Page 43
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6
Research & Reviews: Journal of Material Sciences
MatSciEngg 2018
October 15-17, 2018
October 15-17, 2018 Helsinki, Finland
31
st
Materials Science and Engineering
Conference: Advancement & Innovations
Polymer composite with soft magnetic Fe-Co nano-powders obtained by cavitation method
Kholodkov N S
1
, Bautin V A
1
and Usov N A
2
1
National University of Science and Technology MISiS, Russia
2
IZMIRAN, Russia
C
omposite materials consisting of magnetic particles in polymer matrix have a wide
area of potential application. In most cases the alloy nano-powders are obtained
by means of polyol method or ball milling technique. These fabrication methods are
characterized by low cost efficiency, but need multi-stage production process. In addition,
the magnetic properties of obtained nano-powders do not strictly correspond to alloy
state characteristics. In the present report the new cost effective method of nano-powder
production is provided. It is the cavitation destruction that allows obtaining various
magnetic nanoparticles with good magnetic properties close to those of well-known
solid-state alloys. Cavitation is the process of formation and collapsing of low pressure
bubbles near the surface of quickly moving object in a liquid. The collapse of tiny bubbles
produces the intense shockwave that knocks out small particles from the object’s surface
into liquid. Resonance piezo-ceramic vibrator has been used in home-made laboratory
facility to provide cavitation process. Fe
73
Co
27
nanoparticles with very high saturation magnetization were obtained in different
liquids such as benzyl alcohol, methyl methacrylate and water. Rather narrow particle size distributions not exceeded 18% were
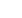
obtained in all liquids studied. It is found that the average particle size strictly depends on the liquid viscosity. It is given by 475
nm in methyl methacrylate, 196 nm in benzyl alcohol and 80 nm in water, respectively. Magnetic properties of 475 nm Fe
73
Co
27
particles in polymeric matrix were investigated. In the fields of approximately 4 kOe composite were almost saturated, and full
saturation was achieved in fields not exceeded 6 kOe. The highest saturation magnetization for this composite was equaled
M
s
=245.3 emu/g. Using cheap Fe
70
Co
27
nano-powders with high saturation magnetization and small coercive force allows us
to reduce the total amount of powder in polymer composite showing increased heating efficiency in alternating magnetic field.
These magnetic particles are promising for biomedical applications, in particular, for hyperthermia treatment.
Biography
Kholodkov N S has completed his Master’s degree in Material Science and Technologies from Moscow University of Steel and Alloys. He has worked in the
field of magnetic measurements of weak magnetic fields produced by corrosion currents. Currently, he is a PhD student of NUST “MISiS” and is working
with soft magnetic powders.
holodkovnikita1993@gmail.comKholodkov N S et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2018, Volume 6
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C5-026
-10000
0
10000
-0.0010
-0.0005
0.0000
0.0005
0.0010
Magneticmoment (emu)
H (Oe)
sample (1)
sample (3)
sample (2)
sample (4)
Fe27Conanoparticles
Figure-1: Hysteresis loops of the
Fe
73
Co
27
particles of 475 nm in size
obtained in methyl metacrylate.