Page 85
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 5
Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2017
September 07-08, 2017
September 07-08, 2017 | Edinburgh, Scotland
Advanced materials & Processing
11
th
International Conference on
Microstructure development affected by electrode geometry during resistance spot welding
Peng-Sheng Wei
National Sun Yat-Sen University, Taiwan
R
esistance spot welding is an important technique often used in joining thin workpieces in different manufacturing, aerospace,
aeronautics and automobile industries. This presentation theoretically and quantitatively investigates and interprets processes
by realistically accounting for transient magneto-fluid mechanics, heat and species transport, and temperature-dependent bulk
resistance in workpiece, and film and constriction resistances at contact interfaces. Since temperature gradient and solidification rate
are found, the computed morphological parameter, namely, the ratio between temperature gradient and solidification rate, shows
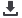
that electrode geometry can be designed to control microstructures of the weld nugget. Figures 1(a) and (b) show that solidification
rate decreases whereas heat flux increases as electrode face radius decrease, respectively. A decrease in electrode face radius therefore
increases the morphology parameter, leading to columnar dendrites, whereas cooling rates can be decreased or increased.
Biography
Dr. Peng-Sheng Wei received Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering Department at University of California, Davis, in 1984. He has been a prof essor in the Department
of Mechanical and Electro-Mechanical Engineering of National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, since 1989. Dr. Wei has contributed to advancing
the understanding of and to the applications of electron and laser beam, plasma, and resistance welding through theoretical analyses coupled with verification
experiments. Investigations also include studies of their thermal and fluid flow processes, and formations of the defects such as humping, rippling, spiking and
porosity. Dr. Wei has published more than 80 journal papers, given keynote or invited speeches in international conferences more than 90 times. He is a Fellow of
AWS (2007), and a Fellow of ASME (2000). He also received the Outstanding Research Achievement Awards from both the National Science Council (2004), and
NSYSU (1991, 2001, 2004), the Outstanding Scholar Research Project Winner Award from National Science Council (2008), the Adams Memorial Membership
Award from AWS (2008), the Warren F. Savage Memorial Award from AWS (2012), and the William Irrgang Memorial Award from AWS (2014). He has been the
Xi- Wan Chair Professor of NSYSU since 2009, and Invited Distinguished Professor in the Beijing University of Technology, China, during 2015-2017.
pswei@mail.nsysu.edu.twPeng-Sheng Wei, Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017, 5:5
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-005
Fig.1
(a) Growth and recession rates of nugget, and (b) heat
flux or temperature gradient in radial and axial directions for
different electrode face radii.