been of focus recently. In this study, a
simple solution-based deposition process has been utilized to fabricate a Cu doped Co
3
O
4
electrode for non-enzymatic glucose
detection. The substitution of Cu into the Co
3
O
4
host lattice resulted in an enhanced electrochemical performance compared
to the pristine Co
3
O
4
as was measured from the Hall Effect measurement. The sensor exhibited two distinctive linear ranges
covering upto 7.6 mM at an applied potential of +0.65 V vs. Ag/AgCl in 0.1 M NaOH solution. The sensor depicted good
repeatability (RSD of <10%), stability and reproducibility (RSD of <10%). The sensitivity of the sensor was determined to be
1333 μA/cm2 mM (lower concentration range) and 141 μA/cm
2
mM (upper concentration range), with a lower detection limit
of 0.15 μM (S/N=3). The as prepared electrode showed a response time of <10 seconds and was very selective towards glucose
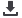
in the presence of various interference species (Figure-1). The ease of fabrication, good electrochemical activity and good inter
and intra electrode reproducibility makes this electrode a promising candidate for non-enzymatic glucose detection.
Figure-1:
Amperometric response of the sensor in the presence of glucose and other interfering species.
Recent Publications:
1. T Gota, MChowdhury and T Ojumu (2017) Non-enzymatic fructose sensor based on Co
3
O
4
thin film.
Electroanalysis
;
29: 2855-2862.
2. Chowdhury M R, Shoko S, Cummings F, Fester V and Ojumu T (2017) Charge transfer between biogenic jarosite
derived Fe
3+
and TiO
2
enhances visible light photocatalytic activity of TiO
2
.
Journal of Environmental Sciences;
54:
256-267.
Biography
Mahabubur Chowdhury has received a Doctoral degree in Chemical Engineering and is currently a Senior Lecturer in the Department of Chemical Engineering at
Cape Peninsula University of Technology. His research is on advanced functional materials for bio sensing and water treatment. His interest is on the relationship
of electronic structure and ionic transport properties in semiconductor electrodes. He has published many journal articles, conference proceedings, book chapter
and patent.
chowdhurym@cput.ac.zaMahabubur Chowdhury et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C3-020