Page 80
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 5
Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2017
September 07-08, 2017
September 07-08, 2017 | Edinburgh, Scotland
Advanced materials & Processing
11
th
International Conference on
Polymeric nanoparticles and gels: Modeling of dynamic behavior and properties using discrete element method
Martin Kroupa, Jose F. Wilson, Miroslav Soos
and
Juraj Kosek
University of Chemistry and Technology Prague, Czech Republic
P
olymeric nanoparticles have a broad spectrum of applications including dispersion (emulsion) paints or thin films. However,
the understanding of their behavior and properties, especially at high concentrations is still limited. We model the dispersions
of polymeric nanoparticles using the dynamic model based on Discrete Element Method (DEM). The interaction model represents
particles that are elastic, adhesive and electrostatically stabilized. The flow-field computation that is included in the model enables us
to evaluate the rheological properties of the dispersion, which are crucial for its behavior. Further characterization of both dispersions
and gels is done using oscillatory simulations, fromwhich the viscoelastic properties are obtained. The model was successfully used to
describe the dynamic behavior of a flowing dispersion including the processes of coagulation, fouling and breakage. These processes
and their relative importance in a specific system determine the transition from a dispersed state to a gel. Due to their specific
position on the boundary between solids and liquids, gels have unique properties that make them suitable to be used e.g., as a porous
structures (or) matrices for drug delivery in the pharmaceutical industry.
Biography
Martin Kroupa obtained his
B.Sc.and
M.Sc. at University of Chemistry and Technology Prague, Czech Republic. His research interests lie in the area of colloidal
and interface science with the main focus on the dynamic behavior of concentrated colloidal dispersions and related phenomena such as coagulation and fouling.
These phenomena are closely connected to the rheology and thus the modeling of rheological behavior is another large area of interest of M.K. He is also active
in the field of electrochemistry.
Martin.Kroupa@vscht.czMartin Kroupa et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017, 5:5
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-005
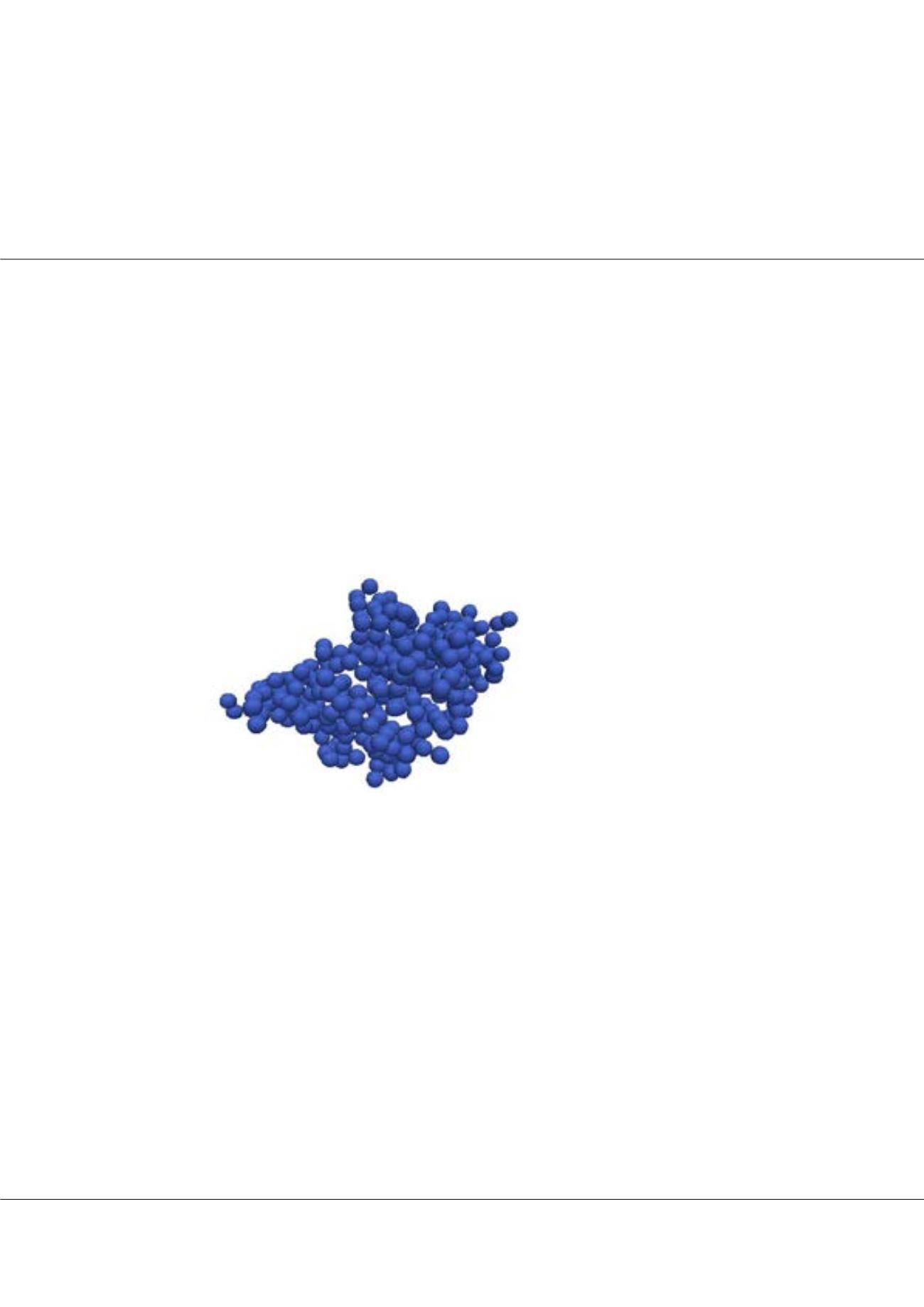
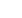
Figure1:
Colloidal aggregate produced by shear-induced
aggregation. Result of a numerical simulation