Page 50
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2018
September 04-06, 2018
September 04-06, 2018 | Zürich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Realizationof conductive aluminumnitride epitaxial layeron silicon substrateby forming spontaneous
nano size via-holes
Noriko Kurose
and
Aoyagi Y
Ritsumeikan University, Japan
Statement of the Problem:
The n-type aluminum gallium nitride (n-AlGaN) vertical field effect transistors on a Si substrate are
promising devices for future super high power devices beyond Si, SiC and GaN devices which are currently being developed.
The AlN buffer layer is indispensable for the growth of AlGaN epitaxial layer on the Si substrate. However, the AlN is an
insulating material and we could not flow current through the buffer layer. We report formation of the conductive AlN buffer
layer (hereafter v-AlN) and details of the formation mechanism of the v-AlN.
Methodology:
The v-AlN is grown on the Si substrate using metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). Al metal
dots are grown on the substrate to form Al-Si alloy dots with successive growth of AlN buffer layer. Spontaneous nano size
via-holes (hereafter via-holes) are formed in AlN buffer layer due to the surface energy difference of Si and Si-Al alloy. The
n-AlGaN is grown on it to fill out the via-holes. The conductive AlN buffer layer with via-holes is formed.
Findings:
We have converted the insulating AlN buffer layer to conductive one by forming cluster of via-holes in the buffer
layer filled with n-AlGaN during the crystal growth. The size of the cluster and the density are controlled and are 0.2~1µm
Φ
and 10
7
~10
8
/cm
2
, respectively. The current flows through these clusters filled with n-AlGaN. The mirror like n-AlGaN epitaxial
layer was successfully grown on it. It is confirmed that the vertical resistivity through the conductive AlN buffer layer was 0.2Ω/
cm
2
which is about 104 times smaller than that of conventional AlN.
Conclusion & Significance:
We have succeeded in growing the conductive AlN buffer layer on the Si substrate. Our technique
and findings open a way to make vertical high power AlGaN FETs, UV-LEDs, UV sensors on the Si substrate and to realize Si
on chip devices.
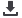
Figure: Steps of the formation of spontaneous via-holes. At the beginning stage of the growth, a small amount of Tri-methyl
Aluminum (TMA) is fed on the Si substrate to form small size Al dots (a). The Al embedded on the Si substrate interacts
with the Si substrate to generate Al-Si alloy dots (b) during the Al feeding time and during the increase of temperature. At a
Si content of approximately 35% β solid phase Si recrystallization is initiated as understood from the phase diagram of Si-Al
alloy(c) and Si is epitaxially grown in the Al-Si alloy dots as shown in (d). No AIN growth occurs on the Al-Si alloy surface
because of the difference of surface energy of Si and Si-Al alloy. Thus, via-holes of AlN are formed in the area where the Al dots
are formed (e). A scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of via-holes is shown underneath of (e). Conductive n-AlGaN is
filled in these via-holes by successive growth of n-AlGaN as shown in (f). Nano cluster via-holes observed by SEM are shown
underneath of (f)
Noriko Kurose et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C3-020