Page 61
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 5
Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2017
September 07-08, 2017
September 07-08, 2017 | Edinburgh, Scotland
Advanced materials & Processing
11
th
International Conference on
Heat transfer performance of double-layer porous copper produced by tape casting with lost carbonate sintering
Mosalagae Mosalagae
1
, Ahmed AAG. Al-Rubaiy
2
, Russell Goodall
1
and
Robert Woolley
2
1
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Sheffield, UK
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Sheffield, UK
P
orous copper tapes with high surface area to thickness ratio are attractive for thermal management in portable electronics where
good heat transfer performance is required. In this study, the porous sheets of thickness down to
1350µm
were investigated for
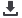
heat transfer performance. The porous copper samples were produced by a novel process combining lost carbonate sintering (LCS)
and tape casting. This process allows the flexibility to produce copper double-layer structure consisting of a porous section with a
wide range of porosities on a dense substrate. Here double-layer structures consisting of a porous layer of porosities ranging from
30-
70%
were investigated. Their suitability for heat sink applications were investigated with simple assessments of the thermal properties
under forced convection using air as a coolant. Through experiments, the heat transfer performance of the thin porous tapes was
systematically studied under two different heating systems; a cylindrical and flat heating systems. The heat generated within the
heating systems was controlled by AC/DC power supply. Also the flow rate of air passing through the samples was varied between the
ranges of 0 – 0.5 kg/s. T- type thermometers and an Infrared thermography sensor were installed in the system to track in and out
and surface temperatures of the system. This allowed behavior of heat dissipation by porous copper tapes to be effectively studied. The
initial experimental results showed that, from the thermal viewpoint, the porous copper heat sinks investigated here have an excellent
heat transfer performance. The outcome of this study is fully discussed in the presentation.
Biography
Mosalagae Mosalagae is a professional, highly motivated and dedicated materials science and engineering researcher. His main interest is on development of
porous metals for heat transfer applications by powder metallurgical processes. He developed a process which combines lost carbonate sintering (Zhao et al, 2004)
and tape casting to process copper powder into thin sheet of porous copper, and further developed a heat transfer rig to investigate the porous heat sinks produced
by simple assessment of thermal properties. In this rig, porous metals are tested under a forced convection using air as a coolant.
mmosalagae1@sheffield.ac.ukMosalagae Mosalagae et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017, 5:5
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-005
Figure1
Schematic diagram showing
processing and heat transfer analysis of
porous copper samples