Page 36
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5, Issue 5
Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017
ISSN: 2321-6212
Advanced Materials 2017
September 07-08, 2017
September 07-08, 2017 | Edinburgh, Scotland
Advanced materials & Processing
11
th
International Conference on
TiO
2
nanotubes as potential vascular stents: effect of oxygen plasma treatment on crystal structure and surface
properties
Metka Benčina
1
, Ita Junkar
1
, Tomaž Lampe
2
, Aleš Iglič
2
, Veronika Kralj-Iglič
2
, Matjaz Valant
3
and
Mukta Kulkarni
4
1
Jožef Stefan Institute, Slovenia
2
University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
3
University of Nova Gorica, Slovenia
4
Palacky University,Czech Republic
D
espite intensive research and applications of different techniques to improve surface properties of vascular stents, currently
available metal stents and their coatings (
DES
- drug eluting stents) still lack of desired surface biocompatibility, mostly due to
mechanical injuries, inflammation, as well as proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells, often with progression to restenosis.
Besides, the durability and stability of DES is still problematic and has been connected with high risk of thrombosis Biomimetic nano-
sized materials, with their crystal structure, surface morphology and chemical properties are one of critical features for their potential
use in vascular stent applications, which should support adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of endothelial cells and prevent
abnormal growth of smooth muscle cells. For example, it was shown that titanium dioxide (TiO
2
) nanotubes (NTs) topography is
essential parameter in optimizing endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell responses to vascular implants. The purpose of this study is
to investigate surface properties and crystal structure of TiO
2
NTs. Since the oxygen, plasma treatment plays significant role in surface
treatment of biomedical devices due to surface cleaning and sterilization, its effect on the mechanical stability and surface chemical
properties was evaluated. Vertically aligned arrays of TiO
2
NTs were synthesized on Ti metallic substrates with electrochemical
anodization. The crystal structure was investigated with X-ray Diffraction Spectroscopy, while morphology and surface properties
were analyzed with Scanning ElectronMicroscopy coupled with Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
and Water Contact Angle analysis. Our results indicate that oxygen plasma treatment of TiO
2
NTs surfaces induces the formation
of oxide layer on the surface of TiO
2
NT, which could result in enhanced biocompatibility. Moreover, plasma treatment removes
undesired electrolyte residues on TiO
2
NTs surface and highly improves its wettability. We showed that plasma treated TiO
2
NTs
possess long-term hydrophilicity and influence on crystallization of amorphous TiO
2
NTs to anatase and/or rutile crystal phase, which
could be the reason for improved wettability. The optimized conditions (power, frequency and time) of oxygen plasma treatment on
the mechanical stability of TiO
2
NTs are also presented. Oxygen plasma treatment can greatly improve the surface characteristics of
biomimetic materials and enhance their biocompatibility. Restenosis and thrombosis still remain a serious concern and should be
given a great deal of attention in order to produce improved tissue-material response.
Biography
Metka Benčina has her expertise in synthesis and characterization of nanomaterials for photocatalytic and biomedical applications. She produced novel metal
oxides with pyrochlore structure and proved their absorption in visible range of EM spectrum and enhanced photocatalytic properties under UV and visible light
irradiation. Currently she is fabricating TiO
2
nanostructural surfaces and investigating their applications in biomedicine - biosensors for detection and treatment
of cancer cells, photo-assisted cancer treatment and biomimicking vascular stents. Her particular research interest is the effect of oxygen plasma treatment of
biomaterials.
metka.bencina@ijs.siMetka Benčina et al., Res. Rev. J Mat. Sci. 2017, 5:5
DOI: 10.4172/2321-6212-C1-005
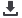
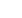
Fig.1:
SEM images of TiO2
NTs after plasma treatment at
a.) non-optimized conditions;
structure is destructed, NTs
are partially closed and b.)
optimized conditions; NTs are
well defined, tops are open.